Overview
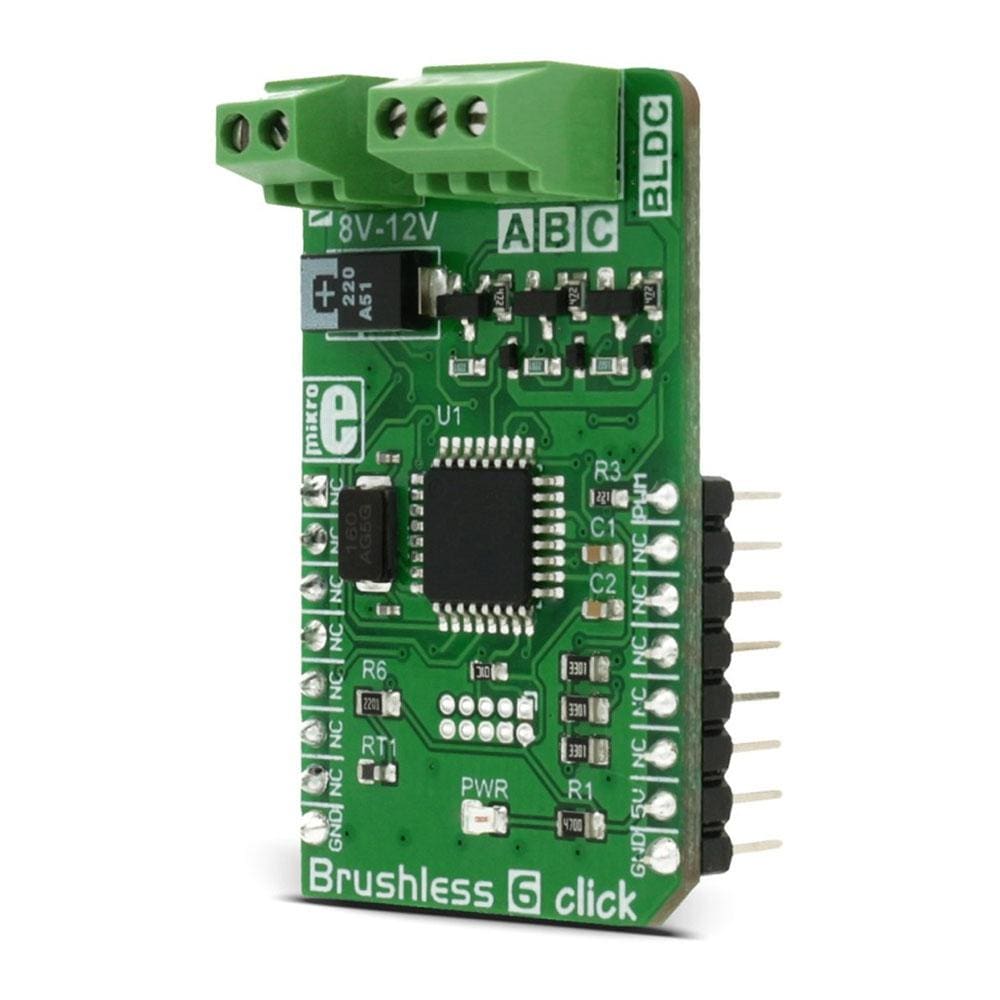
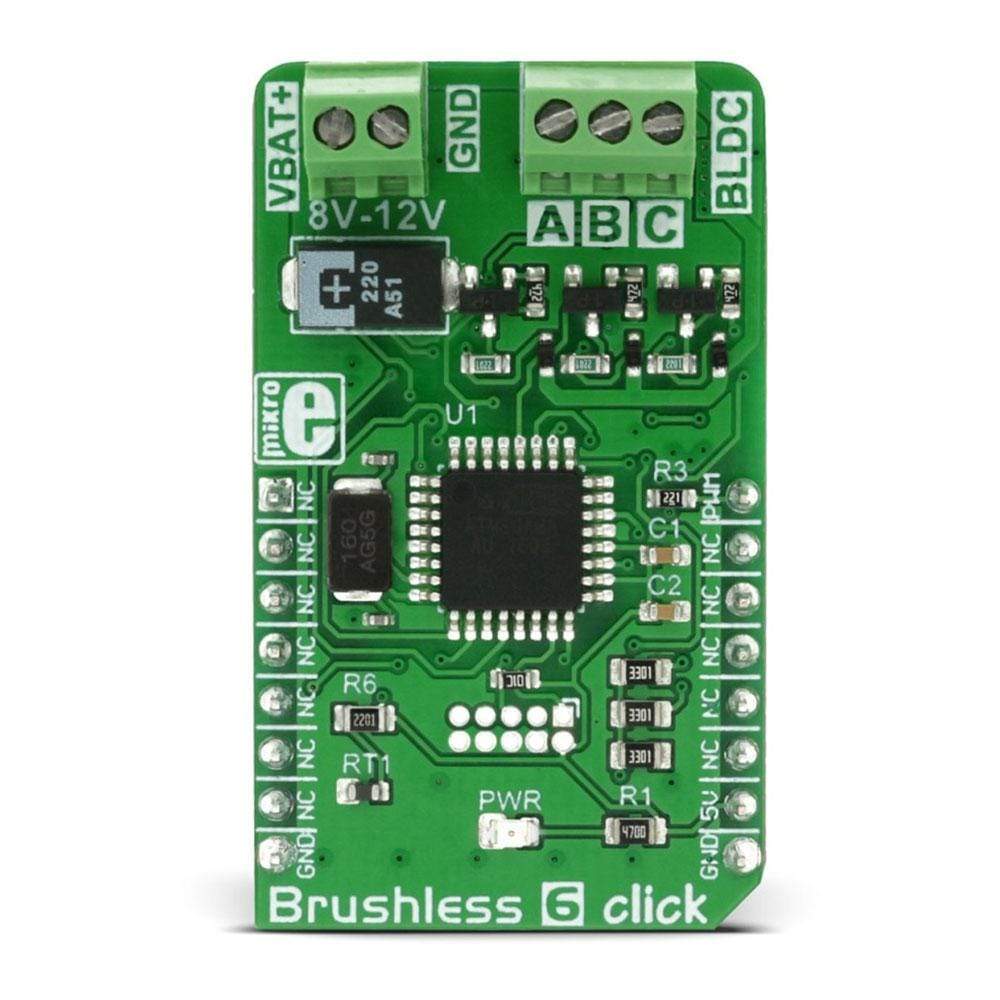
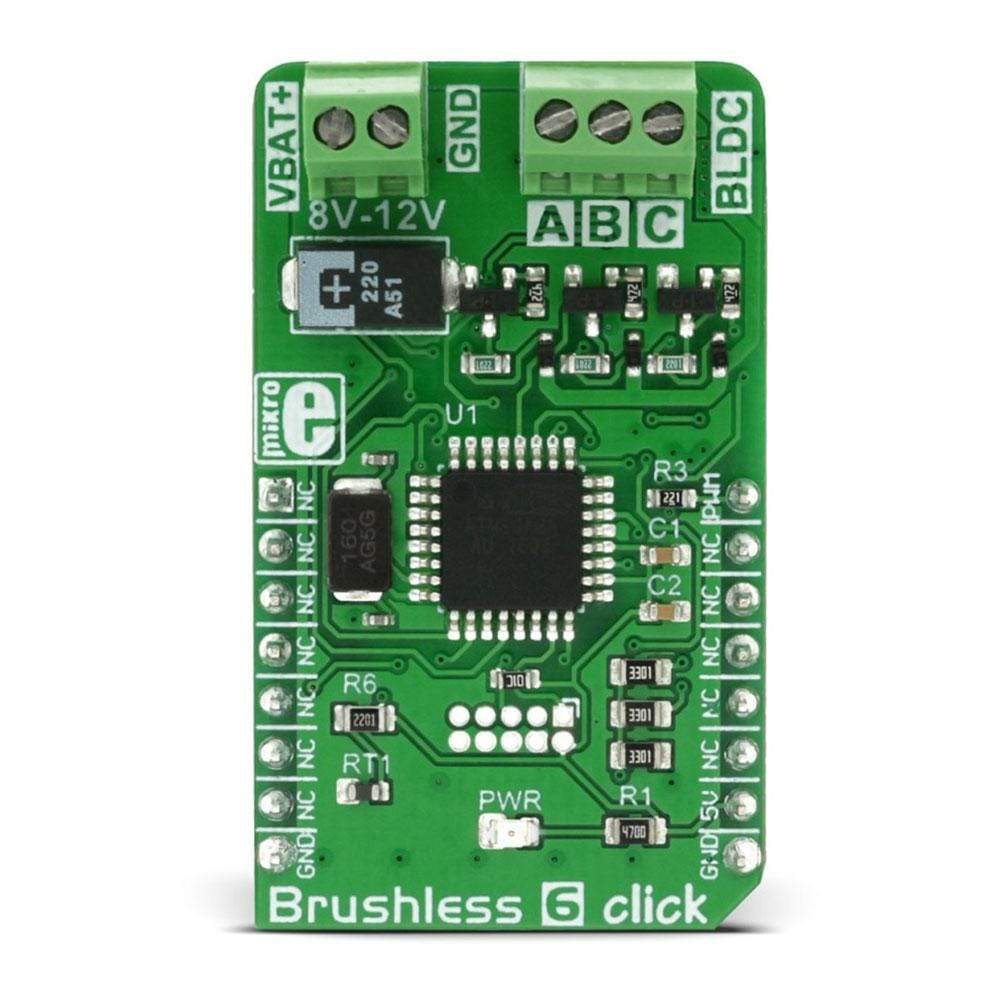
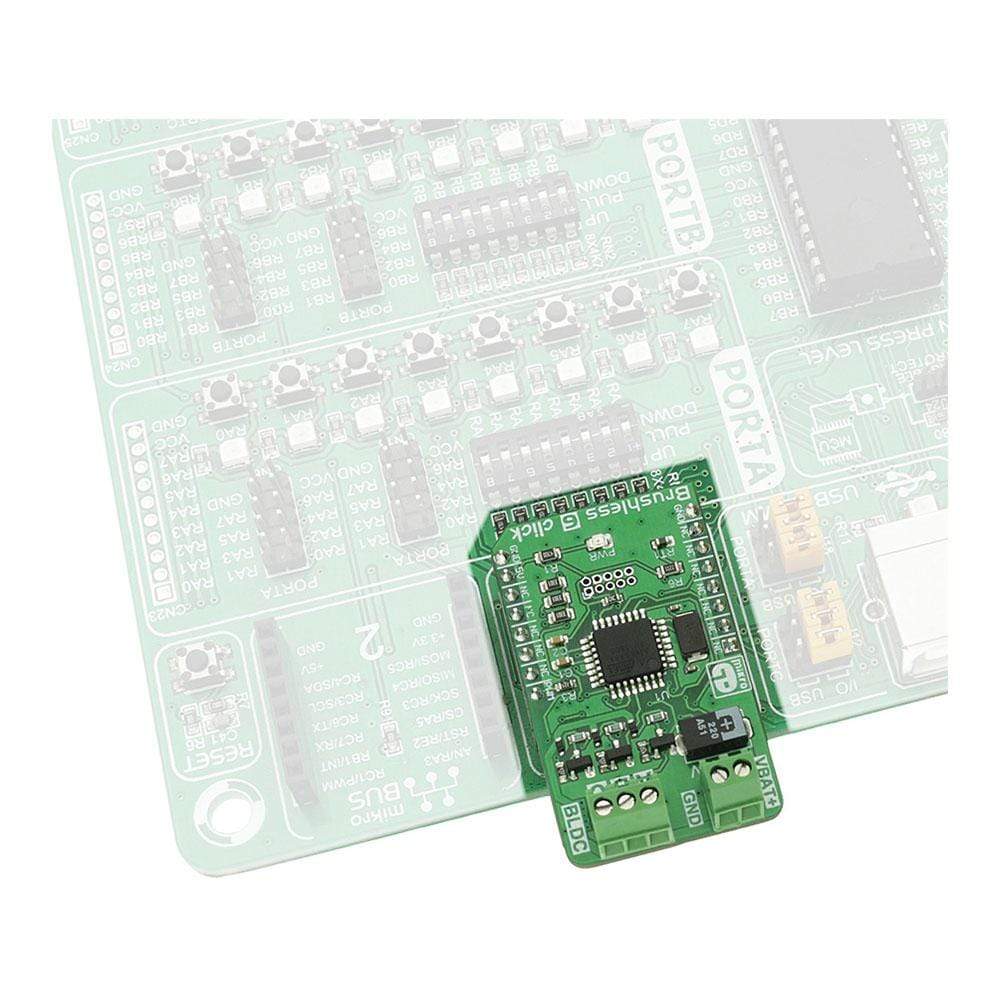
The Brushless 6 Click Board™ is designed to drive a three-phase sensorless, brushless motor, also known as the BLDC motor. The motor rotation is controlled by receiving driving commands via the incoming PWM signal. This Click Board™ fully controls the rotation of the BLDC motor by utilizing the on-board MCU ATmega8A, an 8-bit MCU from Microchip. The on-board MCU outputs are not adequate to power on the coils of the BLDC motor directly, so this MCU is used to control the power circuitry, instead. This circuit consists of 6 MOSFET transistors, used to switch the power from an external power source to the appropriate stator coils.
Downloads
Le Brushless 6 Click Board™ est conçu pour piloter un moteur triphasé sans capteur et sans balai, également connu sous le nom de moteur BLDC. La rotation du moteur est contrôlée par la réception de commandes de pilotage via le signal PWM entrant. Ce Click Board™ contrôle entièrement la rotation du moteur BLDC en utilisant le MCU embarqué ATmega8A, un MCU 8 bits de Microchip. Les sorties du MCU embarqué ne sont pas suffisantes pour alimenter directement les bobines du moteur BLDC, ce MCU est donc utilisé pour contrôler le circuit d'alimentation. Ce circuit se compose de 6 transistors MOSFET, utilisés pour commuter l'alimentation d'une source d'alimentation externe vers les bobines de stator appropriées.
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-2847
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.02 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018712090
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.