




Overview
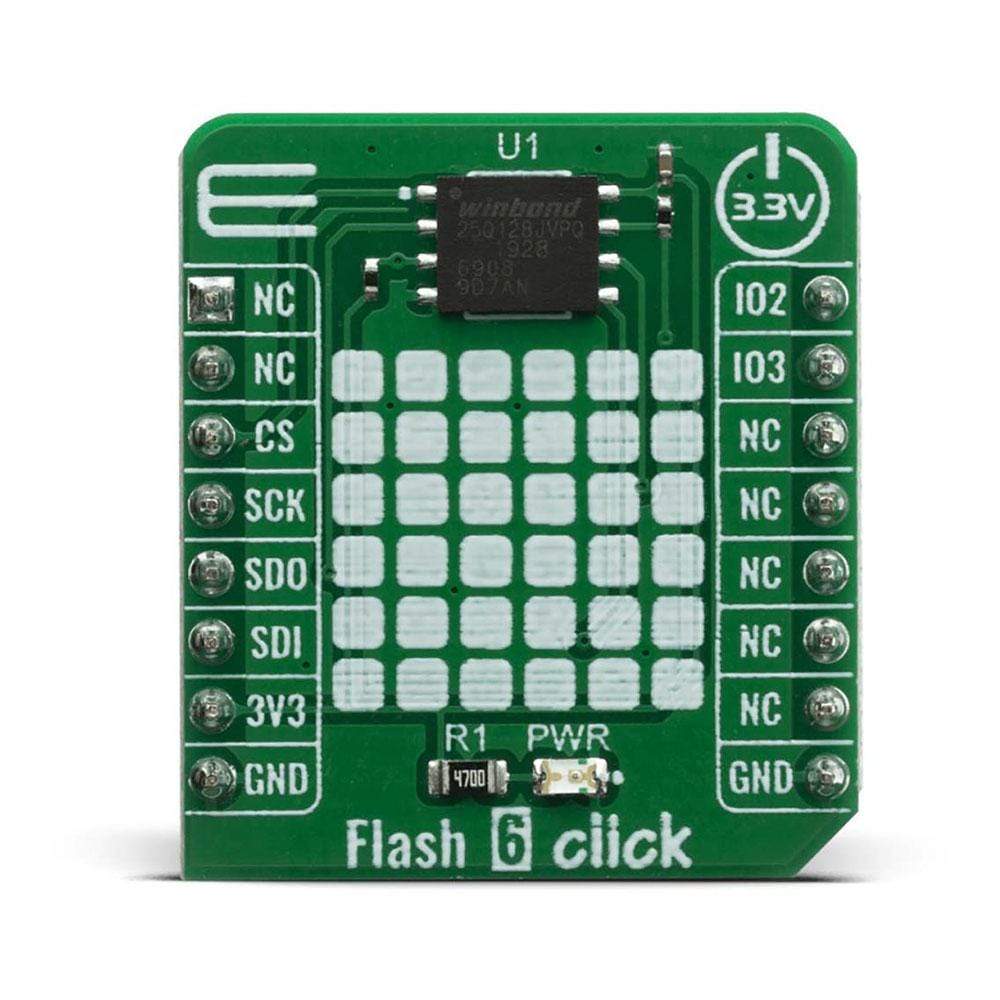
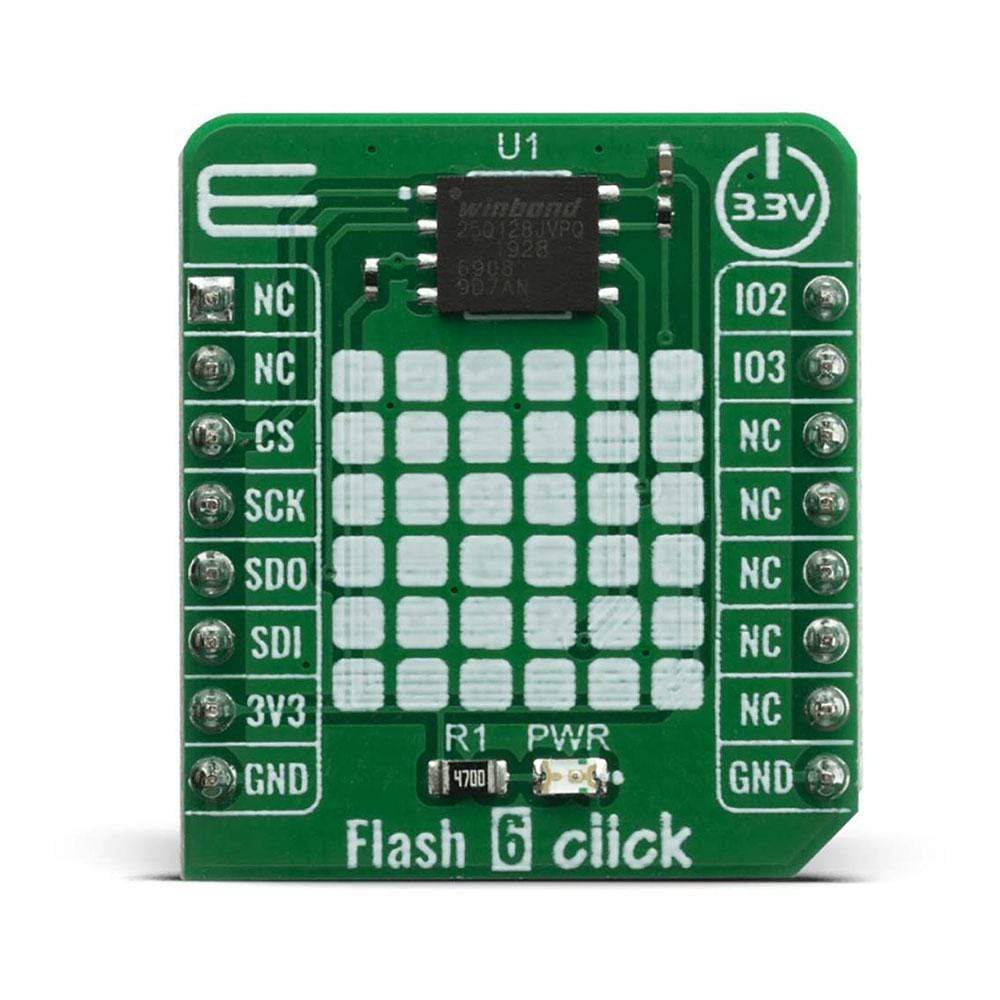
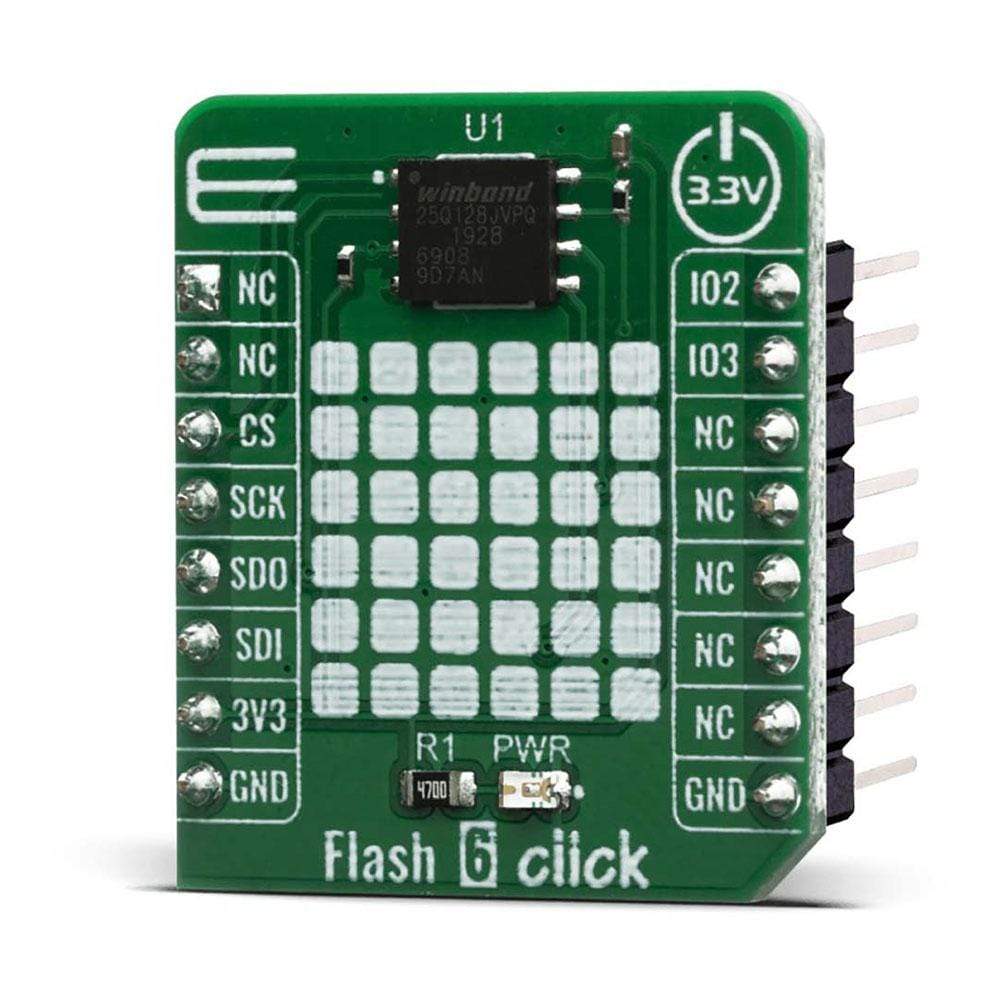
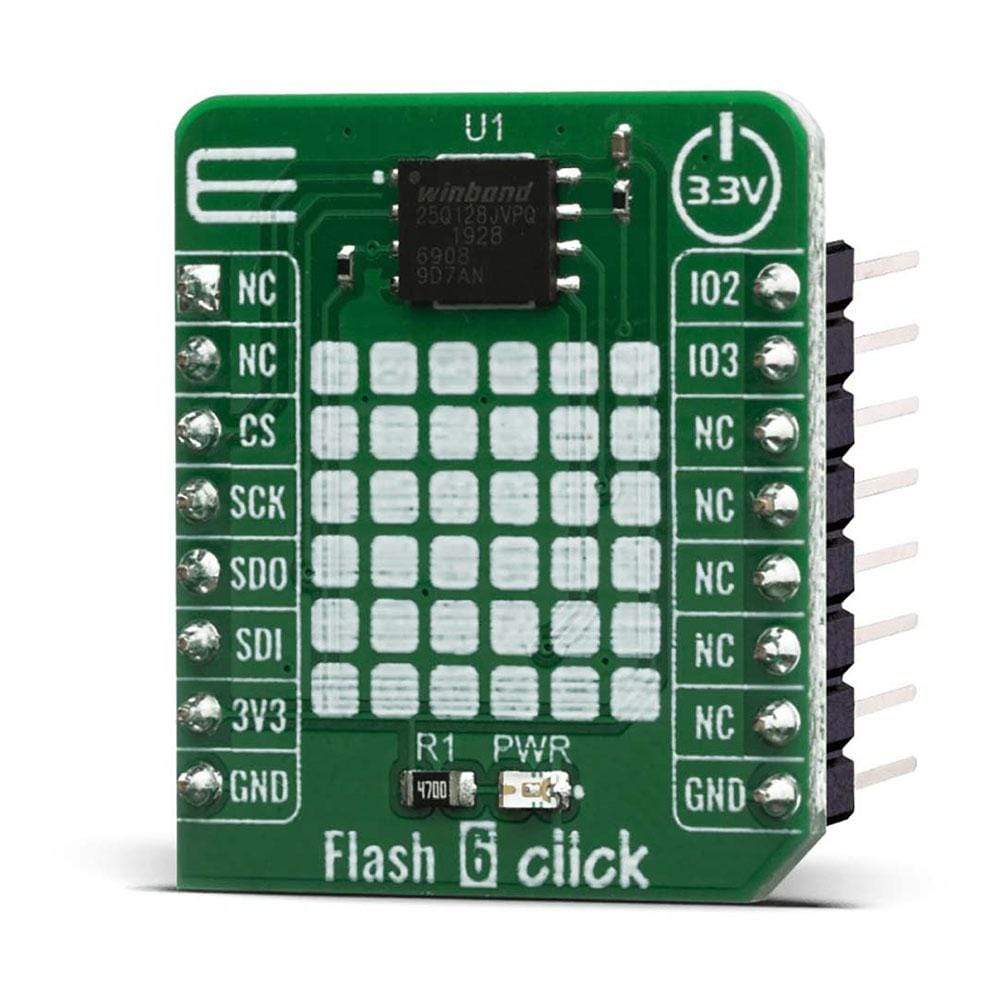
The Flash 6 Click Board™ is based on the W25Q128JV (128M-bit) flash memory from Winbond provides a storage solution for systems with limited space, pins and power. The 25Q series offers flexibility and performance well beyond ordinary Serial Flash devices. They are ideal for code shadowing to RAM, executing code directly from Dual/Quad SPI (XIP) and storing voice, text and data. The small 4KB sectors allow for greater flexibility in applications that require data and parameter storage.
The Flash 6 Click Board™ is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click Board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Downloads
La carte Flash 6 Click Board™ est basée sur la mémoire flash W25Q128JV (128 Mo) de Winbond et offre une solution de stockage pour les systèmes avec un espace, des broches et une alimentation limités. La série 25Q offre une flexibilité et des performances bien supérieures à celles des périphériques Flash série ordinaires. Elles sont idéales pour le shadowing de code sur la RAM, l'exécution de code directement à partir de Dual/Quad SPI (XIP) et le stockage de la voix, du texte et des données. Les petits secteurs de 4 Ko permettent une plus grande flexibilité dans les applications qui nécessitent le stockage de données et de paramètres.
La carte Flash 6 Click Board™ est supportée par une bibliothèque compatible mikroSDK, qui comprend des fonctions qui simplifient le développement logiciel. Cette carte Click Board™ est un produit entièrement testé, prêt à être utilisé sur un système équipé du socket mikroBUS™.
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-4067
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.016 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018717224
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.