
Overview
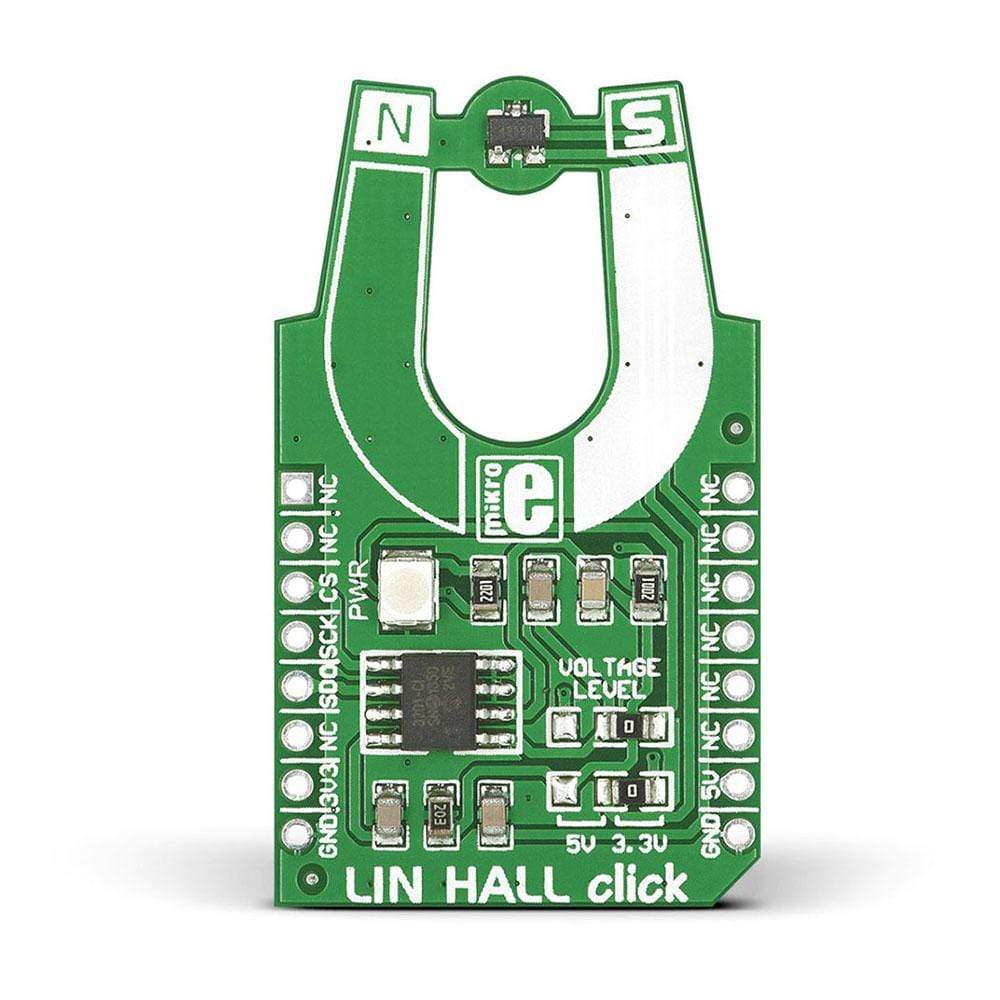
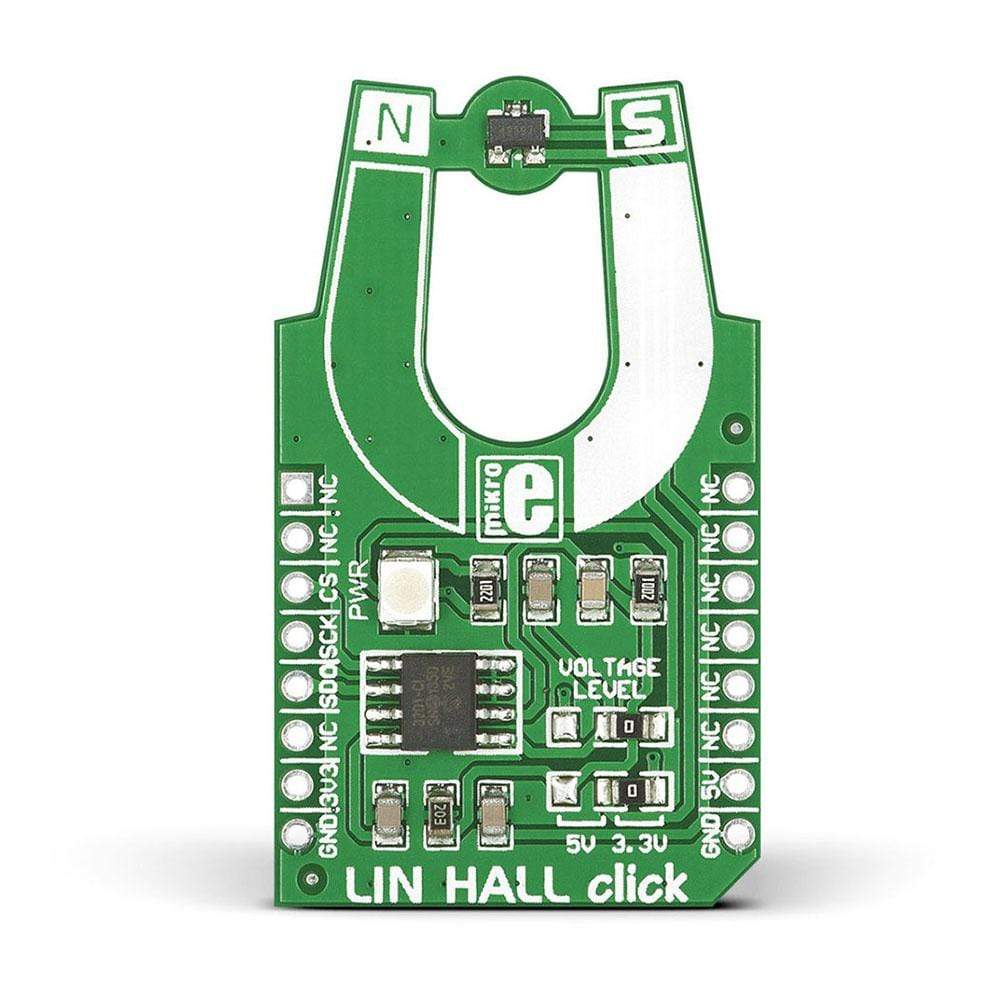
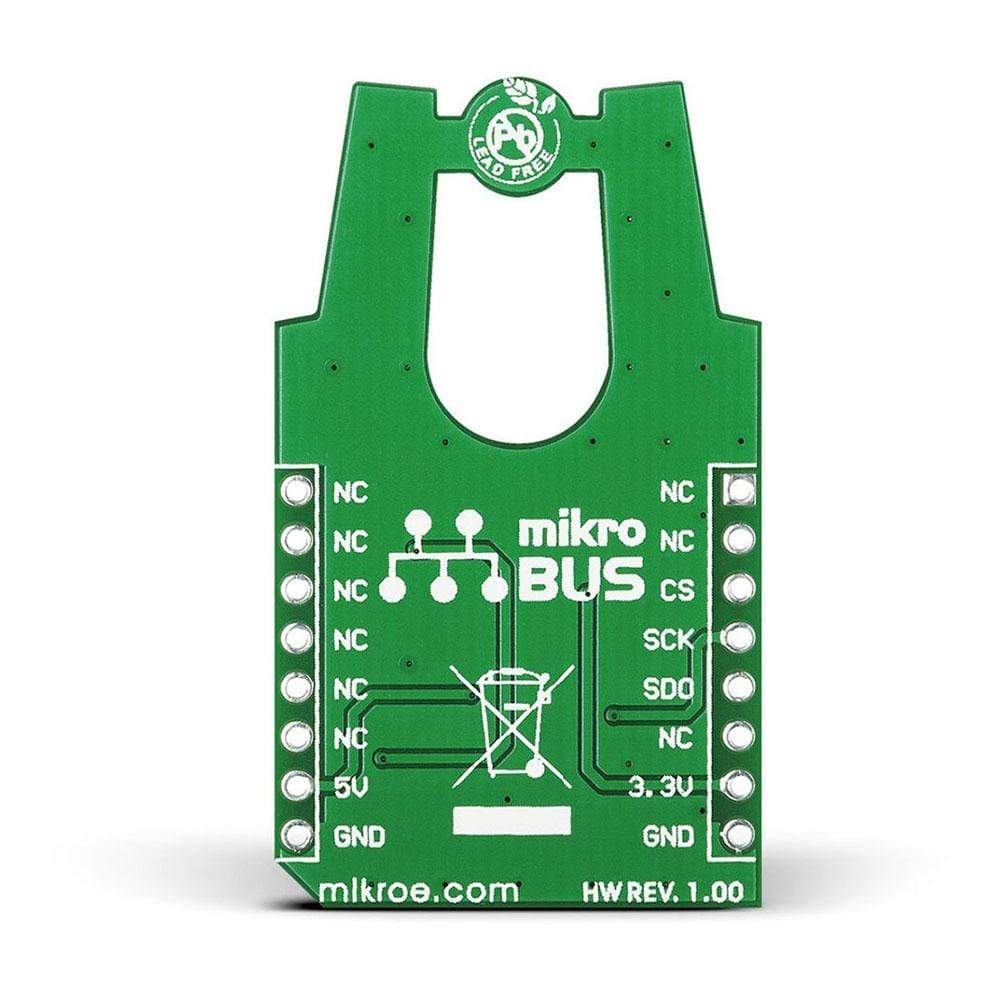
Introduce a linear Hall sensor to your design with the LIN HALL Click Board™. The board includes a Melexis MLX90242 linear Hall sensor IC along with an MCP3201 12-bit ADC. The LIN HALL Click Board™ outputs a signal that is linearly proportional to the flux density of a magnetic field it is exposed to. A north pole magnet field will increase the output, while a south pole field decreases it. Using the MikroBUS SPI lines (CS,.SCK, MISO),
LIN HALL Click Board™ communicates with the target board microcontroller. It uses either a 3.3V or 5V power supply (default is 3.3V).
The linear Hall sensors are used to infer the linear or rotary position of a target object, provided there is a magnet attached or something to disturb an existing magnetic field. It is an ideal choice to measure the strength of different magnets or measure the distance of a magnet from the sensor.
Downloads
Introduisez un capteur Hall linéaire dans votre conception avec la carte Click Board™ LIN HALL . La carte comprend un circuit intégré de capteur Hall linéaire Melexis MLX90242 ainsi qu'un ADC 12 bits MCP3201. La carte Click Board™ LIN HALL génère un signal linéairement proportionnel à la densité de flux d'un champ magnétique auquel il est exposé. Un champ magnétique du pôle nord augmentera la sortie, tandis qu'un champ du pôle sud la diminuera. En utilisant les lignes SPI MikroBUS (CS,.SCK, MISO),
La carte LIN HALL Click Board™ communique avec le microcontrôleur de la carte cible. Elle utilise une alimentation de 3,3 V ou de 5 V (la valeur par défaut est de 3,3 V).
Les capteurs à effet Hall linéaires sont utilisés pour déduire la position linéaire ou rotative d'un objet cible, à condition qu'un aimant soit fixé ou qu'un élément perturbe un champ magnétique existant. C'est un choix idéal pour mesurer la force de différents aimants ou mesurer la distance d'un aimant par rapport au capteur.
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-1648
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.03 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606015075617
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.