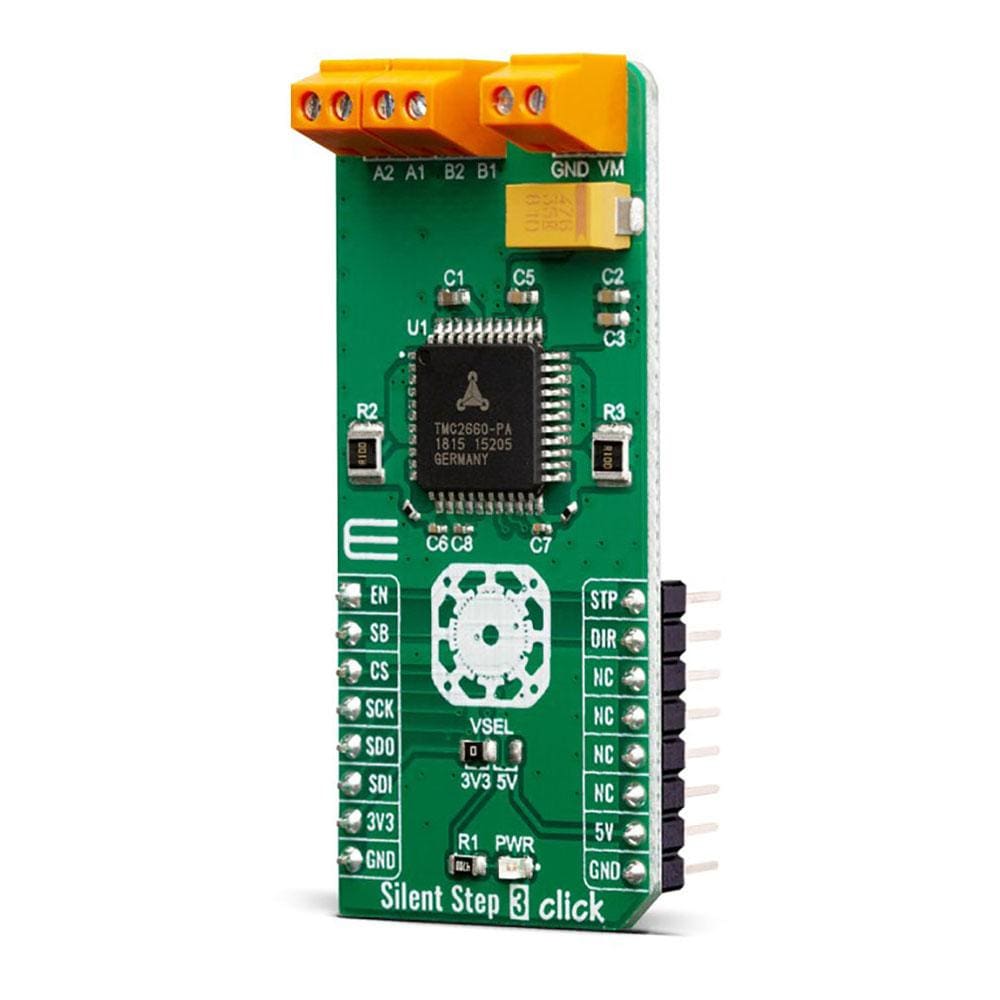



Overview
The Silent Step 3 Click Board™ is the complete integrated bipolar step motor driver solution, rich with many features that allow extremely smooth and silent operation of the connected motor while being able to provide up to 4A peak motor current and withstand up to 30V supply voltage. The specialized TMC2660 IC driver from Trinamic company far exceeds the capabilities of similar step motor drivers that are commonly used. Thereby, the Silent Step 3 Click Board™ is basically the “intelligence and power” between the main MCU, as a motion controller, and the two-phase stepper motor.
The device achieves outstanding performance with a wide range of various step motors, thanks to several technologies featured, such as stallGuard2™ - high precision sensorless motor load detection; spreadCycle™ - highly dynamic motor current control; microPlayer™ - microstep interpolation for increased smoothness with coarse step inputs, and many more.
Downloads
Besides these advanced technologies, the TMC2660 driver employs a set of other features: very high-power density - wide input voltage range and high output current, full output protection and diagnostics, highly efficient low RDSON output MOSFETs, integrated pulse generator for standalone operation, a SPI and simple STEP/DIR GPIO interfaces for driving the motor, and more. All these features allow the developing of a highly integrated and reliable step motor driving solution with outstanding performances. It can be used as a direct substitution for many complex motion controllers for various industrial motion control purposes, such as CNC, textile or sewing Machines, ATMs/Cash recyclers, pumps, valves, printers, scanners, medical devices, and many more.
How Does The Silent Step 3 Click Board™ Work?
The Silent Step 3 Click Board™ uses the TMC2660, a highly integrated bipolar step motor power driver, from the Trinamic company. As already mentioned, this device features many different features, which allow using the driver almost autonomously. There are two control interfaces: the SPI serial interface and the STEP/DIR interface. The SPI interface is used to write control information to the chip and read back status information. This interface must be used to initialize the parameters and modes necessary to enable driving the motor. The motion of the motor can be controlled by using the STEP and DIR signals, or through the SPI interface alone. Technologies, such as stallGuard2™, spreadCycle™, coolStep™, spreadCycle™, and microPlayer™, help to achieve high autonomy and smooth motion of the driven motor, even by using the STEP and DIR input pins to set the direction and step propagation. The internal microstep table maps the sine function from 0° to 90°. Symmetries allow mapping the sine and cosine functions from 0° to 360° with this table.
.jpg)
The TMC2660 supports two motor driver control modes: STEP/DIR mode and SPI mode. STEP/DIR mode is also referred to as the legacy mode. The device is operated similar to other pin-driven step motor controllers/drivers – the step propagation is controlled by pulses on the STEP input, and the direction is determined by the DIR pin. In SPI mode, user has direct access to motor current sign and magnitude, by setting the parameters in DRVCTRL Register. All working parameters can be configured and controlled via the SPI interface in both modes, and also the power and thermal data can be provided back to the MCU for further analysis and optimization.
In STEP/DIR mode, the microPlyer STEP pulse interpolator brings the smooth motor operation of high-resolution microstepping to applications originally designed for coarser stepping and reduces pulse bandwidth. MicroPlyer produces 16 microsteps at 256x resolution, for each active edge on STP pin of the Silent Step 3 click. For a better explanation, the diagram of the motor angle dependence on the step pulses is given:
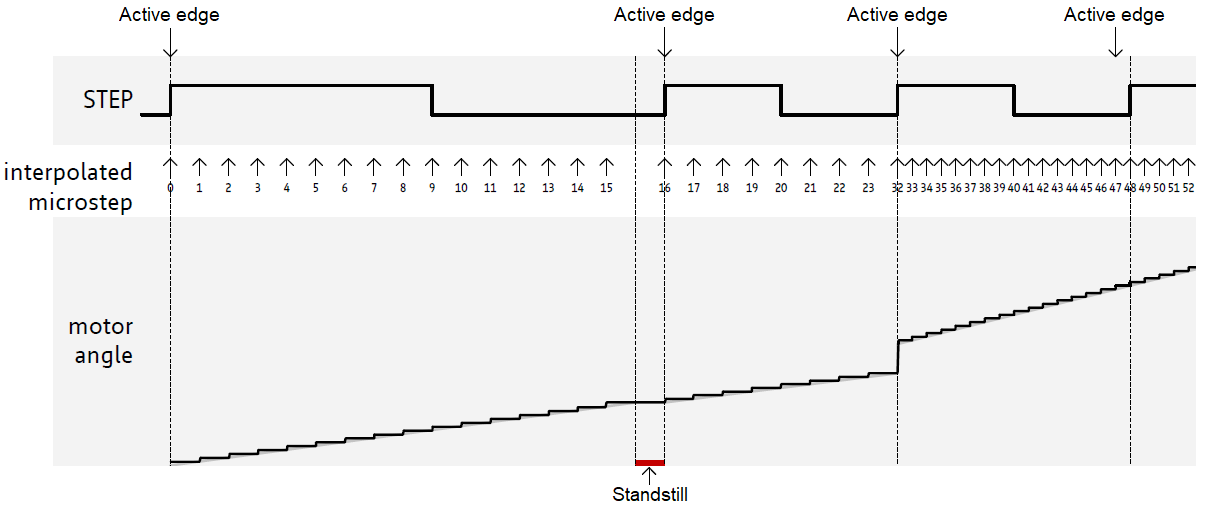
The application may need to change the microstepping resolution to get the best performance from the motor. For example, on an CNC machine, high-resolution microstepping may be used for precision operations on a workpiece, and then full stepping may be used for maximum torque at maximum velocity to advance to the next workpiece. That is also possible, but attention should be paid to the exact moment of resolution changing, which should occur at or near positions that correspond to steps in the lower resolution.
The currents through both motor coils are controlled using choppers, which work independently of each other. There are two chopper modes available: a new high-performance chopper algorithm called spreadCycle and a proven constant off-time chopper mode. The constant off-time mode cycles through three phases: on, fast decay, and slow decay. The spreadCycle mode cycles through four phases: on, slow decay, fast decay, and a second slow decay. For more details about the chopper modes, phases and the parameters that are used for controlling the choppers, refer to the TMC2660 datasheet.
In order to achieve all the previously mentioned features working, the current through the motor coils have to be measured. Because of the high power output of the TMC2660, it requires using the external shunt resistors. Therefore, the Silent Step 3 click has onboard carefully selected, low-inductance type 0.1 Ohm shunt resistors. This minimizes measurement imperfections caused by the switching spikes from the MOSFET bridges for example and maximizes the efficiency of the TMC 2660.
The STEP, DIR, and ENN pins of the TMC2660 are directly routed to the mikroBUS™ pins PWM, INT, and AN, and marked as STP, DIR and EN respectively. The logic levels of the digital I/O pins is easily adjustable by setting the desired voltage to the VCC_IO pin. Therefore, the interface logic level on the Silent Step 3 click can be easily configured for 3.3 V or 5 V logic by moving VSEL jumper to the respective voltage, which allows both 3.3V and 5V MCUs to be interfaced with this Click board™.
The power supply for the connected bipolar stepper motor can be connected between the VM and GND inputs of the terminal. The connected voltage should stay within the range between 9V and 29V. The rest of the terminals allow bipolar stepper motor coils to be connected: A1 and A2 terminal inputs are used to connect the first coil, while the B1 and B2 inputs are used to connect the second motor coil.
Note that while driving the motor with higher currents, the TMC2660 might get warm, affecting its reliability. In that case, proper heat sinks should be used, or the driving current should be reduced.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Type | Stepper |
| Applications | The Silent Step 3 Click Board™ is a perfect solution for building various applications that require precise and reliable stepper motor control, such as the CNC, textile or sewing Machines, ATMs/Cash recyclers, pumps, valves, printers, scanners, medical devices, and many more. |
| On-board modules | TMC2660, a highly integrated bipolar step motor power driver, with the UART interface, from the Trinamic company |
| Key Features | StallGuard2™, coolStep™, spreadCycle™, and microPlayer™ advanced technologies, full output protection and diagnostics, wide input voltage range and reasonably high currents, highly efficient output MOSFETs, etc. |
| Interface | GPIO,SPI |
| Compatibility | mikroBUS |
| Click board size | L (57.15 x 25.4 mm) |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V,5V |
PINOUT DIAGRAM
This table shows how the pinout of the Silent Step 3 Click Board™ corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
| Notes | Pin |  |
Pin | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error Diagnostics OUT | EN | 1 | AN | PWM | 16 | STP | Step trigger IN |
| Motor stall detect output | SB | 2 | RST | INT | 15 | DIR | Motor direction IN |
| Chip Select | CS | 3 | CS | RX | 14 | NC | |
| SPI Clock | SCK | 4 | SCK | TX | 13 | NC | |
| SPI Data Out | SDO | 5 | MISO | SCL | 12 | NC | |
| SPI Data In | SDI | 6 | MOSI | SDA | 11 | NC | |
| Power Supply | 3.3V | 7 | 3.3V | 5V | 10 | 5V | Power supply |
| Ground | GND | 8 | GND | GND | 9 | GND | Ground |
ONBOARD SETTINGS AND INDICATORS
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PWR | PWR | - | Power LED Indicator |
| TB1 | VM | - | The external power supply connector |
| TB2 | A1,A2 | - | Stepper motor coil A connector |
| TB3 | B1,B2 | - | Stepper motor coil B connector |
| JP1 | VSEL | Left | Logic voltage level selection: left position - 3.3V; right position - 5V |
SILENT STEP 3 CLICK ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
| Description | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| External power supply voltage | 9 | - | 29 | V |
| I/O supply voltage | 3 | - | 5.25 | V |
| Current limit (RMS) per channel | - | - | 2.8 | A |
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-3676
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.022 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018716517
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.



