Mikroelektronika d.o.o.
DIGI POT 6 Click Board
DIGI POT 6 Click Board
Couldn't load pickup availability
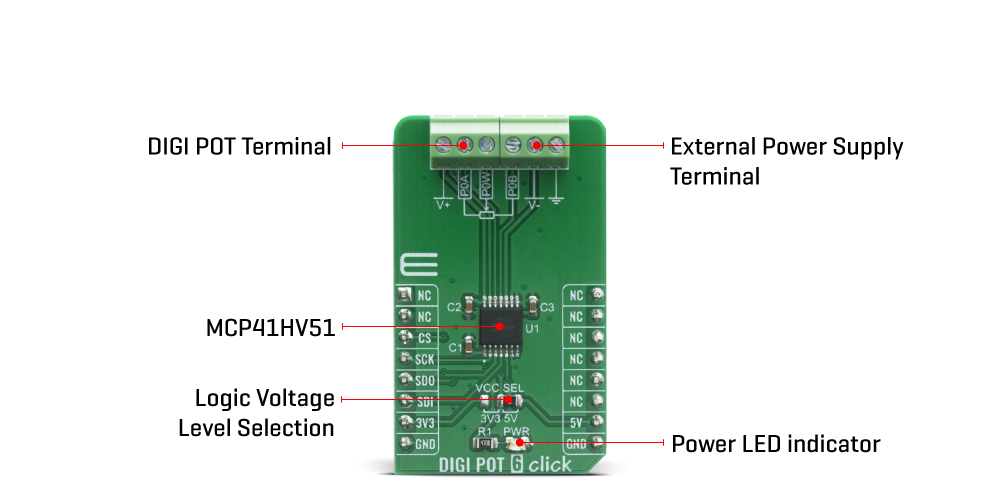
The DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ features the Microchip MCP41HVX1 family of devices which have dual power rails (analogue and digital). The analogue power rail allows the high voltage on the resistor network terminal pins. The analogue voltage range is determined by the V+ and V- voltages. The maximum analogue voltage is +36V, while the operating analogue output minimum specifications are specified from either 10V or 20V. As the analogue supply voltage becomes smaller, the analogue switch resistances increase, which affects certain performance specifications. The system can be implemented as dual-rail (±18V) relative to the digital logic ground (DGND). The device also has a Write Latch (WLAT) function, which will inhibit the volatile wiper register from being updated (latched) with the received data until the Write Latch (WLAT) pin is low. This allows the application to specify a condition where the volatile wiper register is updated (such as zero-crossing).
The DIGI POT 6 Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click Board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.







Overview
The DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ features the Microchip MCP41HVX1 family of devices which have dual power rails (analogue and digital). The analogue power rail allows the high voltage on the resistor network terminal pins. The analogue voltage range is determined by the V+ and V- voltages. The maximum analogue voltage is +36V, while the operating analogue output minimum specifications are specified from either 10V or 20V. As the analogue supply voltage becomes smaller, the analogue switch resistances increase, which affects certain performance specifications. The system can be implemented as dual-rail (±18V) relative to the digital logic ground (DGND). The device also has a Write Latch (WLAT) function, which will inhibit the volatile wiper register from being updated (latched) with the received data until the Write Latch (WLAT) pin is low. This allows the application to specify a condition where the volatile wiper register is updated (such as zero-crossing).
The DIGI POT 6 Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click Board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
How Does The DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ Work?
The DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ as its foundation uses the MCP41HV51, 8-bit dual power rails digital potentiometer with SPI serial interface and volatile memory from Microchip. It has a wide operating voltage range, analog from 10 to 36V and digital from 2.7 to 5.5V or implemented as dual-rail (±18V) for systems requiring wide signal swing or high power-supply voltages. It supports resistor configurations of 255 resistors and 256 steps and high terminal/wiper current, including the ability to sink/source up to 25mA on all terminal pins for driving larger loads.
The resistor network of the MCP41HV51 has an 8-bit resolution where each resistor network allows Zero-Scale to Full-Scale connections. All these features combined with an extended temperature range make the MCP41HV51 well suited for a broad range of high-voltage and high-temperature applications, including those in the industrial, automotive, and audio markets.
The DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ communicates with MCU using the SPI serial interface with a maximum frequency of 10MHz and supports the two most common SPI modes, 0 and 3. This Click board™ also has three terminals labelled as P0A, P0B, and P0W, with an internal architecture that comprises various resistances and switches. The resistance between terminals A and B, RAB, commonly called the "end-to-end" resistance, provides RAB resistance options up to 100 kΩ. In contrast, the wiper terminal, P0W, is digitally programmable to access any 2n tap points on the resistor string.
The DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ can operate with both 3.3V and 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, it is allowed for both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs to properly use the SPI communication lines. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used, as a reference, for further development.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Type | Digital potentiometer |
| Applications | The DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ can be used for precision calibration of set point thresholds, adjustable power supplies, adjustable gain amplifiers and offset trimming, and more. |
| On-board modules | MCP41HV51 - 8-bit dual power rails digital potentiometer with SPI serial interface and volatile memory from Microchip. |
| Key Features | Wide operating voltage range, configurable resistance options, Zero-Scale to Full-Scale wiper operation, low wiper resistance, and more. |
| Interface | SPI |
| Compatibility | mikroBUS |
| Click board size | M (42.9 x 25.4 mm) |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V or 5V |
PINOUT DIAGRAM
This table shows how the pinout of the DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
| Notes | Pin |  |
Pin | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 1 | AN | PWM | 16 | NC | ||
| NC | 2 | RST | INT | 15 | NC | ||
| SPI Chip Select | CS | 3 | CS | RX | 14 | NC | |
| SPI Clock | SCK | 4 | SCK | TX | 13 | NC | |
| SPI Data OUT | SDO | 5 | MISO | SCL | 12 | NC | |
| SPI Data IN | SDI | 6 | MOSI | SDA | 11 | NC | |
| Power Supply | 3.3V | 7 | 3.3V | 5V | 10 | 5V | Power Supply |
| Ground | GND | 8 | GND | GND | 9 | GND | Ground |
ONBOARD SETTINGS AND INDICATORS
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | - | Power LED Indicator |
| JP1 | VCC SEL | Right | Power Supply Voltage Selection 3V3/5V, left position 3V3, right position 5V |
DIGI POT 6 CLICK ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
| Description | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Supply Voltage | 3.3 | - | 5 | V |
| Analog Supply Voltage | 10 | - | 36 | V |
| Maximum Output Current | - | - | 25 | mA |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40 | +25 | +125 | °C |
Software Support
We provide a library for the DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ on our LibStock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MikroElektronika compilers. The demo can run on all the main MikroElektronika development boards.
Library Description
The library covers necessary functions that enable the usage of the DIGI POT 6 Click Board™. User can read and write data to and from Volatile Wiper 0 and Volatile TCON Register or issue increment and decrement commands to Volatile Wiper 0. User can also Connect/Disconnect Resistor 0 Terminal A, Resistor 0 Terminal B, Resistor 0 Wiper and Resistor 0 Hardware Configuration Control.
Key Functions
void digipot6_write_data ( uint8_t reg_adr, uint8_t wr_byte )- Function is used to write single byte of data into user defined register.uint8_t digipot6_read_data ( uint8_t reg_adr );- Function is used to read single byte of data from user defined register.void digipot6_set_r0hw ( uint8_t state );- Function is used to force Resistor 0 into the “shutdown” configuration.
Example Description
The application is composed of three sections :
- System Initialization - Initializes SPI module and LOG structures.
- Application Initialization - Initalizes SPI and device drivers, wakes up the device and connects terminal A, terminal B and wiper to the resistor 0 network.
- Application Task - Demonstrates use of the DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ by setting wiper to step 0, then going through the steps, fifteen at a time and displaying data via USART terminal.
void application_task ( ) { digipot6_write_data( DIGIPOT6_VOLATILE_WIPER_0, 0x00 ); for ( cnt = 0; cnt <= 255; cnt += 15 ) { digipot6_write_data( DIGIPOT6_VOLATILE_WIPER_0, cnt ); Delay_ms( 10 ); wiper_val = digipot6_read_data( DIGIPOT6_VOLATILE_WIPER_0 ); ByteToStr( wiper_val, log_txt ); mikrobus_logWrite( " Wiper step : ", _LOG_TEXT ); Ltrim( log_txt ); mikrobus_logWrite( log_txt, _LOG_LINE ); Delay_ms( 1000 ); } mikrobus_logWrite( "------------------------", _LOG_LINE ); Delay_ms( 1000 ); }The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our LibStock page.
Other mikroE Libraries used in the example:
- SPI
- UART
- Conversions
Additional Notes and Information
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MikroElektronika compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
MIKROSDK
The DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ is supported with mikroSDK - MikroElektronika Software Development Kit. To ensure proper operation of mikroSDK compliant Click board™ demo applications, mikroSDK should be downloaded from the LibStock and installed for the compiler you are using.
Software Support
We provide a library for the DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ on our LibStock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MikroElektronika compilers. The demo can run on all the main MikroElektronika development boards.
Library Description
The library covers necessary functions that enable the usage of the DIGI POT 6 Click Board™. User can read and write data to and from Volatile Wiper 0 and Volatile TCON Register or issue increment and decrement commands to Volatile Wiper 0. User can also Connect/Disconnect Resistor 0 Terminal A, Resistor 0 Terminal B, Resistor 0 Wiper and Resistor 0 Hardware Configuration Control.
Key Functions
void digipot6_write_data ( uint8_t reg_adr, uint8_t wr_byte )- Function is used to write single byte of data into user defined register.uint8_t digipot6_read_data ( uint8_t reg_adr );- Function is used to read single byte of data from user defined register.void digipot6_set_r0hw ( uint8_t state );- Function is used to force Resistor 0 into the “shutdown” configuration.
Example Description
The application is composed of three sections :
- System Initialization - Initializes SPI module and LOG structures.
- Application Initialization - Initalizes SPI and device drivers, wakes up the device and connects terminal A, terminal B and wiper to the resistor 0 network.
- Application Task - Demonstrates use of the DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ by setting wiper to step 0, then going through the steps, fifteen at a time and displaying data via USART terminal.
void application_task ( ) { digipot6_write_data( DIGIPOT6_VOLATILE_WIPER_0, 0x00 ); for ( cnt = 0; cnt <= 255; cnt += 15 ) { digipot6_write_data( DIGIPOT6_VOLATILE_WIPER_0, cnt ); Delay_ms( 10 ); wiper_val = digipot6_read_data( DIGIPOT6_VOLATILE_WIPER_0 ); ByteToStr( wiper_val, log_txt ); mikrobus_logWrite( " Wiper step : ", _LOG_TEXT ); Ltrim( log_txt ); mikrobus_logWrite( log_txt, _LOG_LINE ); Delay_ms( 1000 ); } mikrobus_logWrite( "------------------------", _LOG_LINE ); Delay_ms( 1000 ); }The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our LibStock page.
Other mikroE Libraries used in the example:
- SPI
- UART
- Conversions
Additional Notes and Information
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MikroElektronika compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
MIKROSDK
The DIGI POT 6 Click Board™ is supported with mikroSDK - MikroElektronika Software Development Kit. To ensure proper operation of mikroSDK compliant Click board™ demo applications, mikroSDK should be downloaded from the LibStock and installed for the compiler you are using.
DIGI POT 6 Click Board
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.







