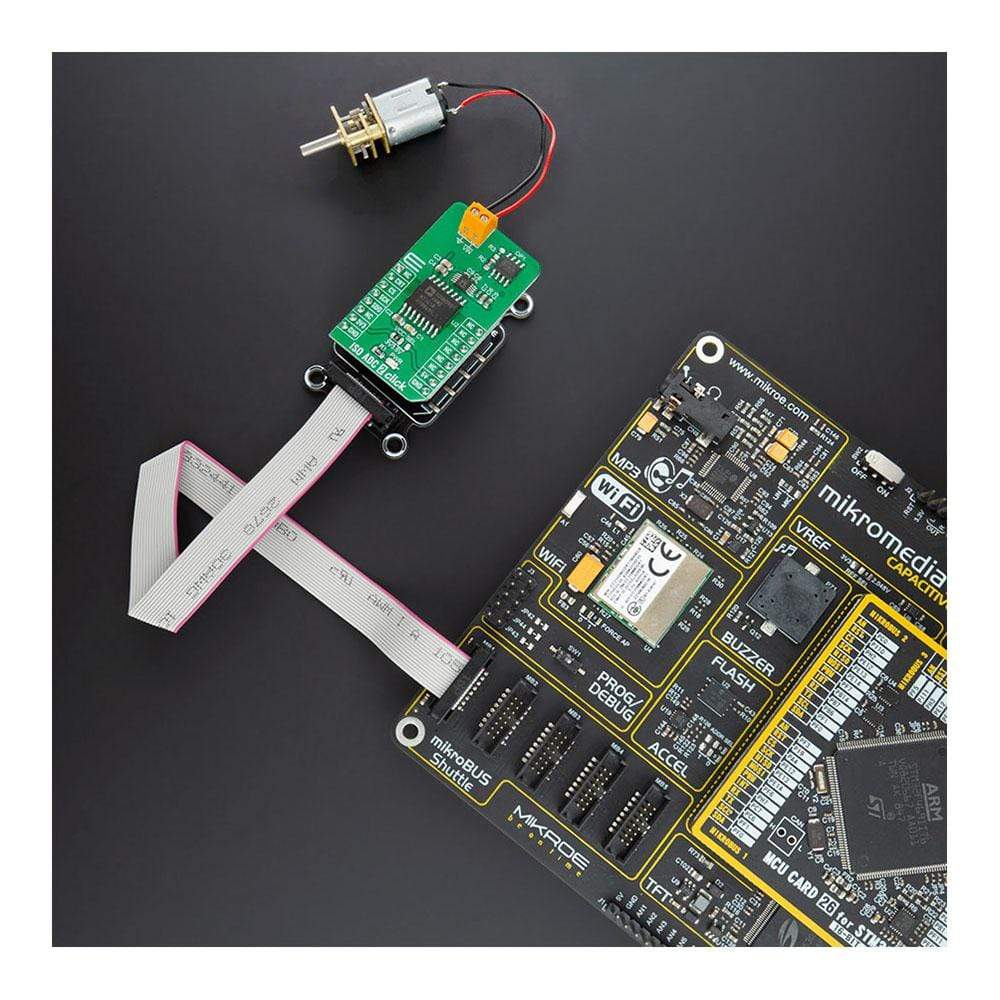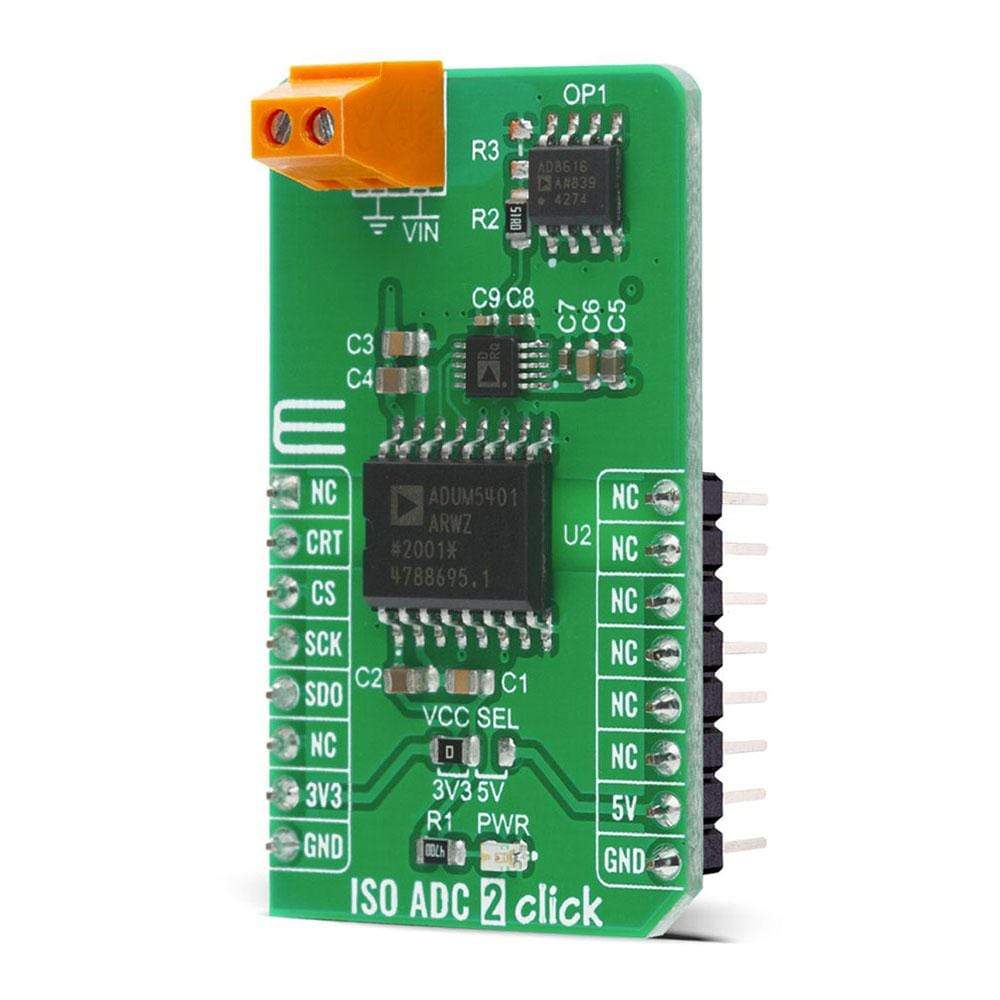

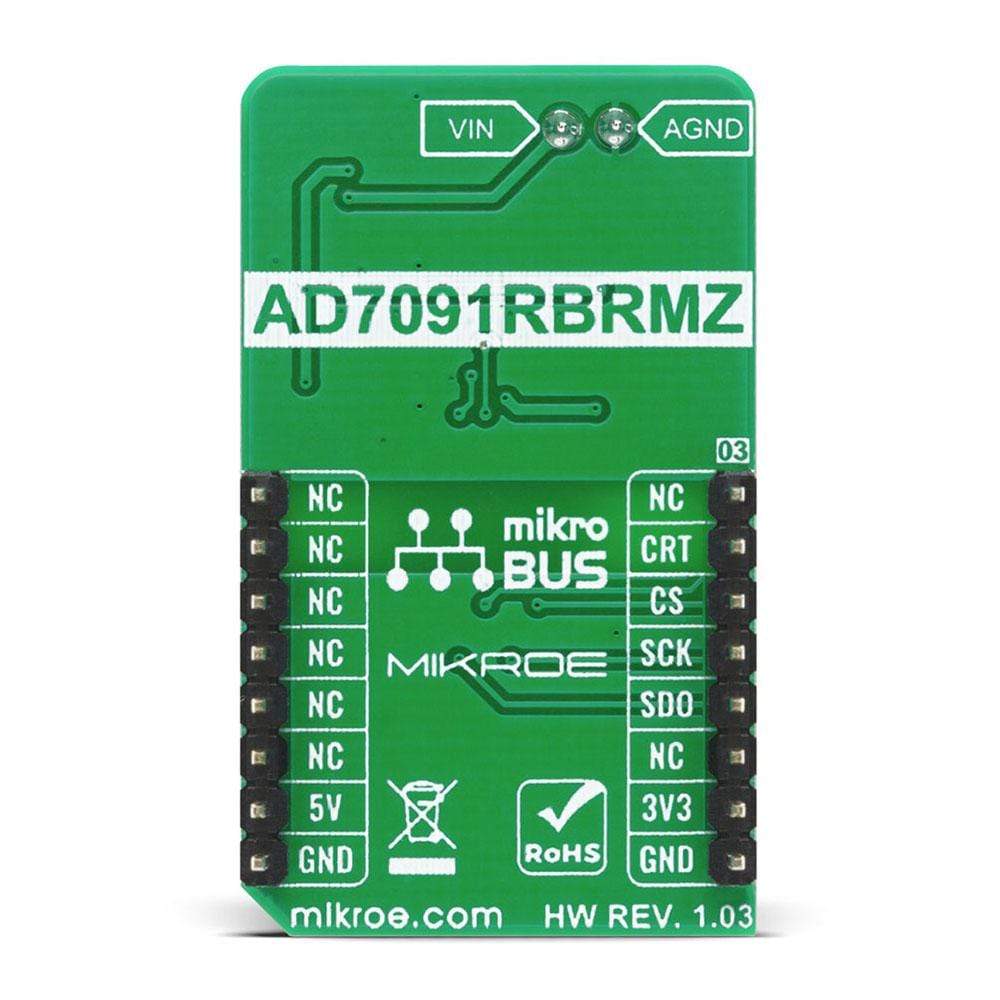

Overview
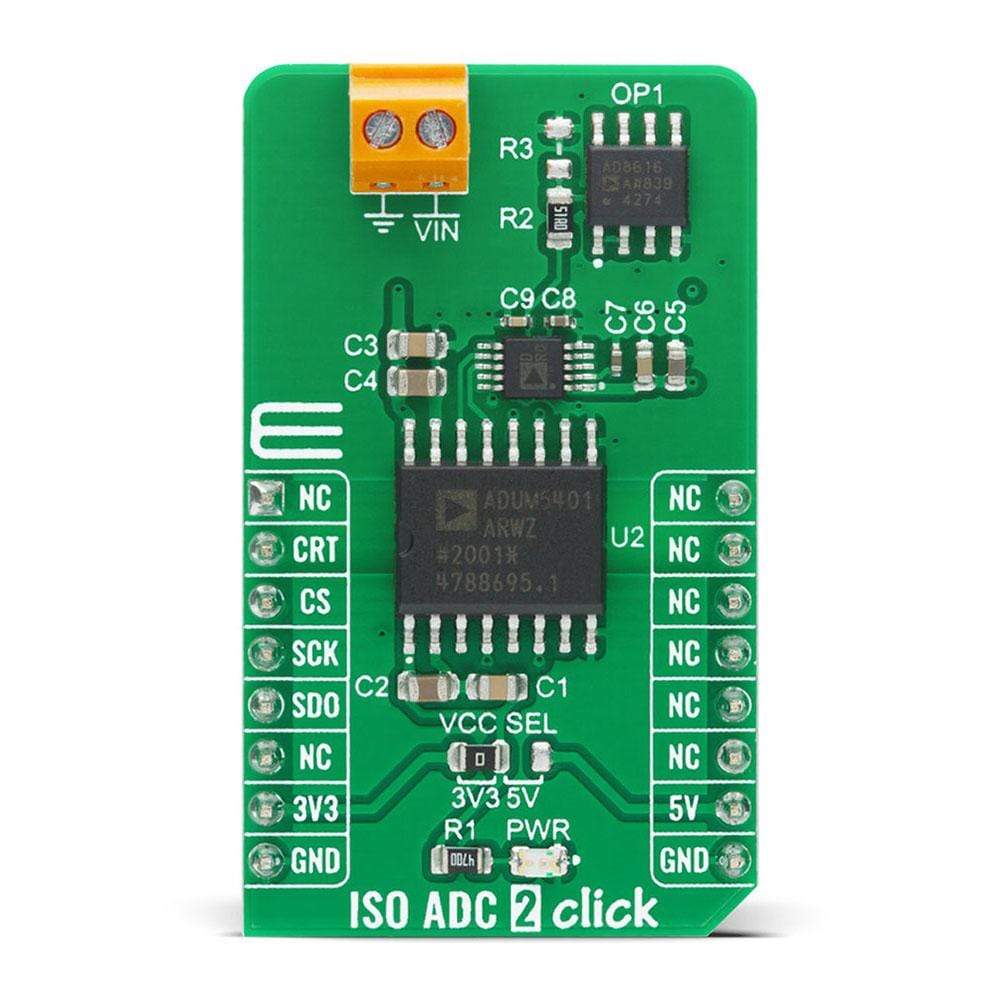
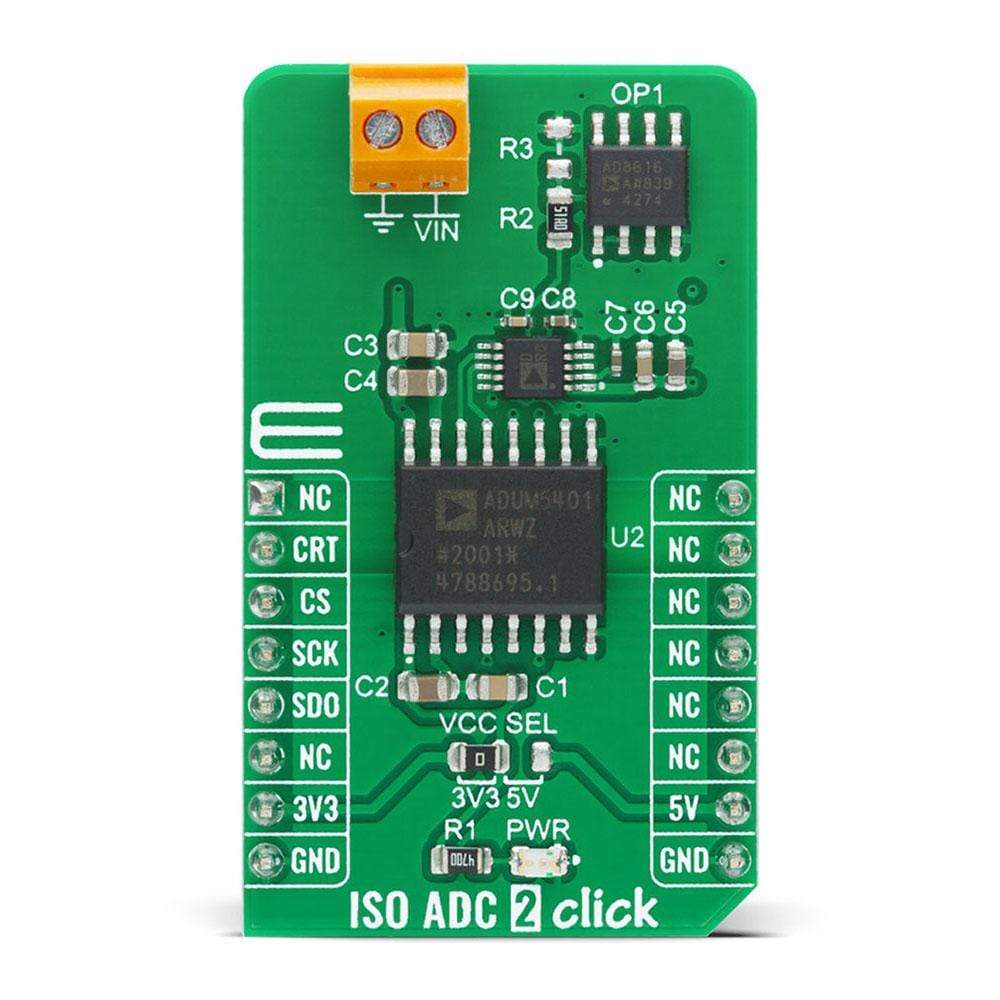
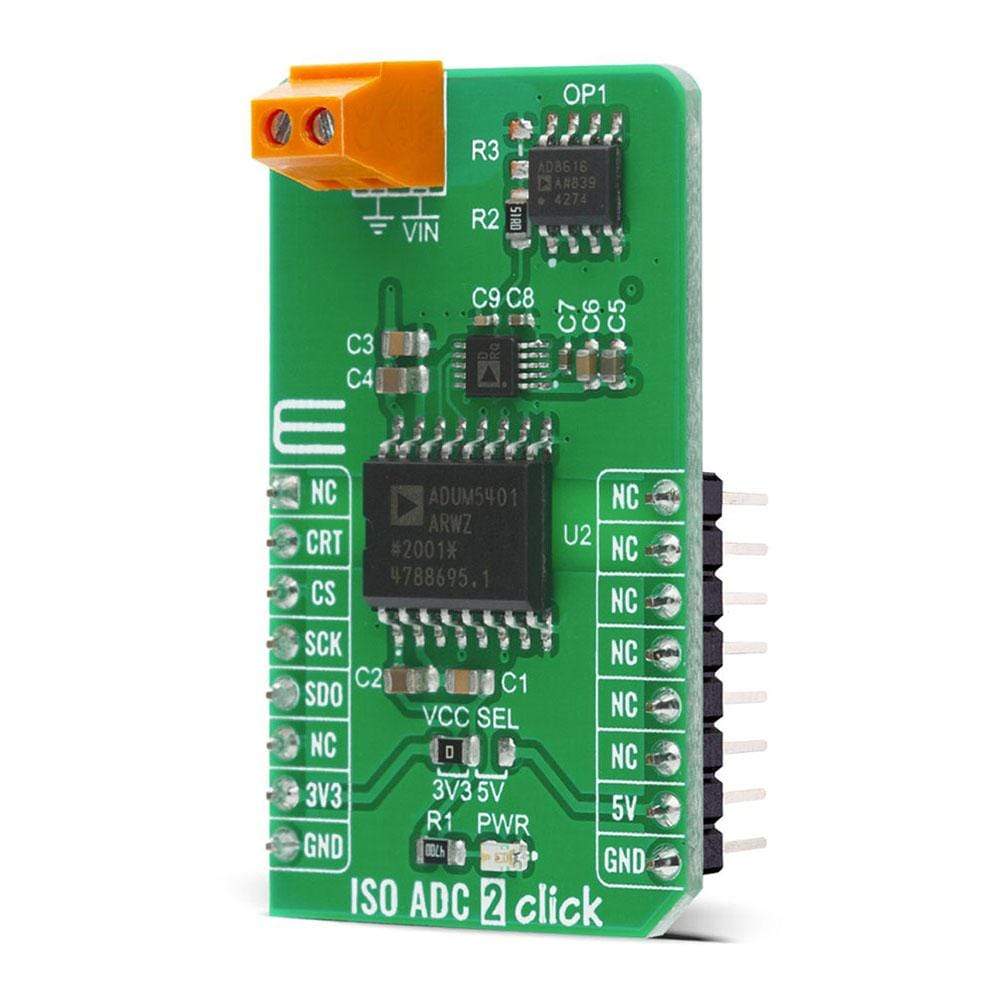
The ISO ADC 2 Click Board™ is a compact add-on board that represents a completely isolated 12-bit, 300 kSPS data acquisition system. This board features the AD7091R, a successive-approximation analog-to-digital converter (ADC) from Analog Devices. It uses the 3-wire SPI serial interface for data communication, achieving up to 1 MSPS throughput rate. This Click Board™ also features the ADU 4-Channel Isolator with DC-DC Converter M5401, isolated DC-DC converter used to isolate the logic signals, power, and feedback paths in the DC-DC converter resulting in total isolation solution. Many features such as high throughput rate with ultralow power consumption, wide input bandwidth, accuracy, and speed make it an ideal choice for a wide variety of industrial measurements, data acquisition systems, monitoring functions, and many more.
The ISO ADC 2 Click Board™ is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click Board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Downloads
How Does The ISO ADC 2 Click Board™ Work?
The ISO ADC 2 Click Board™ is based on the AD7091R, a 12-bit successive-approximation analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with an isolated DC-DC converter, from Analog Devices. This Click board™ allows single-supply operation and consists of three Analog Devices active components: AD8616 a level shifting circuit, AD7091R an ADC stage and ADuM5401 an output isolation stage. The AD8616 is chosen for this application because of its low offset voltage, low bias current, and low noise. The output of the OpAmp is 0.1 V to 2.4 V which matches the input range of the ADC (0 V to 2.5 V) with a 100 mV safety margin to maintain linearity. A single-pole RC filter (R2/C9) follows the OpAmp output stage to reduce the out-of-band noise.
.jpg)
The next part of the circuit is the AD7091R, ADC that is chosen because of its ultralow power which is significantly lower than any competitive A/D converter. It features a power-down option, implemented across the serial interface to save power between conversions, described in the Modes of Operation section in the datasheet. After a successful conversion, the ADC sends the data to the MCU that goes through galvanic isolation provided by the ADuM5401 quad-channel digital isolator with an integrated DC-DC converter. The isolator has a secondary side controller architecture with isolated pulse-width modulation (PWM) feedback, and it works on the principle that is common to most switching power supplies.
The ISO ADC 2 Click Board™ communicates with MCU using the 3-wire SPI serial interface that operates at clock rates up to 50 MHz used for accessing data from the result register and controlling the modes of operation of the device. The CONVST signal of the AD7091R routed to the RST pin on the mikroBUS™ is used to initiate the conversion process, data acquisition, and to select the mode of operation. This ADC requires the user to initiate a software reset upon Power-Up, and it should be noted that failure to apply the correct software reset command may result in a device malfunction.
The ISO ADC 2 Click Board™ uses the SPI communication interface with both 3.3V and 5V. The onboard SMD jumper labelled as VCC SEL allows voltage selection for interfacing with both 3.3V and 5V MCUs. More information about the AD7091R's functionality, electrical specifications, and typical performance can be found in the attached datasheet. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library that contains easy to use functions and a usage example that may be used as a reference for the development.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Type | ADC,Isolators |
| Applications | The ISO ADC 2 Click Board™ can be used for a wide variety of industrial measurements, data acquisition systems, monitoring functions, and many more. |
| On-board modules | ISO ADC 2 Click is based on the AD7091R, a 12-bit successive-approximation analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with an isolated DC-DC converter, from Analog Devices. |
| Key Features | Low power consumption, fast throughput rate, wide input bandwidth, and more. |
| Interface | GPIO,SPI |
| Compatibility | mikroBUS |
| Click board size | M (42.9 x 25.4 mm) |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V or 5V |
PINOUT DIAGRAM
This table shows how the pinout of the ISO ADC 2 Click Board™ corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
| Notes | Pin |  |
Pin | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 1 | AN | PWM | 16 | NC | ||
| Conversion Initialization | CRT | 2 | RST | INT | 15 | NC | |
| SPI Chip Select | CS | 3 | CS | RX | 14 | NC | |
| SPI Clock | SCK | 4 | SCK | TX | 13 | NC | |
| SPI Data OUT | SDO | 5 | MISO | SCL | 12 | NC | |
| NC | 6 | MOSI | SDA | 11 | NC | ||
| Power Supply | 3.3V | 7 | 3.3V | 5V | 10 | 5V | Power Supply |
| Ground | GND | 8 | GND | GND | 9 | GND | Ground |
ONBOARD SETTINGS AND INDICATORS
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | - | Power LED Indicator |
| JP1 | VCC SEL | Left | Power Supply Voltage Selection 3V3/5V: Left position 3V3, Right position 5V |
ISO 2 ADC CLICK ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
| Description | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | -0.3 | - | 7 | V |
| SPI Clock Frequency | - | - | 50 | MHz |
| Resolution | 12 | - | - | bits |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40 | - | +125 | °C |
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-4166
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.019 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606027380266
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.