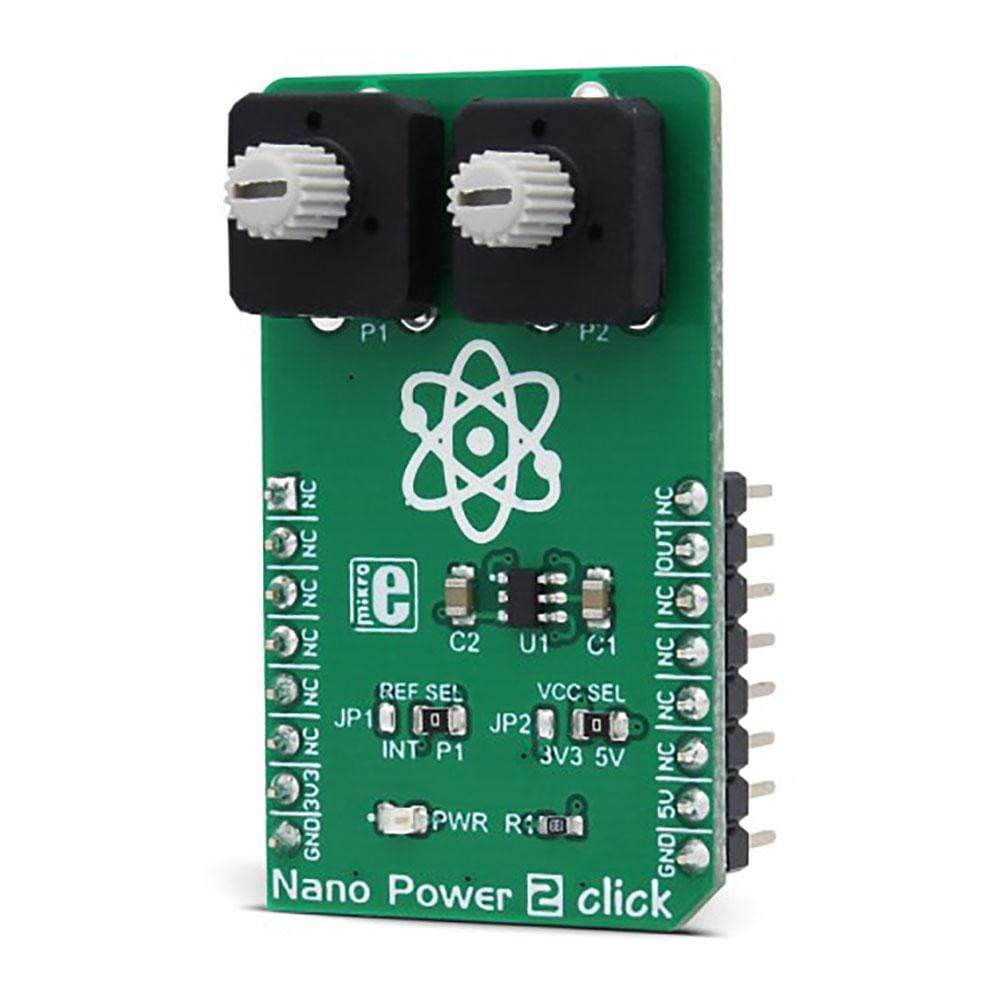
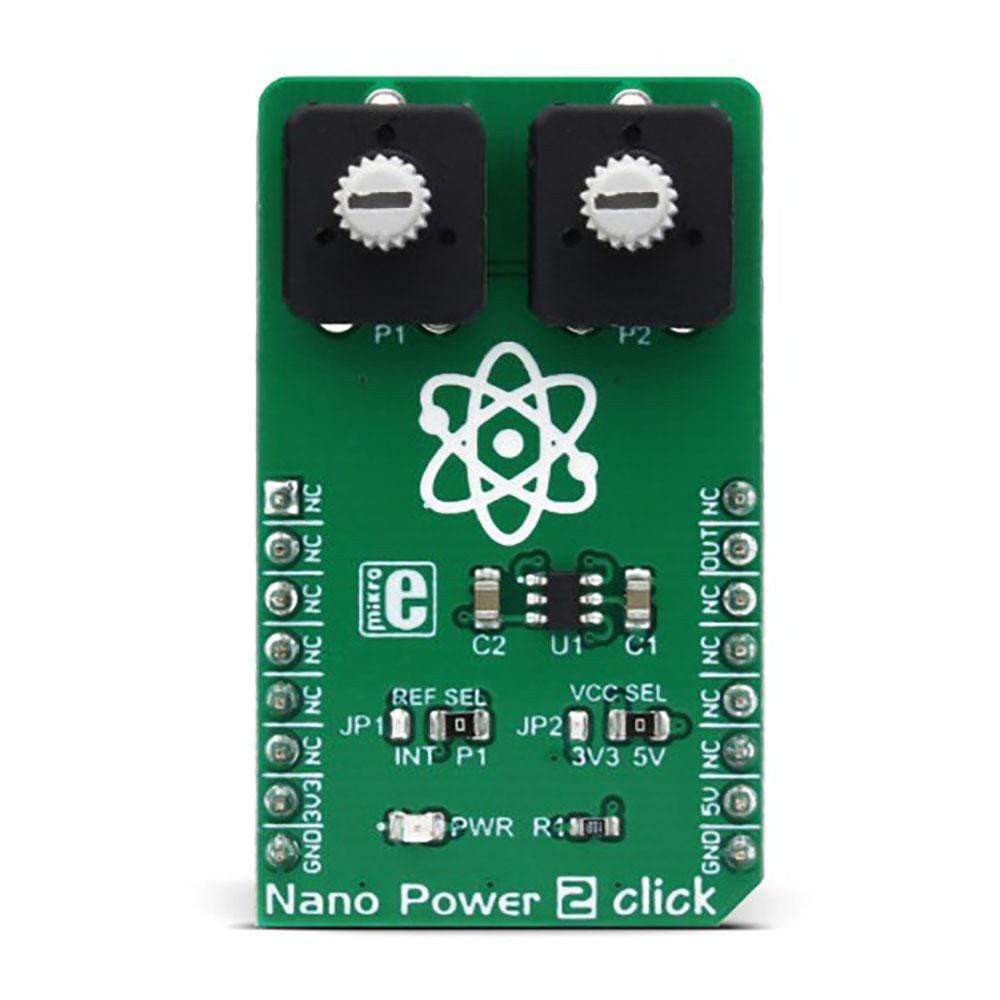


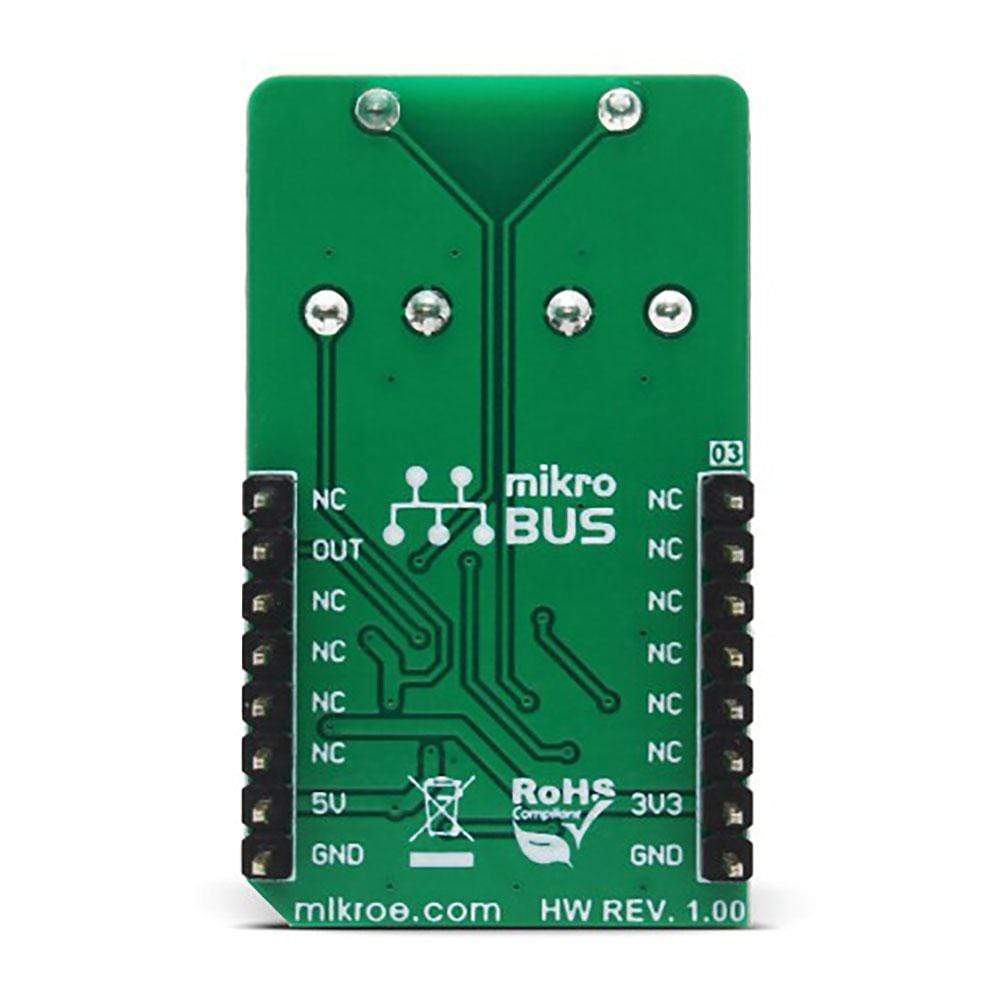
Overview
The Nano Power 2 Click Board™ is a very low power voltage comparator, aimed at portable and battery-powered applications. It allows detecting a difference of two voltage potentials, applied on two input pins. The device can detect differences very precisely, avoiding oscillations that can occur when both input voltages are equal by employing an internal hysteresis.
The Nano Power 2 Click Board™ offers a choice to select one of the input voltages from the internal fixed reference of 1.2V, or by setting both input voltages by the onboard potentiometers.
Downloads
The Nano Power 2 Click Board™ is a very low-power voltage comparator, aimed at portable and battery-powered applications. It allows detecting a difference of two voltage potentials, applied on two input pins. The device can detect differences very precisely, avoiding oscillations that can occur when both input voltages are equal by employing an internal hysteresis. Nano Power 2 Click Board™ offers a choice to select one of the input voltages from the internal fixed reference of 1.2V, or by setting both input voltages by the on-board potentiometers.
The current consumption of the Nano Power 2 Click Board™ ensures that there is no significant load to the measured inputs, and compared to other similar devices, it is several magnitudes lower. It produces clean output signals, which are used to indicate the result of the comparison. Both the logic level and the power supply levels can be selected between 3.3V and 5V, allowing a wide range of MCUs to be used with this Click Board™. With its two high-quality potentiometers, this Click Board™+J1984™ represents a unique testing platform for the integrated nanoPower comparator IC used on the Nano Power 2 Click Board™.
How Does The Nano Power 2 Click Board™ Work?
The Click Board™ is equipped with an integrated comparator IC, labelled as MAX40000AUT12+, a nanoPower comparator with built-in reference, produced by Maxim Integrated. This company offers several variants of the same IC, of which the used IC variant offers reference voltage of 1.2V on one of its pins. This reference voltage can be used at the comparator input, providing an accurate reference voltage throughout the fully operational temperature range, if required by the custom application.

The IC itself requires a very low number of external components. It has two input pins, used as the comparator inputs. Each of these inputs can use -0.2V up to VCC + 0.2V. The VCC is the power supply voltage, and it can be selected via the SMD jumper labelled as LOGIC, between the 3.3V and 5V rails from the mikroBUS™. One of the comparator inputs, labelled as IM on the MAX40000 IC, is routable to either the on-board potentiometer (P1) or the REF pin of the IC, which provides the referent voltage of 1.2V. The routing can be done by another SMD jumper, labelled as REF SEL. The second comparator input (labelled as IP on the MAX40000 IC) is routed to the second on-board potentiometer (P2). Both potentiometers can be used to set any voltage between the GND and VCC, which is selected by the LOGIC jumper, as described above.
As mentioned before, the comparator has two inputs. One of them it is the inverting input and it is labelled as IM. The other input is a non-inverting input, labelled as IP. When the IP voltage becomes higher than the IM voltage, the output state becomes logic HIGH; otherwise, the output is set to a LOW state. A special case is when both voltages are very close, or at the same level, at any given moment. This would result in an appearance of oscillation at the output due to noise or parasitic feedback. To cope with this problem, an internal hysteresis of ±2.5mV is applied.
The output of the MAX40000 IC is routed to the mikroBUS™ INT pin, labelled as OUT on the Click Board™. The output stage employs a unique break-before-make topology, capable of rail-to-rail operation with up to ±2mA loads. The output stage also uses a unique design, which minimizes supply current surges when the switching occurs, resulting in very clean output and low EM radiation. The MAX40000 has a push-pull output stage topology, which can both sink and source the current.
Working with the Nano Power 2 Click Board™ is very easy and straightforward. Only a single pin is used, which can be used to either trigger an interrupt (therefore it is routed to the INT pin), or its status can be read via the input pin of the host MCU. However, MikroElektronika provides a library that contains a function which can be used for simplified control of the Nano Power 2 Click Board™. The library also contains an example application, which demonstrates the use of the function. This example application can be used as a reference for custom designs.
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-3036
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.021 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018713059
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.




