

Overview
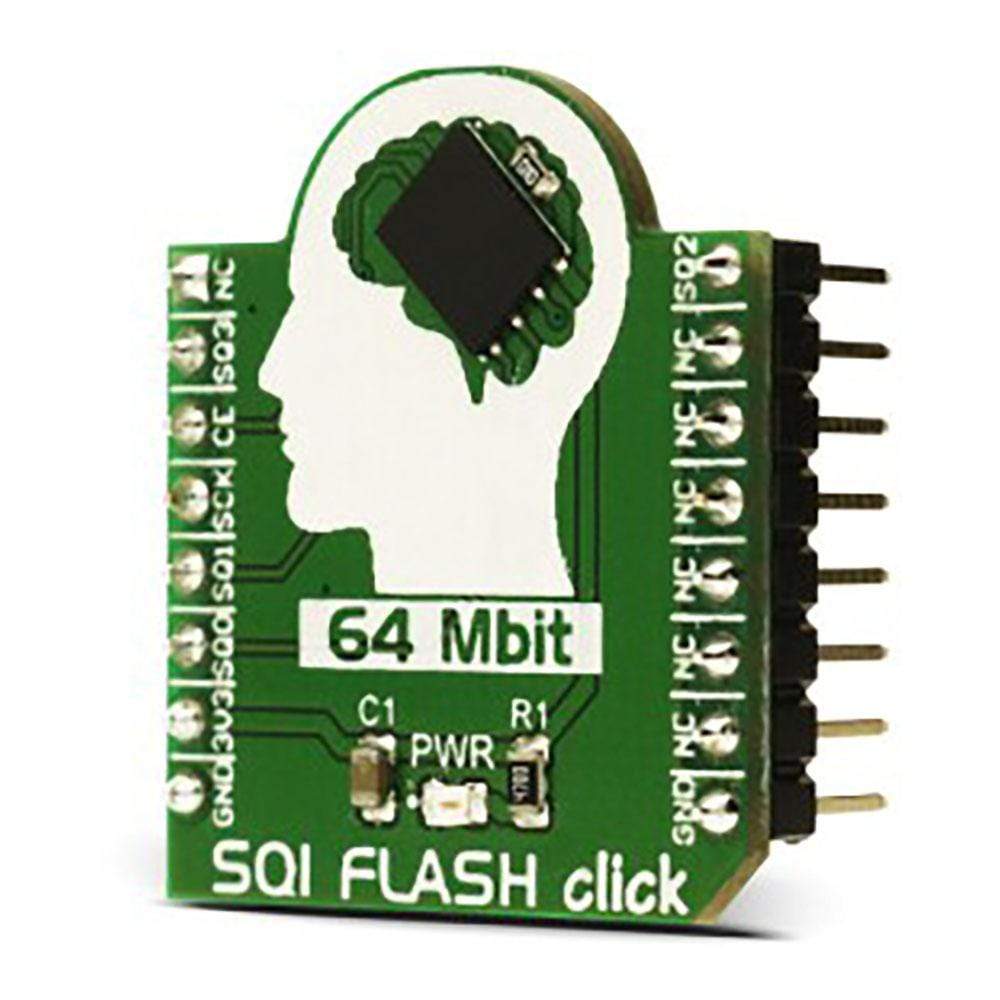
The SQI FLASH Click Board™ is based on the SST26VF064B, a 64 Mbit Serial Quad I/O flash device from Microchip. The chip utilizes a 4-bit multiplexed I/O serial interface to boost the performance. The Click Board™ is a very fast solid-state, non-volatile data storage medium, that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. Operating at 104 MHz, the SST26VF064B enables minimum latency execute-in-place (XIP) capability, without the need for code shadowing.
Downloads
La carte SQI FLASH Click Board™ est basée sur le SST26VF064B, un périphérique flash 64 Mbit Serial Quad I/O de Microchip. La puce utilise une interface série E/S multiplexée 4 bits pour améliorer les performances. Le Click Board™ est un support de stockage de données non volatile à semi-conducteurs très rapide, qui peut être effacé et reprogrammé électriquement. Fonctionnant à 104 MHz, le SST26VF064B permet une capacité d'exécution sur place (XIP) à latence minimale, sans avoir besoin de mise en miroir du code.
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-2828
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.018 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018711956
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.




