


Overview
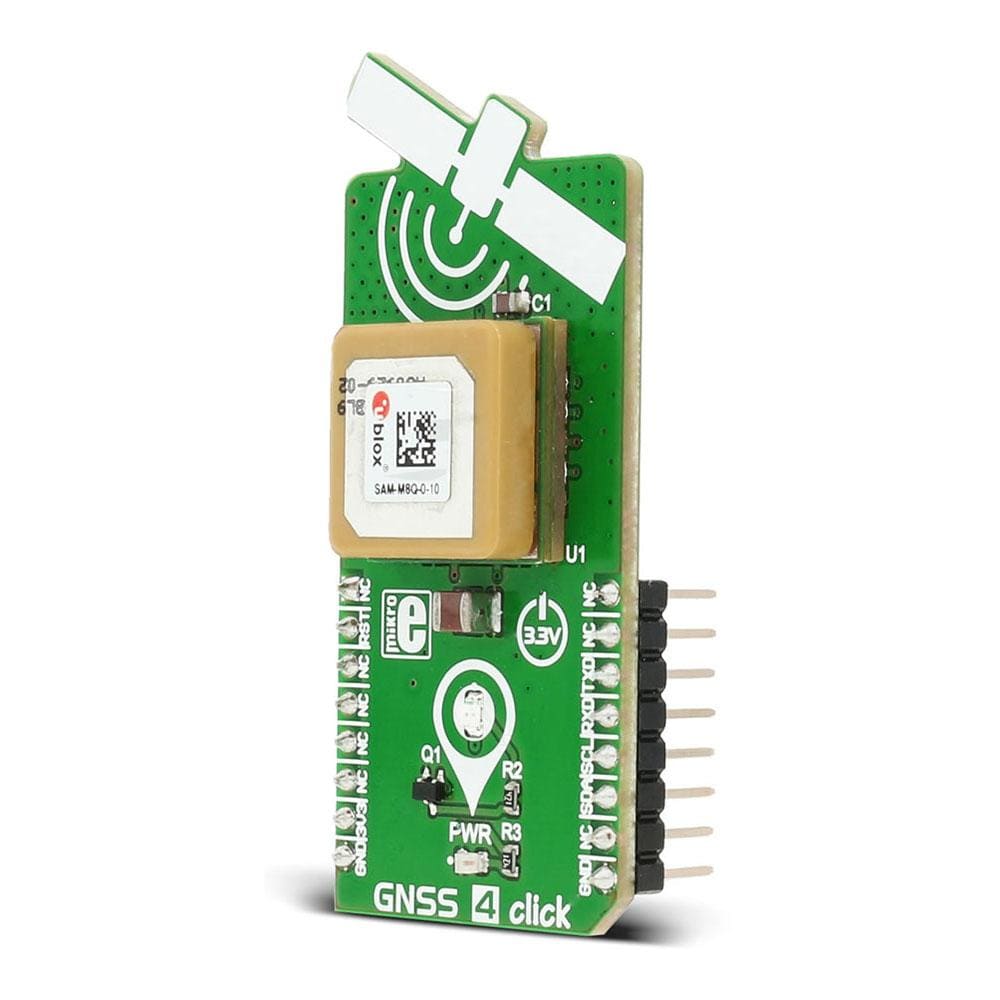
The GNSS 4 Click Board™ is based on the SAM-M8Q patch antenna module from u-blox. It is designed to run on a 3.3V power supply. It communicates with the target microcontroller over I2C or UART interface.
Downloads
The GNSS 4 Click Board™ carries SAM-M8Q patch antenna module from u-blox. The click is designed to run on a 3.3V power supply. It communicates with the target microcontroller over I2C or UART interface.
What Is GNSS?
GNSS stands for Global Navigation Satellite System, an umbrella term that describes both the United States GPS, the Russian GLONASS global positioning systems and European Galileo.
SAM-M8Q Module
The SAM-M8Q module utilizes concurrent reception of up to three GNSS systems (GPS/Galileo and GLONASS), recognizes multiple constellations simultaneously and provides outstanding positioning accuracy in scenarios where urban canyon or weak signals are involved.
Patch Antenna
The GNSS patch antenna is RHCP (right hand circular polarization) and has a peak gain of 3 dBic. The patch antenna is insensitive to surroundings and has high tolerance against frequency shifts.
Power Management
u-blox M8 technology offers a power-optimized architecture with built-in autonomous power saving functions to minimize power consumption at any given time. Furthermore, the receiver can be used in two operating modes: Continuous mode for best performance or Power Save Mode for optimized power consumption.
Good In Hostile Environments
Thanks to all these features the SAM-M8Q module is good in GNSS-hostile environments - indoor spaces, urban canyons (when a street is flanked by buildings on both sides), etc.
AssistNow™ Service
The u-blox SAM-M8Q module can also benefit from the u-blox AssistNow assistance service. The Online service provides GNSS broadcast parameters, e.g. ephemeris, almanac plus time or rough position to reduce the receiver's time to first fix significantly and improve acquisition sensitivity.
The extended validity of AssistNow Offline data (up to 35 days) and AssistNow Autonomous data (up to 3 days) provide faster acquisition after a long off time.
How Does The GNSS 4 Click Board™ Work?
A constellation of satellites sends a continuous signal towards Earth. Onboard every satellite is an atomic clock, and all of them are synchronized, thanks to a reference time scale defined by the whole system. So, that the signals coming from the different satellites of the same constellation share the same reference time scale.
If the user wants to utilize GNSS to determine a position, they must have an antenna that receives the signals coming from the satellites, and a receiver that translates these signals. The antenna position will be deduced from the measurements of the time delay between the emission time (satellite) and the reception time (receiver) for at least 4 signals coming from different satellites.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Type | GPS+GNSS |
| Applications | The GNSS 4 Click Board™ is suitable for asset tracking, for navigation devices based on GPS and GLONASS, road navigation devices, public transport, wearable devices, etc. |
| On-board modules | SAM-M8Q from u-blox |
| Key Features | High accuracy, I2C and UART interface, 3.3V power supply |
| Interface | GPIO,I2C,UART |
| Compatibility | mikroBUS |
| Click board size | M (42.9 x 25.4 mm) |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V |
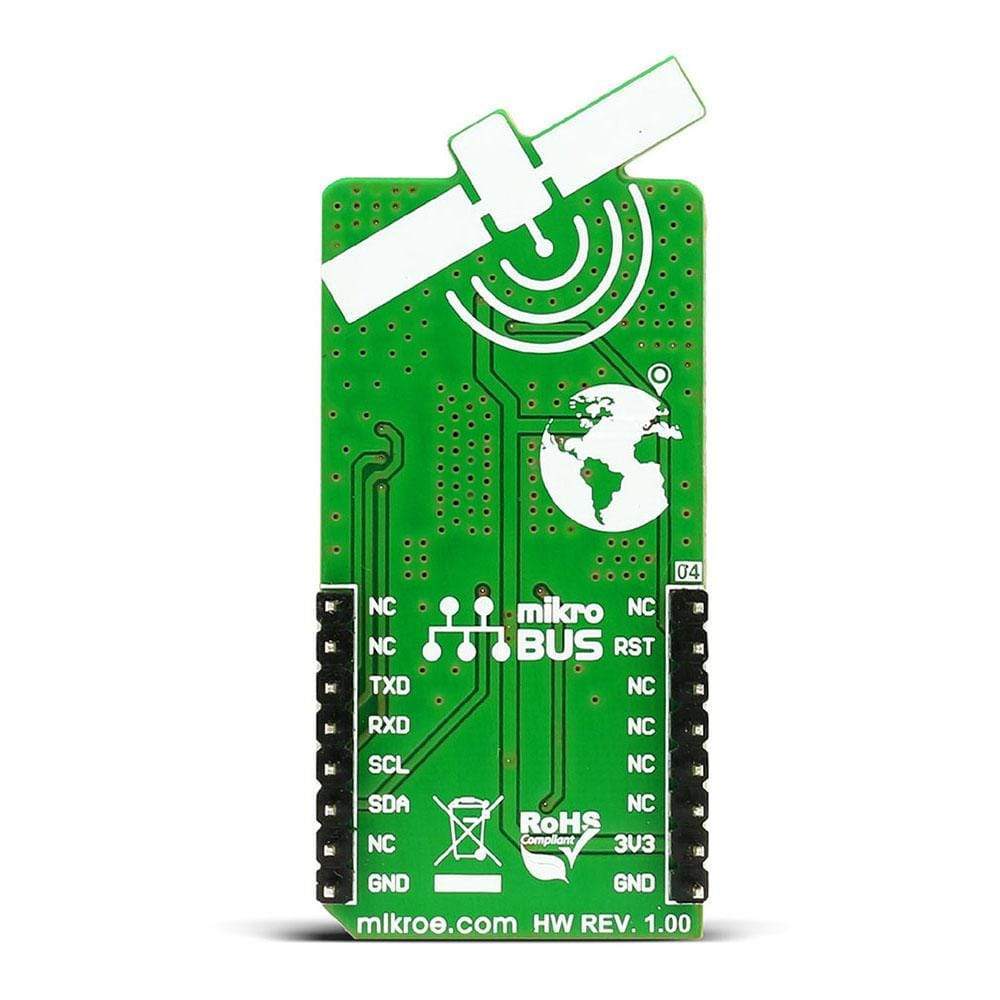
PINOUT DIAGRAM
This table shows how the pinout of the GNSS 4 Click Board™ corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
| Notes | Pin |  |
Pin | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 1 | AN | PWM | 16 | NC | ||
| Active Low | RST_N | 2 | RST | INT | 15 | NC | |
| NC | 3 | CS | TX | 14 | TXD | UART transmit | |
| NC | 4 | SCK | RX | 13 | RXD | UART receive | |
| NC | 5 | MISO | SCL | 12 | SCL | I2C Clock | |
| NC | 6 | MOSI | SDA | 11 | SDA | I2C Data | |
| Power supply | +3.3V | 7 | 3.3V | 5V | 10 | NC | |
| Ground | GND | 8 | GND | GND | 9 | GND | Ground |
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-2045
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.03 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018710072
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.




