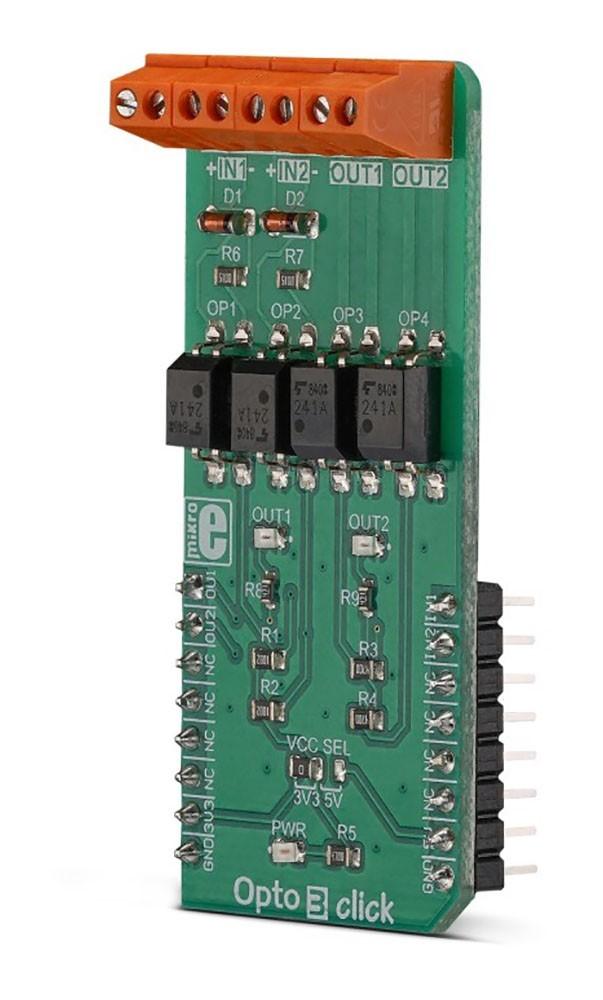
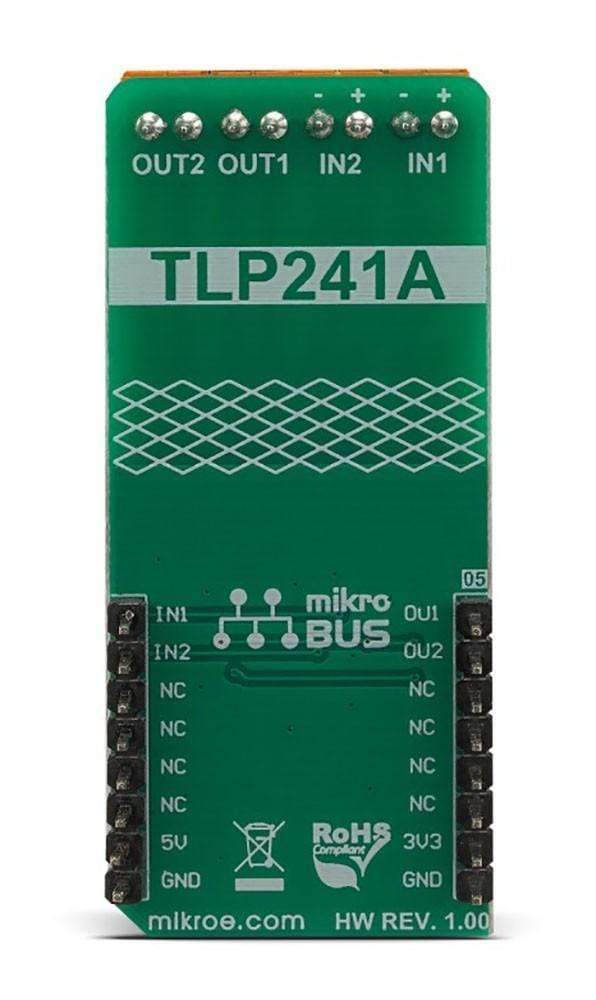
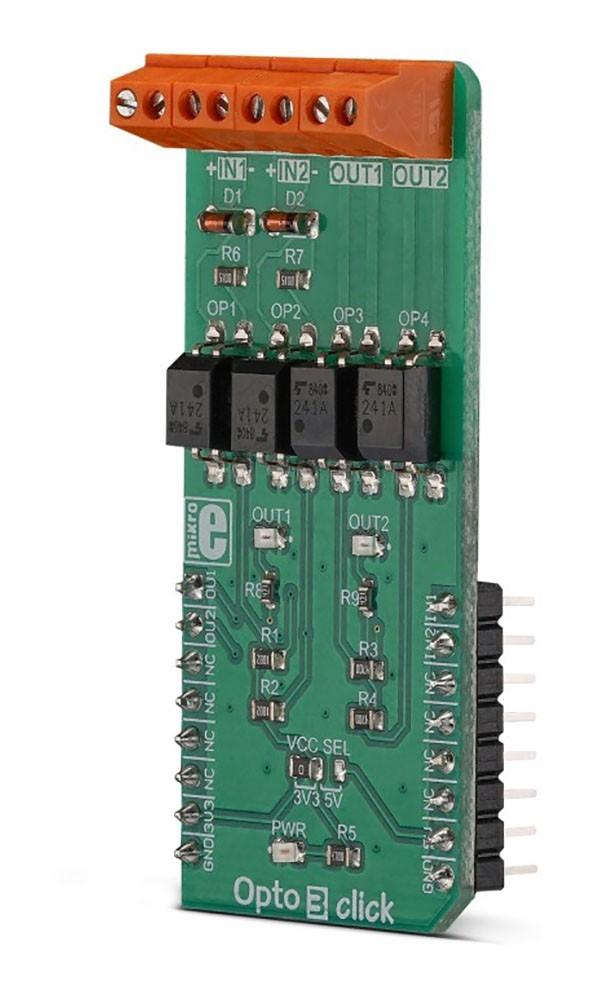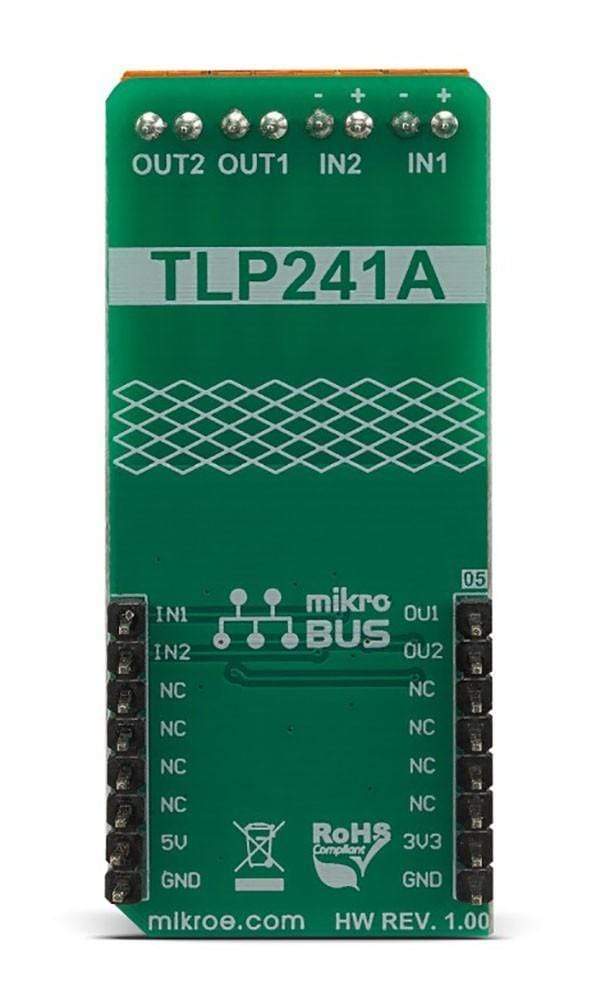

Overview
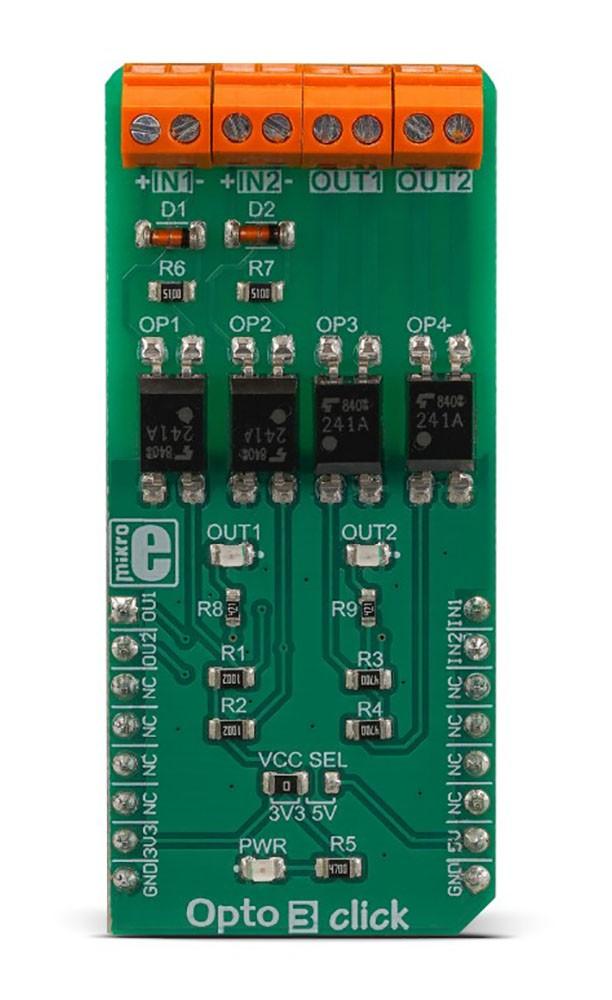
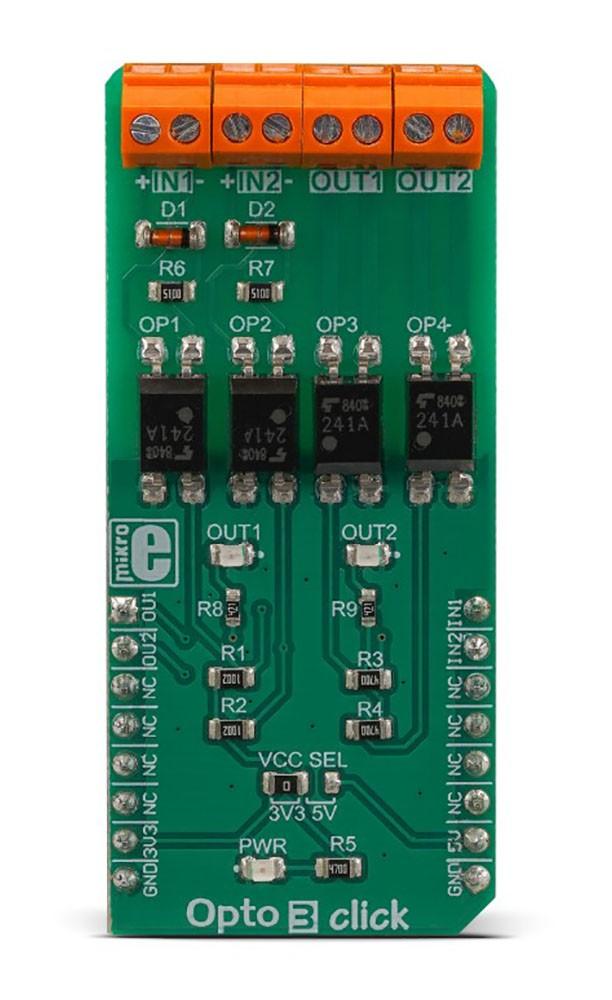
The Opto 3 Click Board™ is equipped with two pairs of optically isolated solid-state relays (SSR). One pair of SSRs is used to provide reinforced galvanic isolation for the external signals used to drive the microcontroller (MCU) pins, while the other pair of SSRs are used to allow the host MCU to drive some external equipment, allowing up to 40V between the SSR contacts in OFF state, and currents up to 2A while in ON state, thanks to a very low ON-state resistance.
The Opto 3 Click Board™ is to be used in applications that require reinforced galvanic isolation for both their input and output stages.
Downloads
Featuring good quality TLP241A SSRs, the Opto 3 Click Board™ represents an ideal solution for the development of various PLC-based applications, where it can be used as a replacement for mechanical relays, bringing the whole range of inherited benefits: no mechanical parts which can wear off, constant ON-state resistance, immunity to environmental influences and mechanical shock, no contact bouncing effect, and more. Two onboard LEDs provide visual feedback on the state of the output SSR pair, while the input SSR pair is protected from inverse polarization and the damage it may cause, by low voltage drop Schottky diodes.
How Does The Opto 3 Click Board™ Work?
The Opto 3 Click Board™ features two pairs of normally opened, high-quality solid-state relays labelled as TLP241A, by Toshiba. The TLP241A is an optically isolated solid-state relay (SSR), featuring an integrated IR LED and two output MOSFETs. The output stage does not have any electrical contact with the input stage; it is activated by infrared light, produced by an integrated IR LED. This allows reinforced galvanic isolation between the input and the output stage. The output stage can sustain up to 40V while OFF. When activated, due to a very low RDSON of the integrated MOSFETs, it can conduct up to 2A of current.
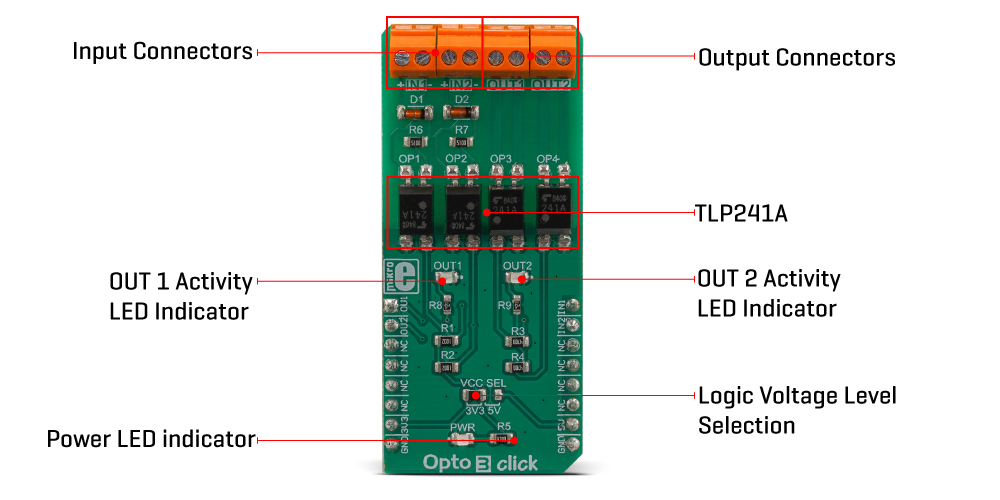
The TLP241A are able to effectively replace traditionally used mechanical relays, bringing up the full set of inherited benefits: virtually unlimited number of cycles since there are no moving parts that would wear off, no bouncing effect on the output contacts, high resistance to mechanical shock and environmental influence, low current required for the activation, constant resistance since no carbon and rust can build up on contacts, there is no sparking or electric arc forming while operated, compact size, higher isolation voltage, and so on. However, unlike optocouplers (similar devices which are designed for much lower currents and voltages), SSRs are not designed to be used as signal line isolators. SSR typically has a slow signal propagation time. Still, it can be used for various communication protocols which use lower data rates, including UART/RS232, 1-Wire, and similar.
One pair of SSRs is driven by the host MCU. This pair can be used to activate an external circuit, utilizing the full potential of the TLP241A SSR. One or two SSRs can be used as relays, allowing the host MCU to control heavier loads such as DC motors, some other electrical circuit that operates on higher potential, LED strips, LED arrays, etc. A HIGH logic level on mikroBUS™ pins AN or RST labelled as OU1 and OU2 respectively will activate the integrated IR LED. It will turn ON the MOSFETs in the SSR, allowing the current to flow through an external circuit. Two red LEDs, labelled as OUT1 and OUT 2, are connected to each of the MCU output pins. These LEDs provide visual feedback about the SSR state: if ON, the respective SSR is in a conductive state. SSR outputs are routed to two screw terminals labelled OUT1 and OUT2, allowing an external circuit to be securely connected.
The other pair of SSRs are used to provide optical isolation for external signals, offering protection for sensitive MCU pins that way. While the SSR is not activated, PWM and INT pins of the mikroBUS™ labelled as IN1 and IN2 respectively, are pulled to a HIGH logic level by a resistor. A signal on the input terminal will activate the respective SSR, pulling the IN1 (IN2) pin to a LOW logic level. Since galvanically isolated, the signal at the input terminal can be at a different potential than the host MCU, preventing any stray currents to flow between two GNDs. This will also protect the host MCU from the electrostatic discharge (ESD) that might occur. It is important to connect the input signal correctly. Therefore, two input terminals have their ports clearly labelled with + and - signs. A Schottky diode in series provides some protection to the input IR LED, however, care should be taken not to exceed specifications from the TLP241A datasheet.
Pull-up resistors on the input side SSRs are connected to the power supply from mikroBUS™, providing a HIGH logic level while the SSR is not active. The voltage of the power supply directly determines the voltage level that will be applied to IN1 and IN2 pins in this case. Therefore, an SMD jumper labelled as VCC SEL is provided on the Click board™, allowing the user to select the logic voltage level between 3.3V and 5V, depending on the used MCU and its capabilities.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Type | Optocoupler |
| Applications | The Opto 3 Click Board™ represents an ideal solution for the development of various PLC-based applications, where it can be used as a replacement for mechanical relays, bringing the whole range of inherited benefits |
| On-board modules | TLP241A, a solid-state photo-relay by Toshiba |
| Key Features | One input and one output pair of high-quality SSRs, reasonably high current and voltage on the output side, low driving current, two LEDs for visual feedback of the output stage, protection diodes on the input side, the whole range of inherited benefits, typical for SSRs, etc. |
| Interface | GPIO |
| Compatibility | mikroBUS |
| Click board size | M (42.9 x 25.4 mm) |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V or 5V |
PINOUT DIAGRAM
This table shows how the pinout on Opto 3 Click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
| Notes | Pin |  |
Pin | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relay 1 OUT | OU1 | 1 | AN | PWM | 16 | IN1 | Relay 1 IN |
| Relay 2 OUT | OU1 | 2 | RST | INT | 15 | IN2 | Relay 2 IN |
| NC | 3 | CS | RX | 14 | NC | ||
| NC | 4 | SCK | TX | 13 | NC | ||
| NC | 5 | MISO | SCL | 12 | NC | ||
| NC | 6 | MOSI | SDA | 11 | NC | ||
| Power Supply | +3V3 | 7 | 3.3V | 5V | 10 | +5V | Power Supply |
| Ground | GND | 8 | GND | GND | 9 | GND | Ground |
ONBOARD SETTINGS AND INDICATORS
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | OUT1 | - | OUT1 Activity LED indicator |
| LD2 | OUT2 | - | OUT2 Activity LED indicator |
| LD3 | PWR | - | Power LED indicator |
| JP1 | VCC SEL | Left | Logic voltage level selection: left position 3.3V, right position 5V |
| CN1, CN2 | IN1, IN2 | - | Input connectors |
| CN3, CN4 | OUT1, OUT2 | - | Output connectors |
OPTO 3 CLICK ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
| Description | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input forward current (I F ) | 5 | 7.5 | 25 | mA |
| Peak transient input forward current (I FPT ) | - | - | 2 | A |
| Output current (I O ) | - | - | 32 | V |
| Operating temperature | -20 | - | +65 | ℃ |
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-3319
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.023 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018714261
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.