
Overview
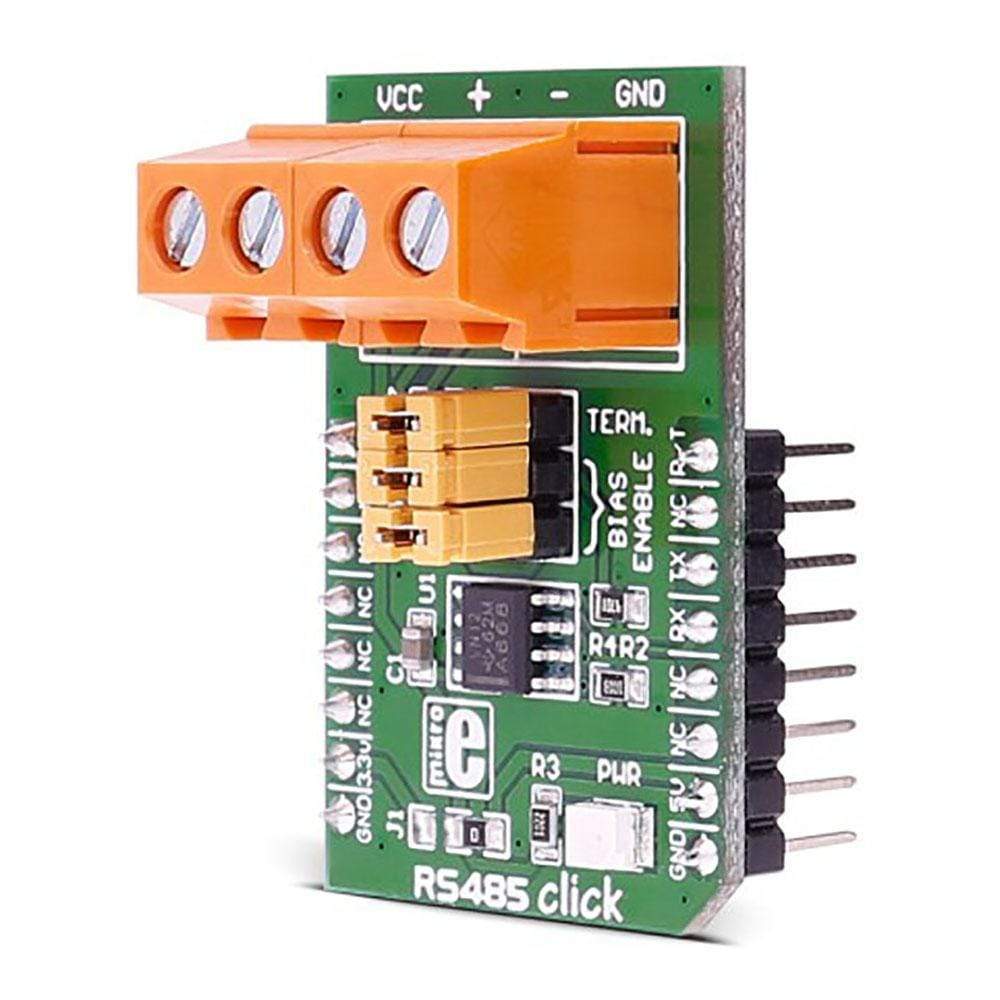
The RS485 5 Click Board™ is equipped with the MAX485, low-power, slew-rate-limited transceiver for RS-485 and RS-422 communication, from Maxim Integrated. This device supports half-duplex RS-485 communication and can be used as an interface between the TTL level UART and the RS485 communication bus. Thanks to the low power consumption and reduced slew-rate drivers that minimize EMI and reduce reflections caused by improperly terminated cables, error-free data transmission up to 250kbps is supported.
The RS485 5 Click Board™ is perfectly suitable for EMI-Sensitive Applications, such as industrial-control local area networks, building automation, HVAC systems, and many more.
Downloads
Le Carte RS485 5 Click™ est équipé du MAX485, un émetteur-récepteur à faible consommation et à vitesse de balayage limitée pour la communication RS-485 et RS-422, de Maxim Integrated. Cet appareil prend en charge la communication RS-485 en semi-duplex et peut être utilisé comme interface entre l'UART de niveau TTL et le bus de communication RS485. Grâce à la faible consommation d'énergie et aux pilotes à vitesse de balayage réduite qui minimisent les interférences électromagnétiques et réduisent les réflexions causées par des câbles mal terminés, une transmission de données sans erreur jusqu'à 250 kbps est prise en charge.
Le RS485 5 Click Board™ est parfaitement adapté aux applications sensibles aux EMI, telles que les réseaux locaux de contrôle industriel, l'automatisation des bâtiments, les systèmes CVC et bien d'autres.
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-925
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.034 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606015073262
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.