
Overview
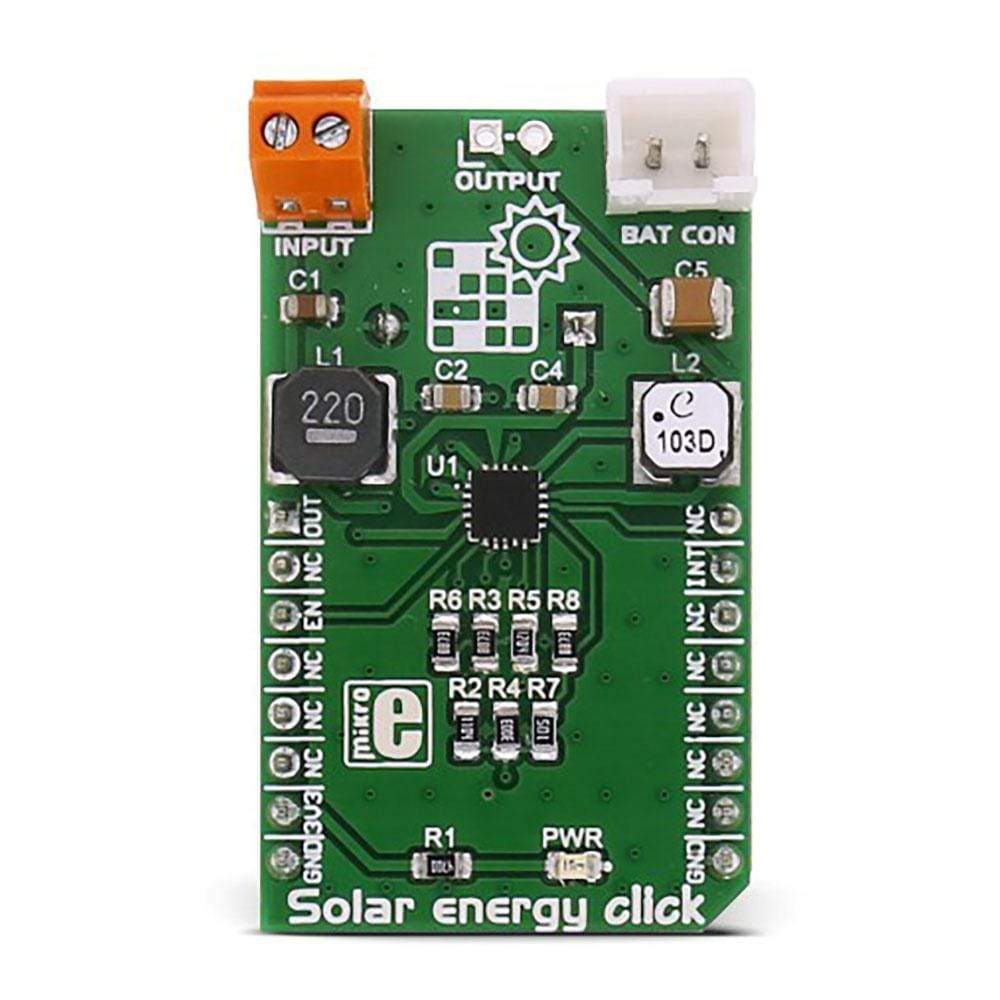
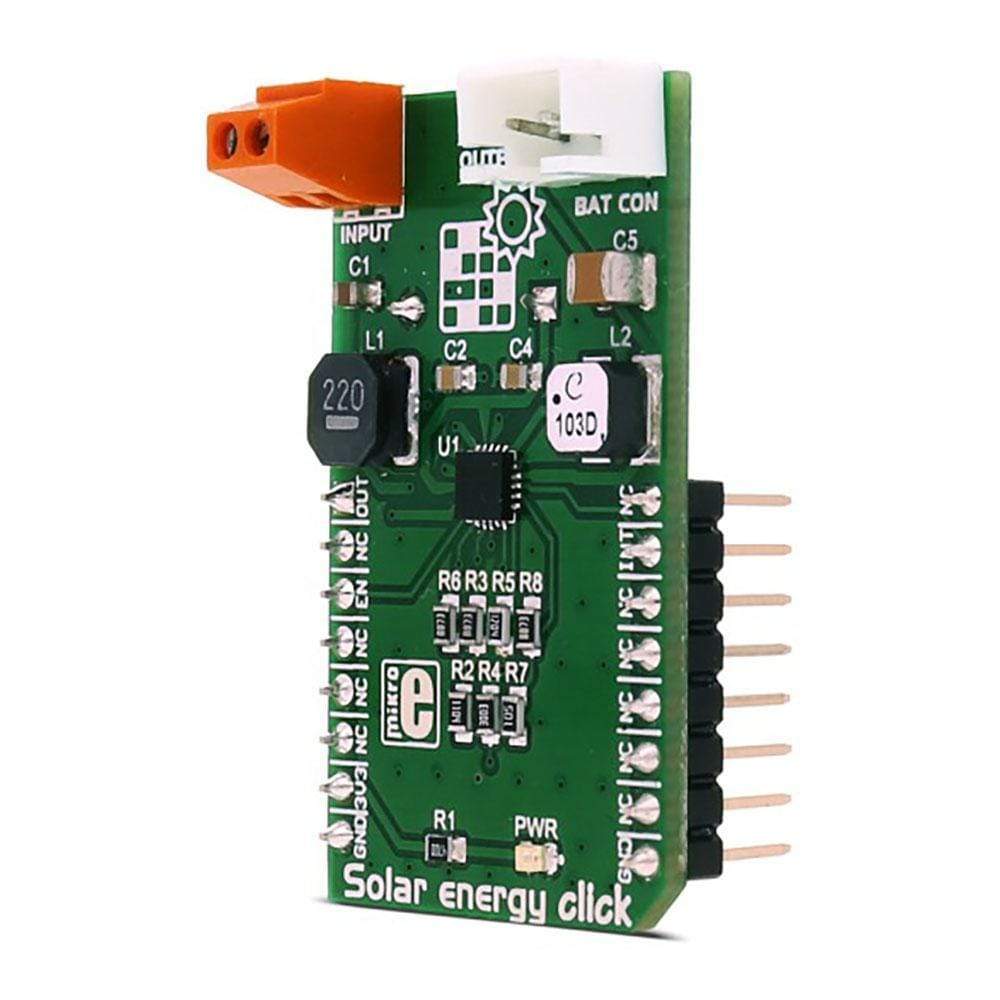
There are many battery chargers and solar energy harvesters out there already, but the Solar Energy Click Board™ has the unique feature - it encompasses both of these devices in a single package. The Click Board™ uses Texas Instruments BQ25570 - a nano-power high-efficiency boost charger and buck converter device, designed to work with very low power energy harvesting elements, such as the photo-voltaic and thermoelectric generators.
The Solar Energy Click Board™ recharges the connected Li-Po battery or the onboard 220mF super-capacitor, using the photovoltaic element. This is done by utilising the BQ25570's charging and power harvesting capabilities and clever nano-power management features. This Click Board™ can also power up low power consumption devices by using the stored energy, providing a way for continuous power operation of low power devices.
These features make the Solar Energy Click Board™ an ideal solution for powering wireless sensor networks, environmental monitoring devices, portable and wearable health monitoring devices and similar low power self-sustained devices.
Downloads
Es gibt bereits viele Batterieladegeräte und Solarenergiesammler, aber das Solar Energy Click Board™ hat eine einzigartige Funktion: Es vereint beide Geräte in einem einzigen Paket. Das Click Board™ verwendet Texas Instruments BQ25570 – ein hocheffizientes Nano-Power-Boost-Lade- und Abwärtswandlergerät, das für den Einsatz mit Energiesammlerelementen mit sehr geringem Stromverbrauch wie Photovoltaik- und thermoelektrischen Generatoren entwickelt wurde.
Das Solar Energy Click Board™ lädt den angeschlossenen Li-Po-Akku oder den integrierten 220-mF-Superkondensator mithilfe des Photovoltaikelements auf. Dies geschieht durch die Nutzung der Lade- und Energiegewinnungsfunktionen des BQ25570 und der cleveren Nano-Energieverwaltungsfunktionen. Dieses Click Board™ kann auch Geräte mit geringem Stromverbrauch mit der gespeicherten Energie versorgen und bietet so eine Möglichkeit für den Dauerbetrieb von Geräten mit geringem Stromverbrauch.
Diese Funktionen machen das Solar Energy Click Board™ zu einer idealen Lösung für die Stromversorgung drahtloser Sensornetzwerke, Umweltüberwachungsgeräte, tragbarer und am Körper tragbarer Geräte zur Gesundheitsüberwachung und ähnlicher autarker Geräte mit geringem Stromverbrauch.
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-2814
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.02 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018711864
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.





