Key Features
Overview
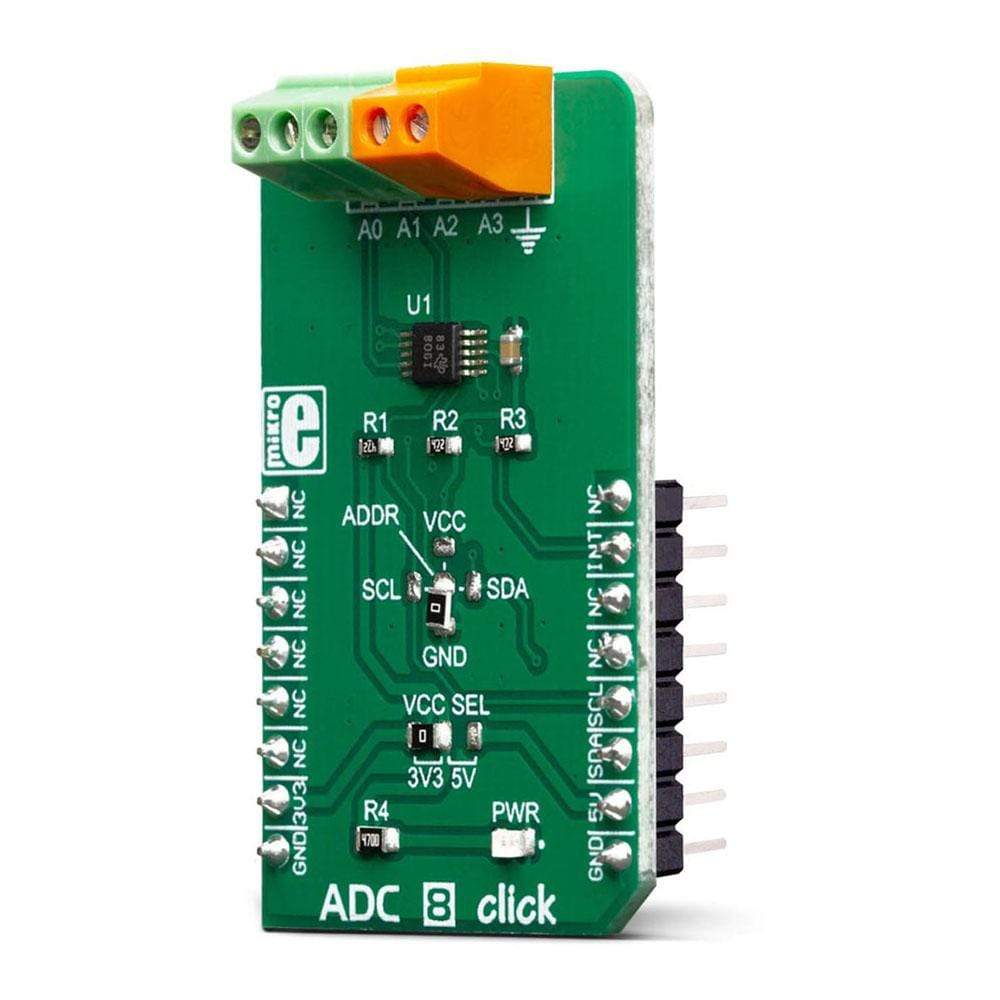
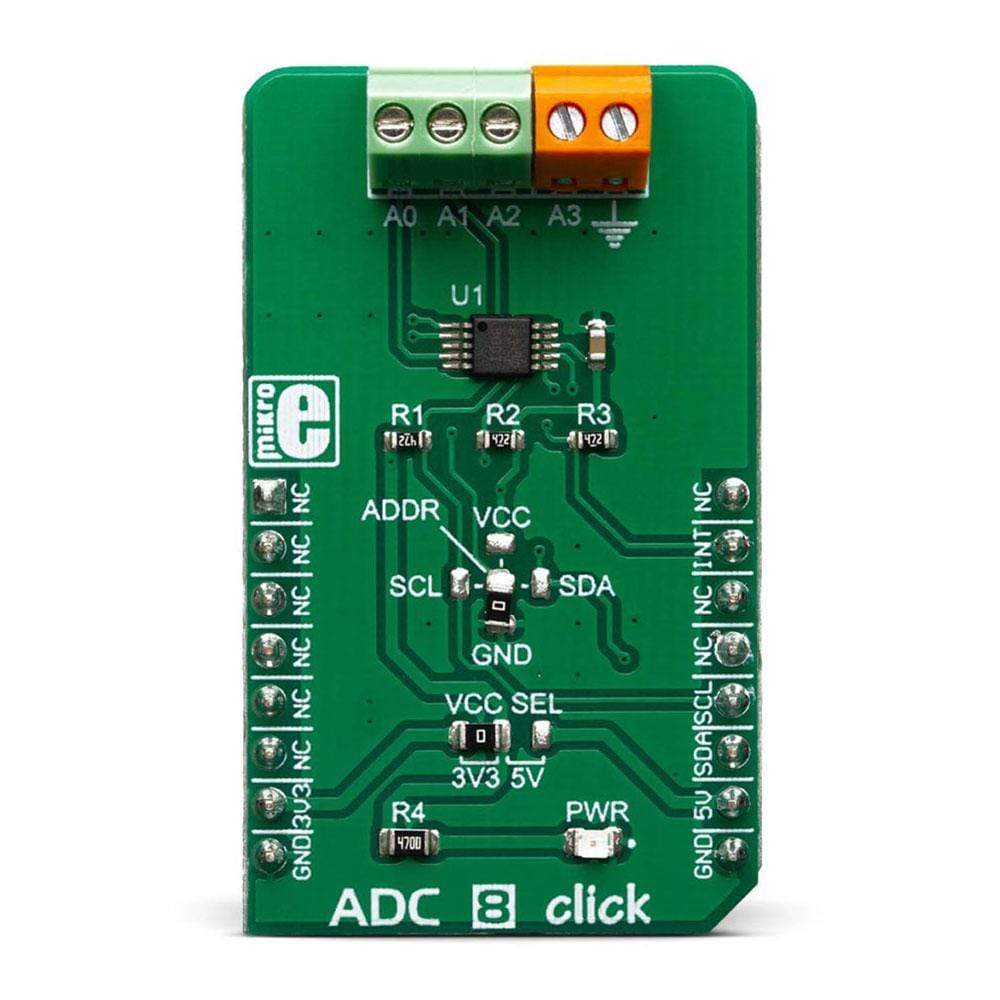
The ADC 8 Click Board™ is a high precision, low-power, 16-bit analogue-to-digital converter (ADC), based around the ADS1115 IC. It is capable of sampling signals on four single-ended or two differential input channels.
Although the ADS1115 cannot use an external reference, it incorporates a low-drift programmable voltage reference, along with the programmable gain amplifier (PGA). This allows for great flexibility in terms of the input signal level: it can sample signals from ±256 mV, up to 6.144 V, allowing a very high precision for a wide range of input signals, making it an excellent choice for various instrumentation applications.
Downloads
The ADS1115 ADC can operate either in continuous or in a single-shot mode. While operating in a single-shot mode, the current consumption is significantly reduced, since the ADS1115 powers down after each conversion. Its maximum sample rate in continuous mode is up to 860 SPS. An overvoltage on the input can be detected and reported over the ALERT pin. These features, along with the selectable operating voltage (3.3V or 5V), make the ADC 8 click perfectly suited for portable instrumentation applications, battery voltage, and current monitoring, analog sensor output conversion, etc.
How Does The ADC 8 Click Board™ Work?
The main component of ADC 8 Click Board™ is the ADS1115 IC, an ultra-small, low-power, high-precision, 16-bit A/D converter, from Texas Instruments. It is a delta-sigma converter with an integrated high-precision voltage reference, which can be programmed in several different steps. The maximum data rate of this ADC is 860 SPS, however, it features an excellent signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The ADS1115 has two differential or four single-ended inputs. The internal multiplexer is used to select the active input. The input pins are routed to two input terminals on the edge of the Click board™, allowing it to be easily interfaced with the analog signal source.
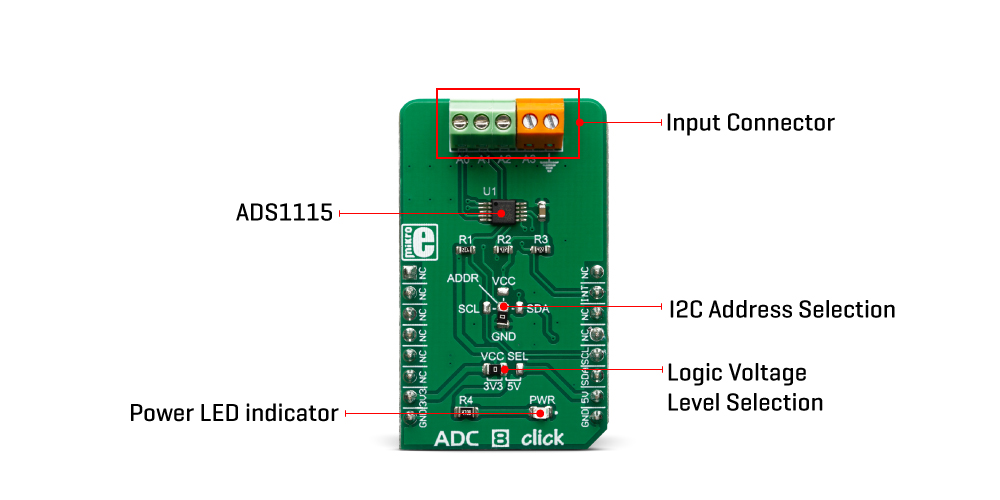
Besides power supply pins and I2C interface pins, the ADS1115 has an additional ALERT/RDY pin used to signal that there is a conversion data available on the output register. This pin can also be set to output an overvoltage event. An internal comparator module can detect if the input signal exceeds the voltage reference level and report the overvoltage event at the ALERT/RDY pin. This pin is routed to the mikroBUS™ INT pin. Both I2C pins along with the ALERT/RDY pin, are pulled to a HIGH logic level by the pull-up resistors.
The conversion output is available over the I2C interface, in 16-bit two's complement LSB/MSB format. A positive input signal can have values in the range from 0x0001 to 0x7FFF, while the negative input signal can have values in the range from 0x0000 to 0x8000. The slave I2C address of the device can be selected by moving the SMD jumper labeled as ADDR. It allows four different I2C addresses to be selected and thus, up to four different ADC 8 clicks can be used on a single I2C bus.
Signal to Noise ratio (SNR) depends on two factors: the reference voltage and the output data rate. Delta-sigma ADCs are based on the oversampling principle: the input signal is sampled at a higher frequency and it is subsequently filtered and decimated, until the output value is obtained, at the requested output data rate. The ratio between the high sampling frequency (modulator) and the output data rate is called oversampling ratio (OSR). By increasing the OSR, less noise appears at the output, since more values are included in the averaging process.
As already mentioned, the ADS1115 IC cannot use an external voltage reference. However, it has a high-precision internal reference with low drift over temperature. It can be selected from several available values: ±0.256, ±0.512, ±1.024, ±2.048V, ±4.096, and ±6.144. Note, however, that the input signal should not be greater than VCC + 0.3V. In other words, it is not possible to use the 4.096V if the power supply source is 3.3V. ADC 8 click is equipped with the SMD jumper labeled as VCC SEL, which allows selection between 3.3V and 5V.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Type | ADC |
| Applications | It is well suited for portable instrumentation applications, battery voltage, and current monitoring, analog sensor output conversion, etc. |
| On-board modules | ADS1115 IC, an ultra-small, low-power, high-precision, 16-bit A/D converter, from Texas Instruments. |
| Key Features | Analog to digital conversion from 4 single-ended channels or 2 differential input channels, sampling resolution of 16 bits over the I2C interface, programmable high-precision internal reference… |
| Interface | I2C |
| Compatibility | mikroBUS |
| Click board size | M (42.9 x 25.4 mm) |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V or 5V |
PINOUT DIAGRAM
This table shows how the pinout on the ADC 8 Click Board™ corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
| Notes | Pin |  |
Pin | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 1 | AN | PWM | 16 | NC | ||
| NC | 2 | RST | INT | 15 | INT | Alert/Data Ready | |
| NC | 3 | CS | RX | 14 | NC | ||
| NC | 4 | SCK | TX | 13 | NC | ||
| NC | 5 | MISO | SCL | 12 | SCL | I2C Clock | |
| NC | 6 | MOSI | SDA | 11 | SDA | I2C Data | |
| Power Supply | 3.3V | 7 | 3.3V | 5V | 10 | 5V | Power supply |
| Ground | GND | 8 | GND | GND | 9 | GND | Ground |
ONBOARD SETTINGS AND INDICATORS
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | - | Power LED indicator |
| JP1 | VREF SEL | Left | Power supply voltage selection, left position 3.3V, right 5V |
| JP2, JP3 | ADDR | Down | Slave I2C Address Selection |
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-3394
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.02 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018714674
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.