
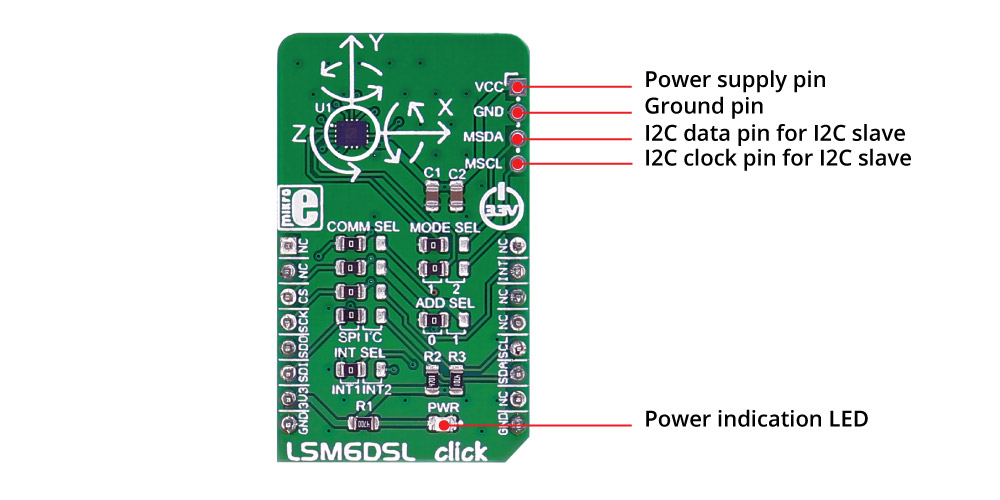
Overview
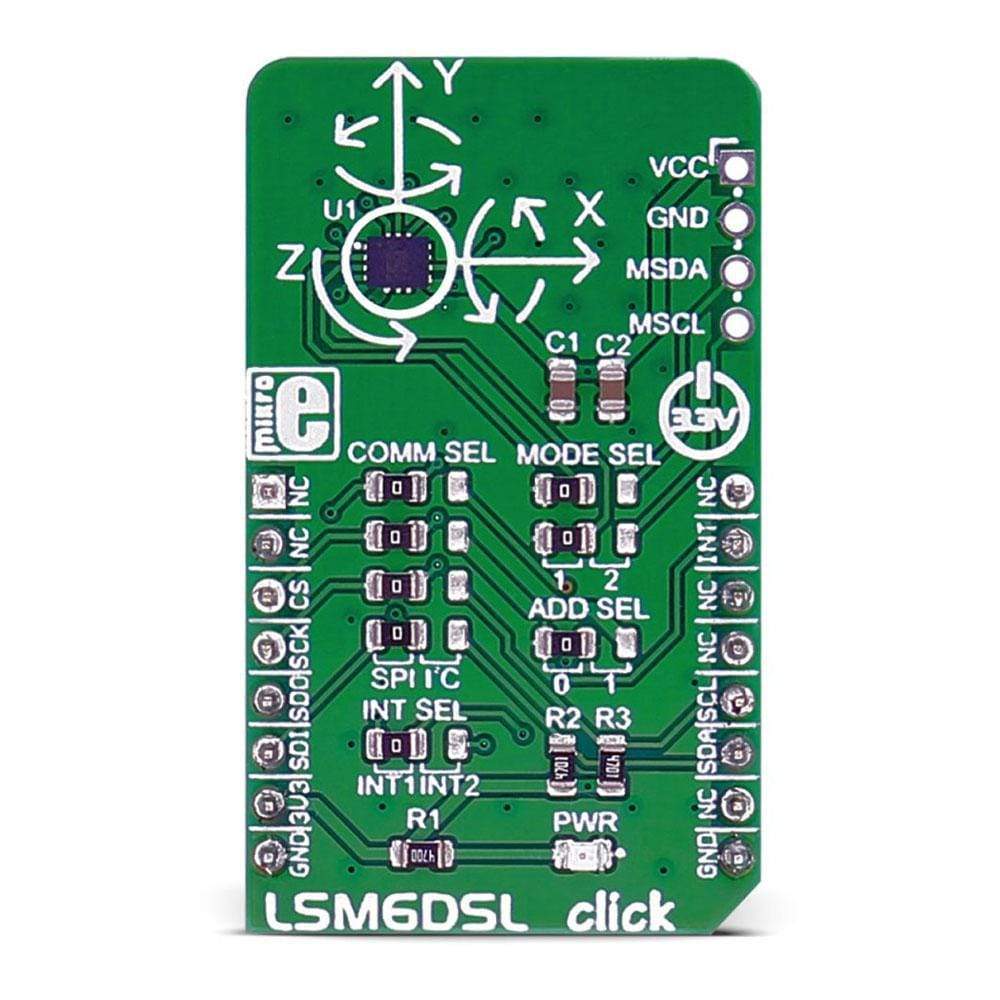
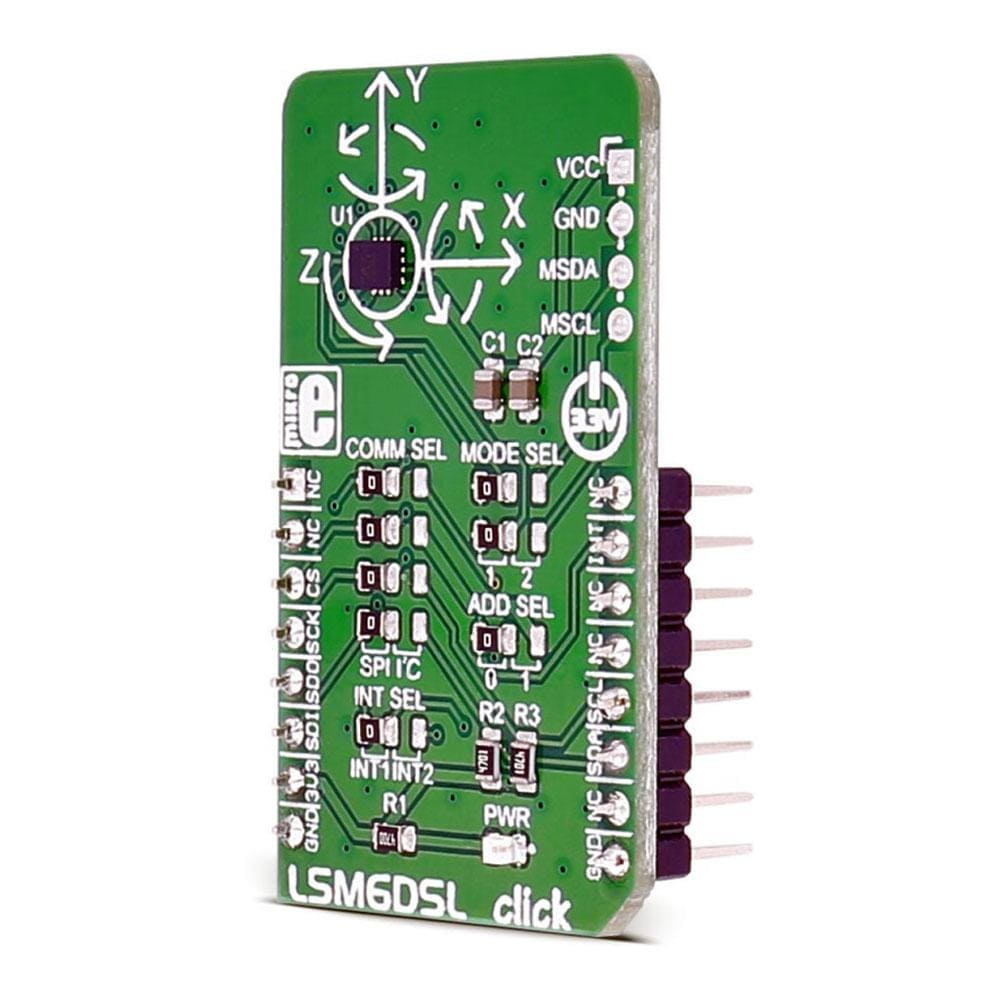
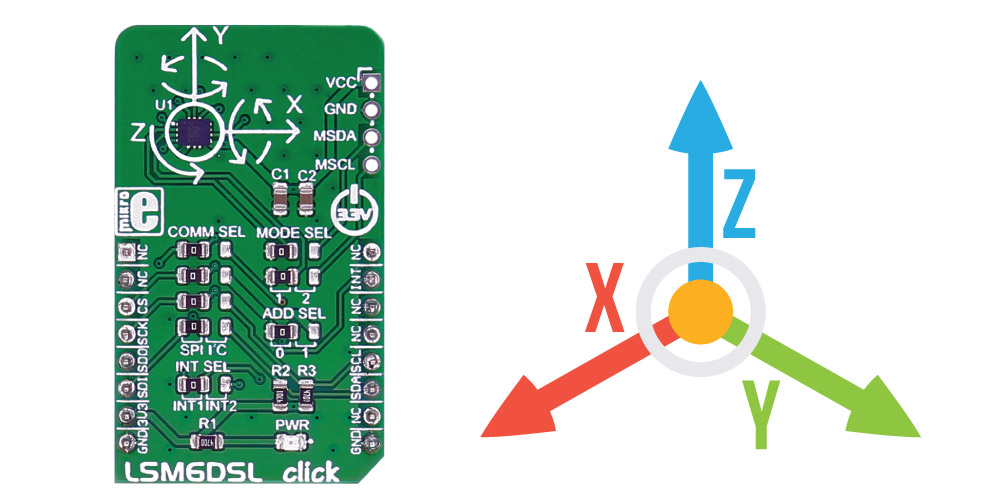
The LSM6DSL Click Board™ measures linear and angular velocity with six degrees of freedom. It carries the LSM6DSL high-performance 3-axis digital accelerometer and 3-axis digital gyroscope. The Click Board™ is designed to run on a 3.3V power supply.
The LSM6DSL Click Board™ communicates with the target microcontroller over SPI or I2C interface, with additional functionality provided by the INT pin on the MikroBUS line.
Downloads
The LSM6DSL Click Board™ measures linear and angular velocity with six degrees of freedom. It carries the LSM6DSL high-performance 3-axis digital accelerometer and 3-axis digital gyroscope. The click is designed to run on a 3.3V power supply. The LSM6DSL Click Board™ communicates with the target microcontroller over SPI or I2C interface, with additional functionality provided by the INT pin on the mikroBUS™ line.
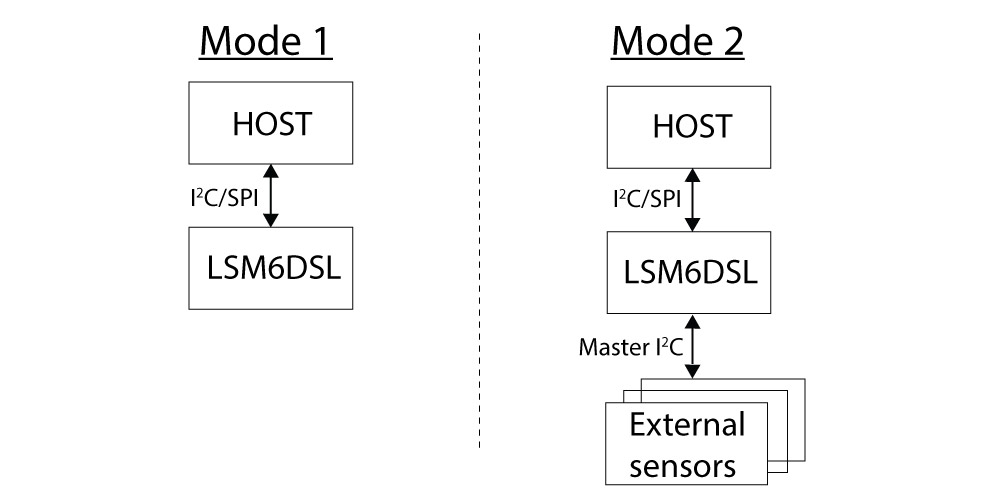
Mode 1: I2C slave interface or SPI serial interface is available.
Mode 2: I2C slave interface, or SPI serial interface and I2C interface master for external sensor connections, are available.
LSM6DSL INERTIAL MODULE FEATURES
The LSM6DSL is a system-in-package featuring a 3D digital accelerometer and a 3D digital gyroscope performing at 0.65 mA in high-performance mode and enabling always-on low-power features for an optimal motion experience.
The event-detection interrupts enable efficient and reliable motion tracking and contextual awareness, implementing hardware recognition of free-fall events, 6D orientation, click and double-click sensing, activity or inactivity, and wakeup events
The LSM6DSL has a full-scale acceleration range of ±2/±4/±8/±16 g and an angular rate range of ±125/±245/±500/±1000/±2000 dps (degrees per second).
SPECIFICATIONS
| Type | Acceleration,Gyroscope,Motion |
| Applications | Motion tracking and gesture detection, indoor navigation, vibration monitoring and compensation, etc. |
| On-board modules | LSM6DSL |
| Key Features | Power consumption: 0.4 mA in combo normal and 0.65 mA in combo high-performance mode; hard, soft ironing for external magnetic sensor corrections |
| Interface | I2C,SPI |
| Compatibility | mikroBUS |
| Click board size | M (42.9 x 25.4 mm) |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V |
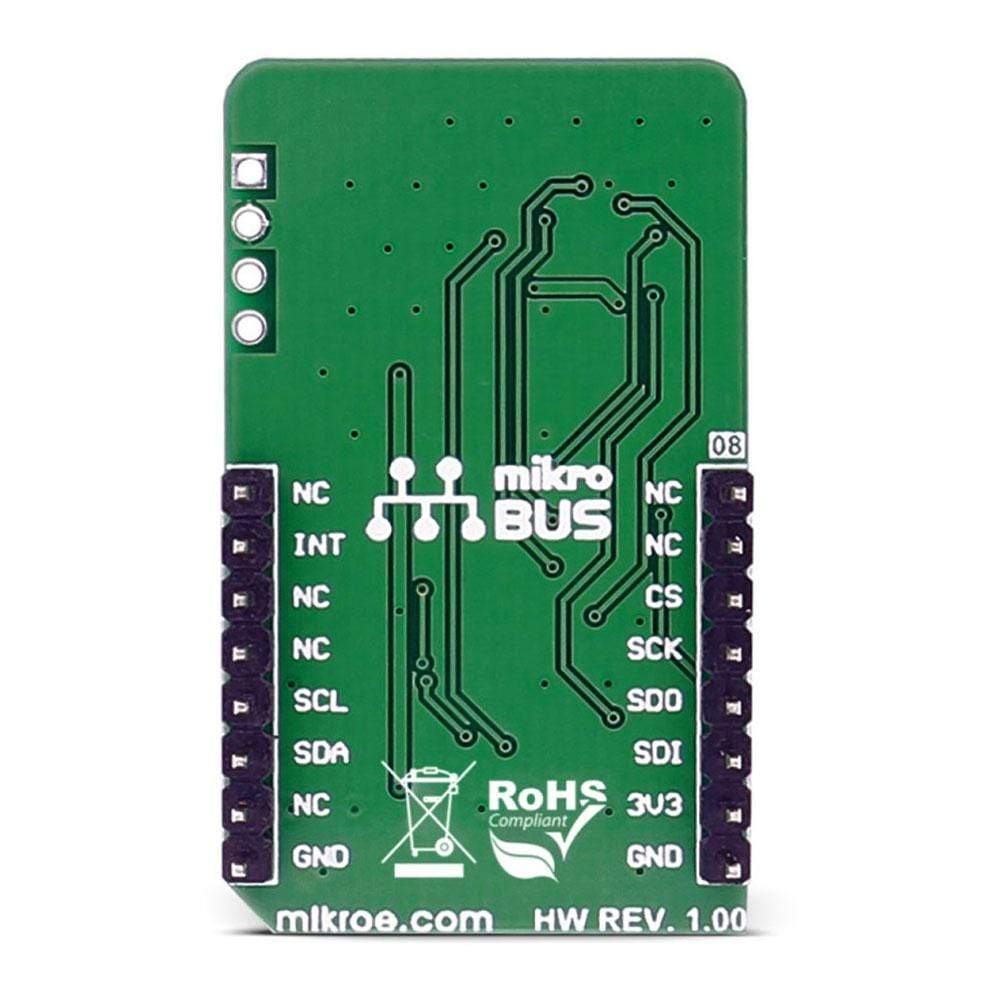
PINOUT DIAGRAM
This table shows how the pinout of the LSM6DSL Click Board™ corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
| Notes | Pin |  |
Pin | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 1 | AN | PWM | 16 | NC | ||
| NC | 2 | RST | INT | 15 | INT | Programmable interrupt | |
| Chip select | CS | 3 | CS | TX | 14 | NC | |
| SPI clock | SCK | 4 | SCK | RX | 13 | NC | |
| Master input slave output | MISO | 5 | MISO | SCL | 12 | SCL | I2C clock |
| Master output slave input | MOSI | 6 | MOSI | SDA | 11 | SDA | I2C data |
| Power supply | +3.3V | 7 | 3.3V | 5V | 10 | NC | |
| Ground | GND | 8 | GND | GND | 9 | GND | Ground |
JUMPERS AND SETTINGS
| Designator | Name | Default Position | Default Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP1 | COMM SEL | Left | SPI | Communication Interface Selection SPI/I2C, left position SPI, right position I2C |
| JP2 | COMM SEL | Left | SPI | Communication Interface Selection SPI/I2C, left position SPI, right position I2C |
| JP3 | COMM SEL | Left | SPI | Communication Interface Selection SPI/I2C, left position SPI, right position I2C |
| JP4 | INT SEL | Left | INT1 | Interrupt selection INT1/INT2, left position INT1, right position INT2 |
| JP5 | COMM SEL | Left | SPI | Communication Interface Selection SPI/I2C, left position SPI, right position I2C |
| JP6 | MODE SEL | Left | 1 | Mode Selection 1/2, left position 1, right position 2 |
| JP7 | MODE SEL | Left | 1 | Mode Selection 1/2, left position 1, right position 2 |
| JP8 | ADD SEL | Left | 0 | I2C slave address selection 0/1, left position 0, right position 1 |
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-2731
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.018 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018711239
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.