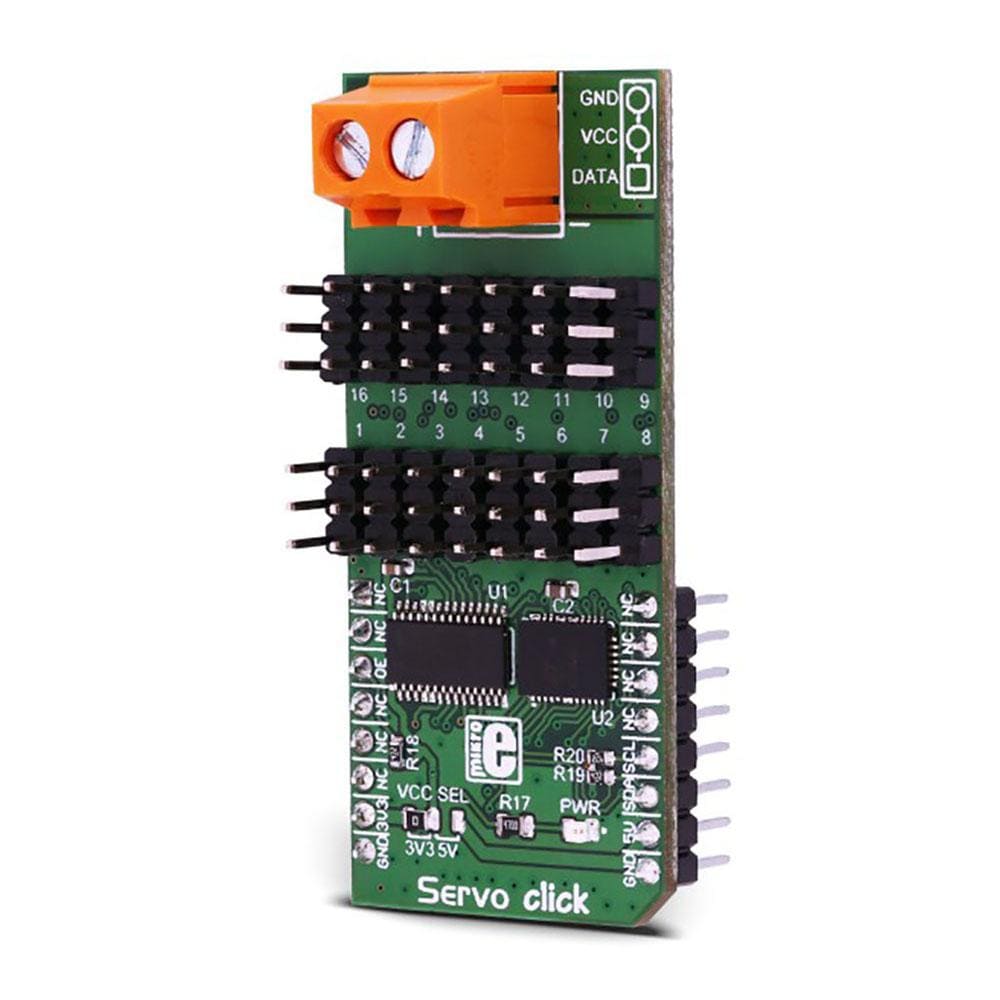
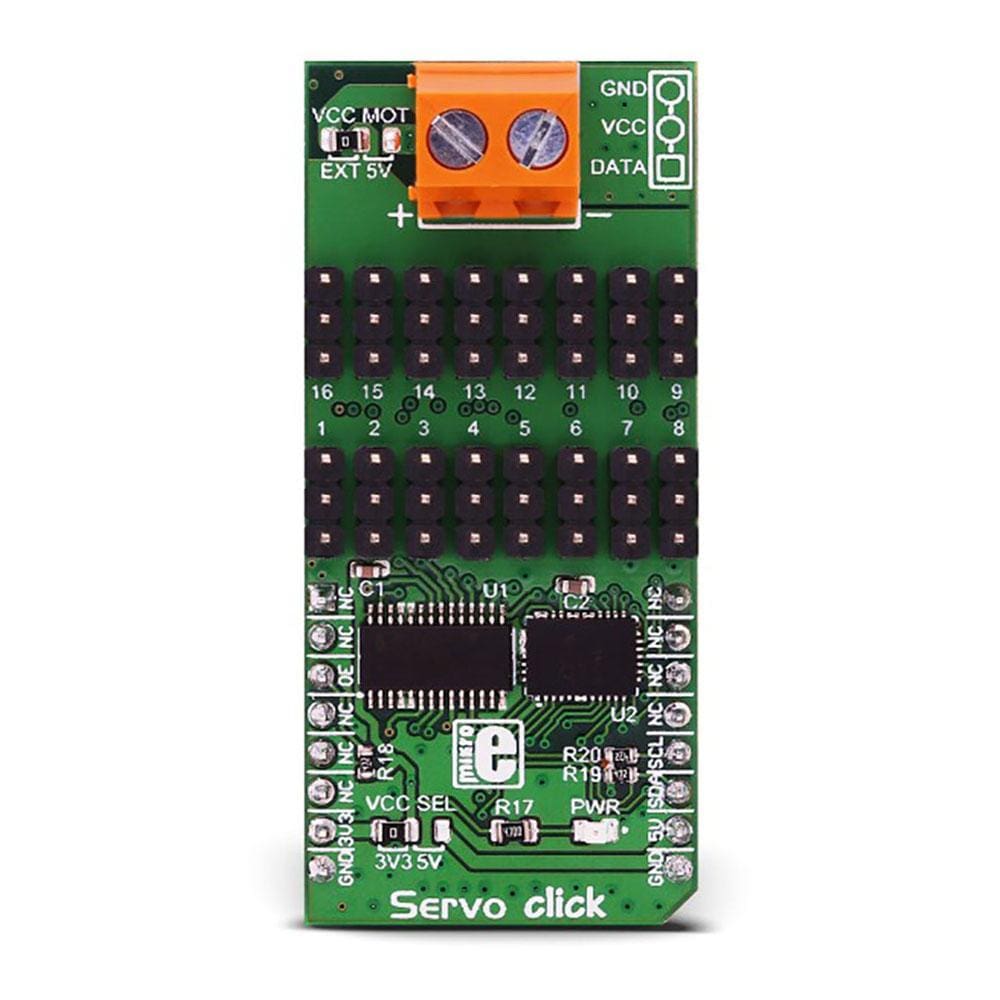
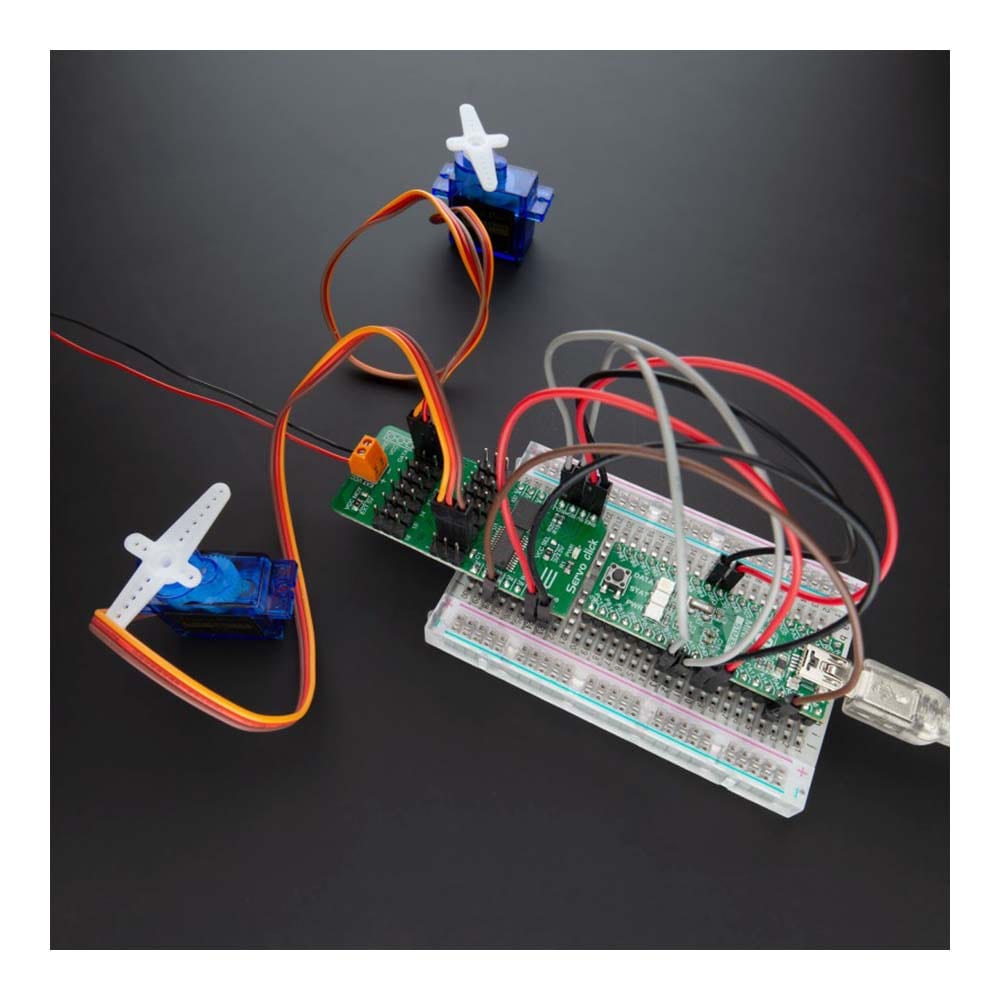


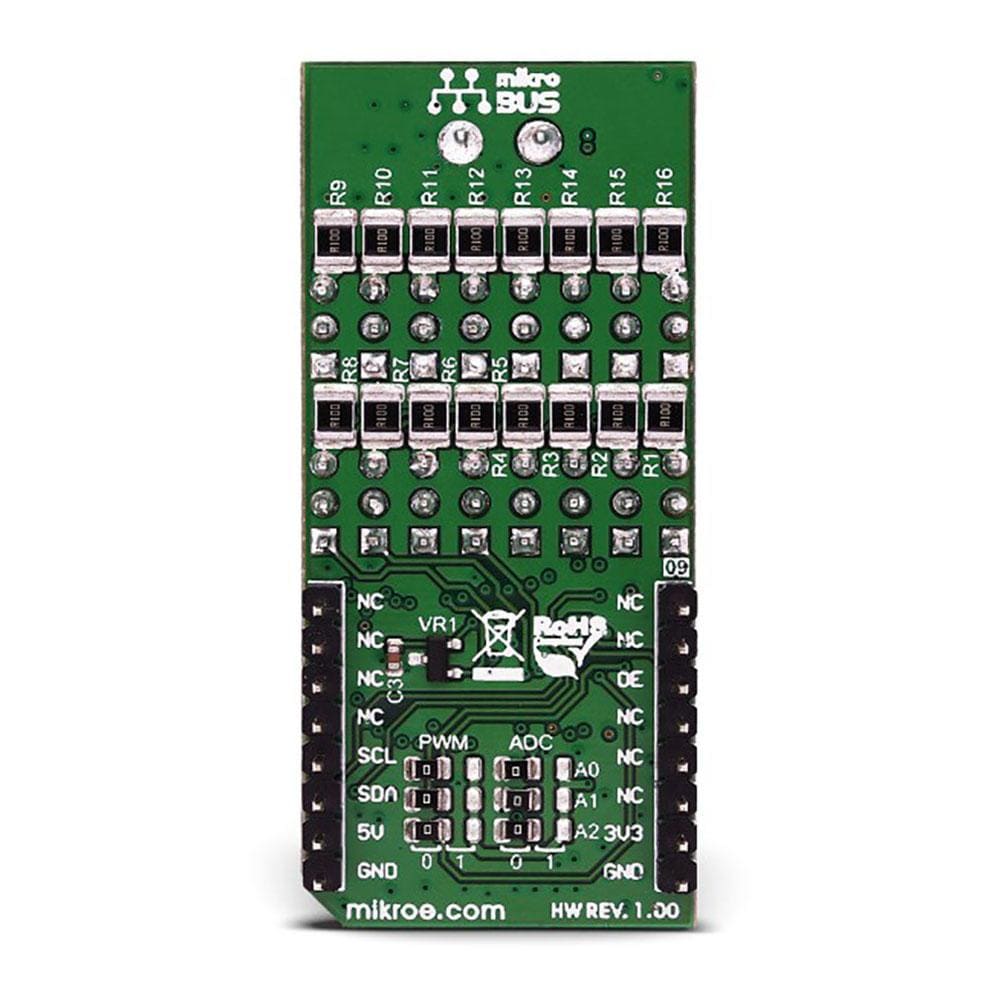
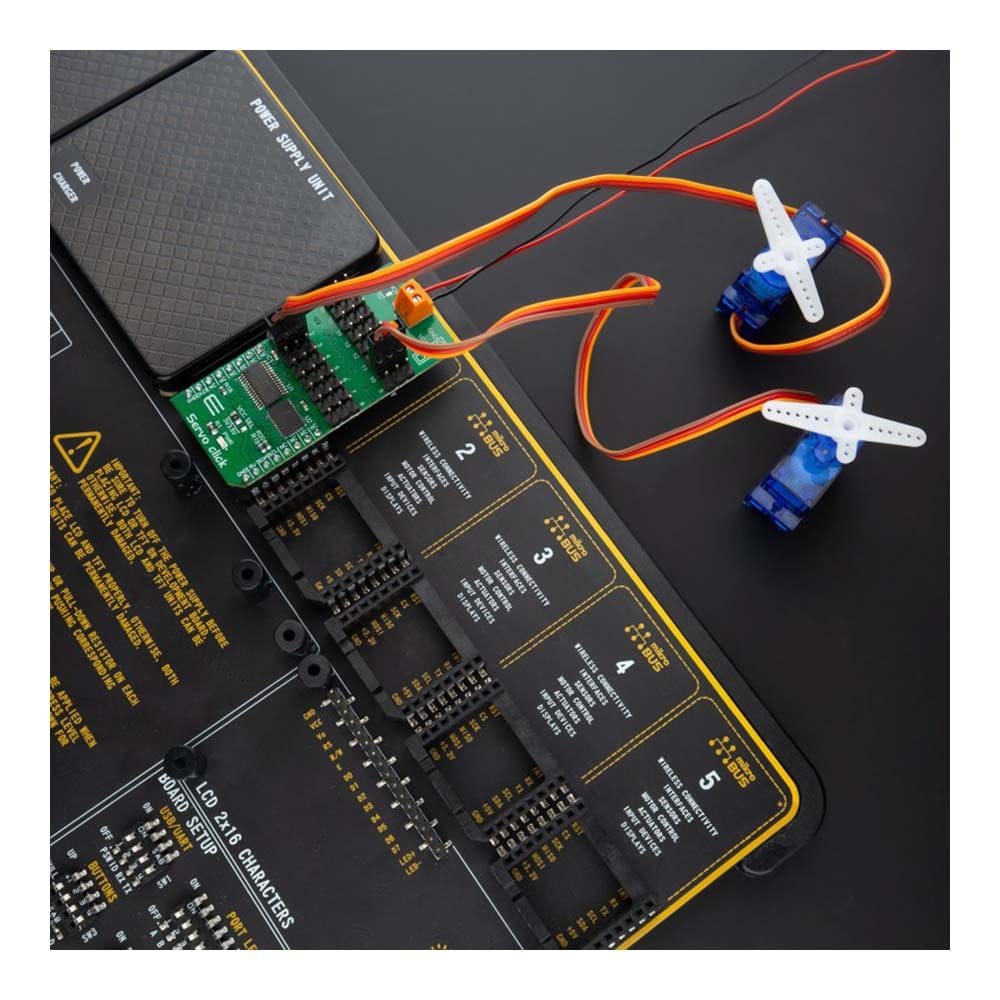
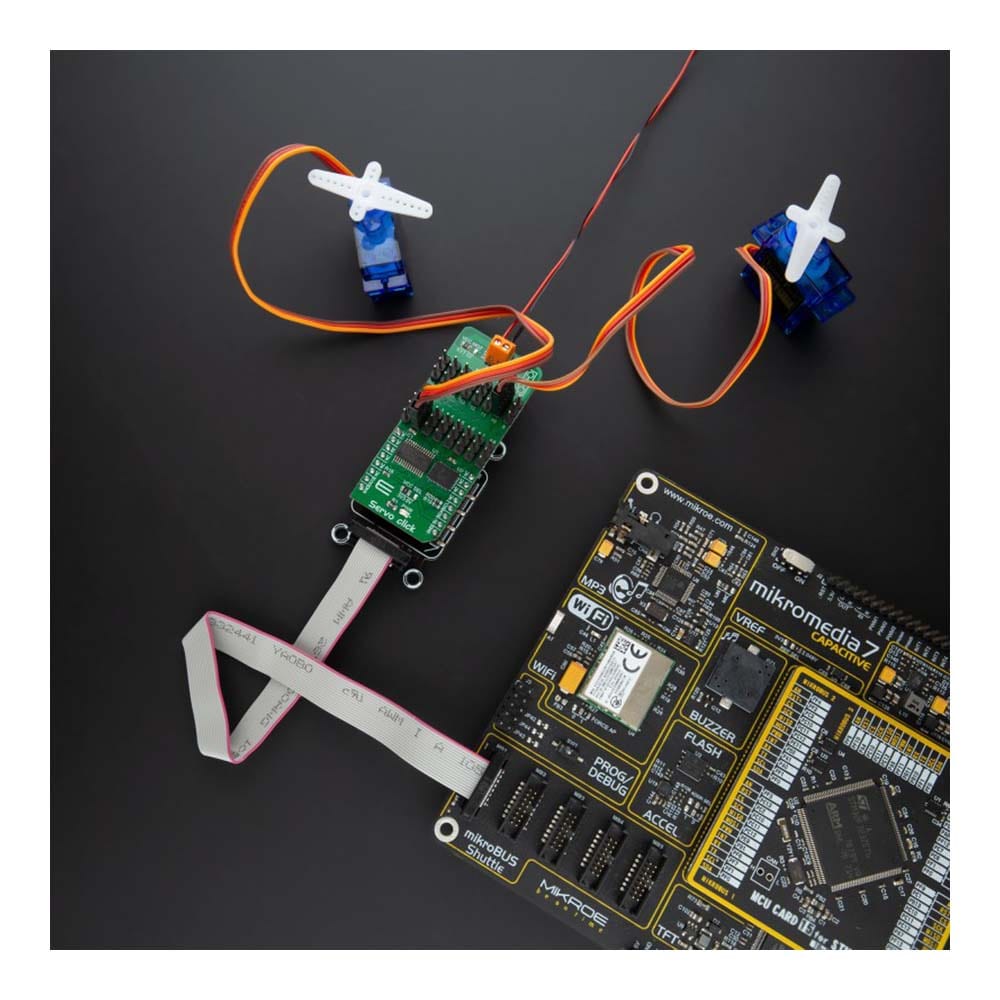
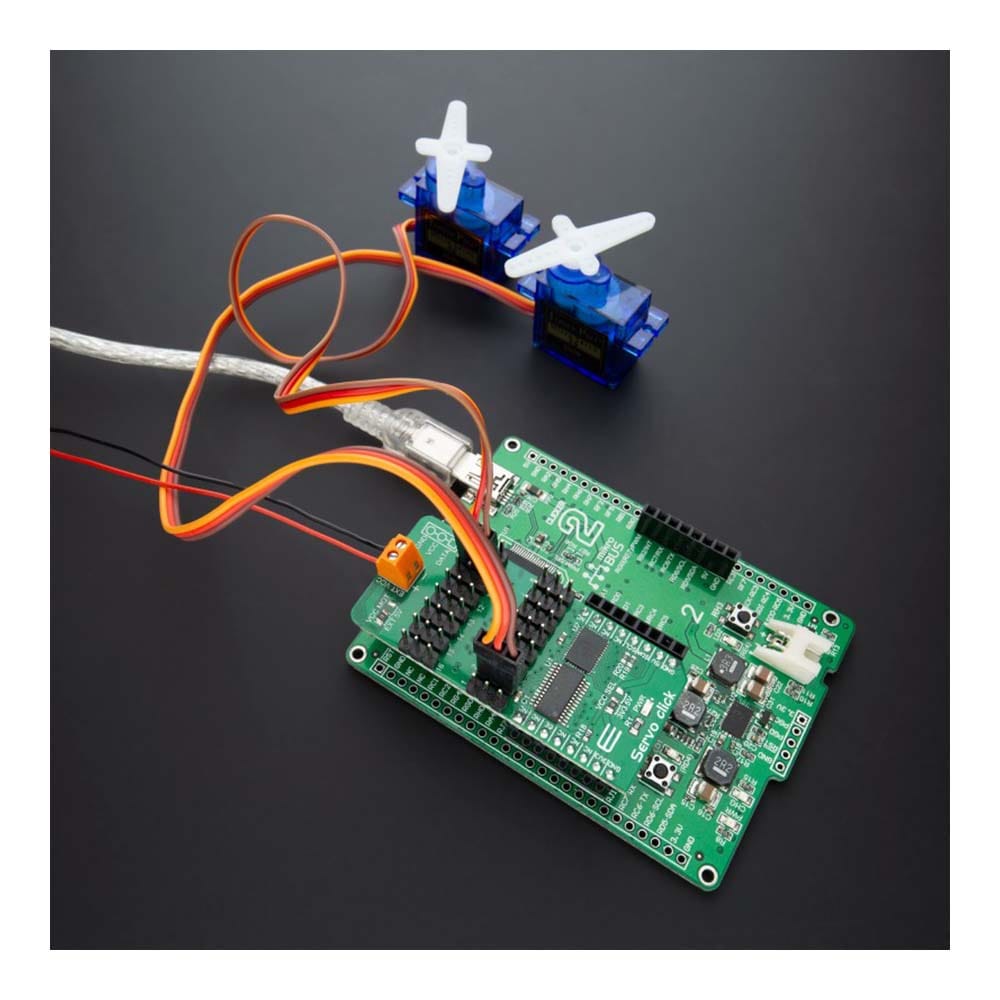

Overview
Introducing the Servo Click Board™: Revolutionize Your Servo Control
Are you tired of struggling with limited servo control options? Look no further! The Servo Click Board™ is here to transform your servo control experience.
Unleash the Power of 16-Channel PWM Control
Say goodbye to single-channel limitations. With the Servo Click Board™, you can simultaneously control a whopping 16 servo motors! Each servo enjoys its own programmable PWM signal, giving you unparalleled flexibility and precision in your projects.
Fine-Tune Your Servo Performance
Precision matters. That's why we equipped the Servo Click Board™ with a programmable PWM signal frequency range from 24 Hz to 1526 Hz. This range is meticulously chosen to cater to various servo types, ensuring that your creations move with the utmost precision and accuracy.
Real-Time Insights with Voltage Sensing
What sets the Servo Click Board™ apart is its 16-bit A/D converter, which samples the voltage drop across each channel's shunt resistor. This means you get real-time feedback on servo current consumption, allowing you to optimize performance and prevent overheating without any need for modifying your servos.
Why Choose the Servo Click Board™?
- Effortless Control: Control up to 16 servos with ease, streamlining your projects and saving you time.
- Precision in Every Move: Fine-tune your servos to perfection with a wide PWM signal frequency range.
- Protect Your Servos: Monitor current consumption in real-time to prevent damage and enhance longevity.
Make the smart choice and experience a new level of servo control with the Servo Click Board™. Elevate your projects, unlock limitless possibilities, and join the ranks of satisfied customers who have already made the switch.
Ready to revolutionize your servo control? Click the button below and take the first step towards a brighter, more precise future!
Get Your Servo Click Board™ Now
Don't miss out on this game-changing innovation. Upgrade your servo control today!
Downloads
Présentation du Servo Click Board™ : révolutionnez votre servocommande
Vous en avez assez de vous débattre avec des options de contrôle de servo limitées ? Ne cherchez plus ! Le Servo Click Board™ est là pour transformer votre expérience de contrôle de servo.
Libérez la puissance du contrôle PWM à 16 canaux
Dites adieu aux limitations d'un seul canal. Avec le Servo Click Board™, vous pouvez contrôler simultanément 16 servomoteurs ! Chaque servomoteur bénéficie de son propre signal PWM programmable, vous offrant une flexibilité et une précision inégalées dans vos projets.
Ajustez les performances de votre servo
La précision est importante. C'est pourquoi nous avons équipé le Servo Click Board™ d'une plage de fréquences de signal PWM programmable de 24 Hz à 1526 Hz. Cette plage est soigneusement choisie pour s'adapter à différents types de servomoteurs, garantissant que vos créations se déplacent avec la plus grande précision et exactitude.
Informations en temps réel grâce à la détection de tension
Ce qui distingue le Servo Click Board™, c'est son convertisseur A/N 16 bits, qui échantillonne la chute de tension sur la résistance shunt de chaque canal. Cela signifie que vous obtenez un retour d'information en temps réel sur la consommation de courant du servo, ce qui vous permet d'optimiser les performances et d'éviter la surchauffe sans avoir à modifier vos servos.
Pourquoi choisir le Servo Click Board™ ?
- Contrôle sans effort : contrôlez jusqu'à 16 servos en toute simplicité, rationalisez vos projets et gagnez du temps.
- Précision à chaque mouvement : réglez vos servos à la perfection avec une large plage de fréquences de signal PWM.
- Protégez vos servos : surveillez la consommation de courant en temps réel pour éviter les dommages et améliorer la longévité.
Faites le bon choix et découvrez un nouveau niveau de contrôle des servomoteurs avec le Servo Click Board™. Améliorez vos projets, débloquez des possibilités illimitées et rejoignez les rangs des clients satisfaits qui ont déjà fait le changement.
Prêt à révolutionner votre servocommande ? Cliquez sur le bouton ci-dessous et faites le premier pas vers un avenir plus brillant et plus précis !
Obtenez votre Servo Click Board™ maintenant
Ne manquez pas cette innovation révolutionnaire. Mettez à niveau votre servocommande dès aujourd'hui !
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-3133
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.027 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018713448
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.







