

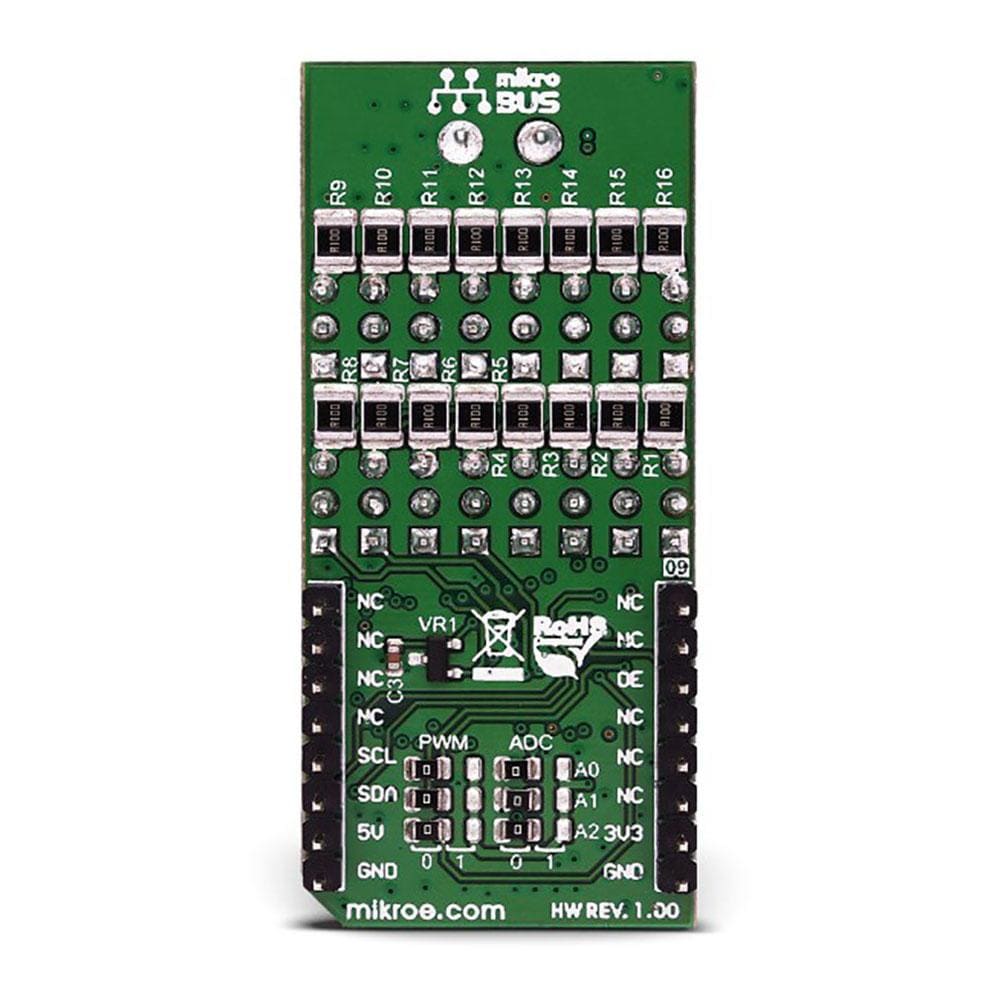
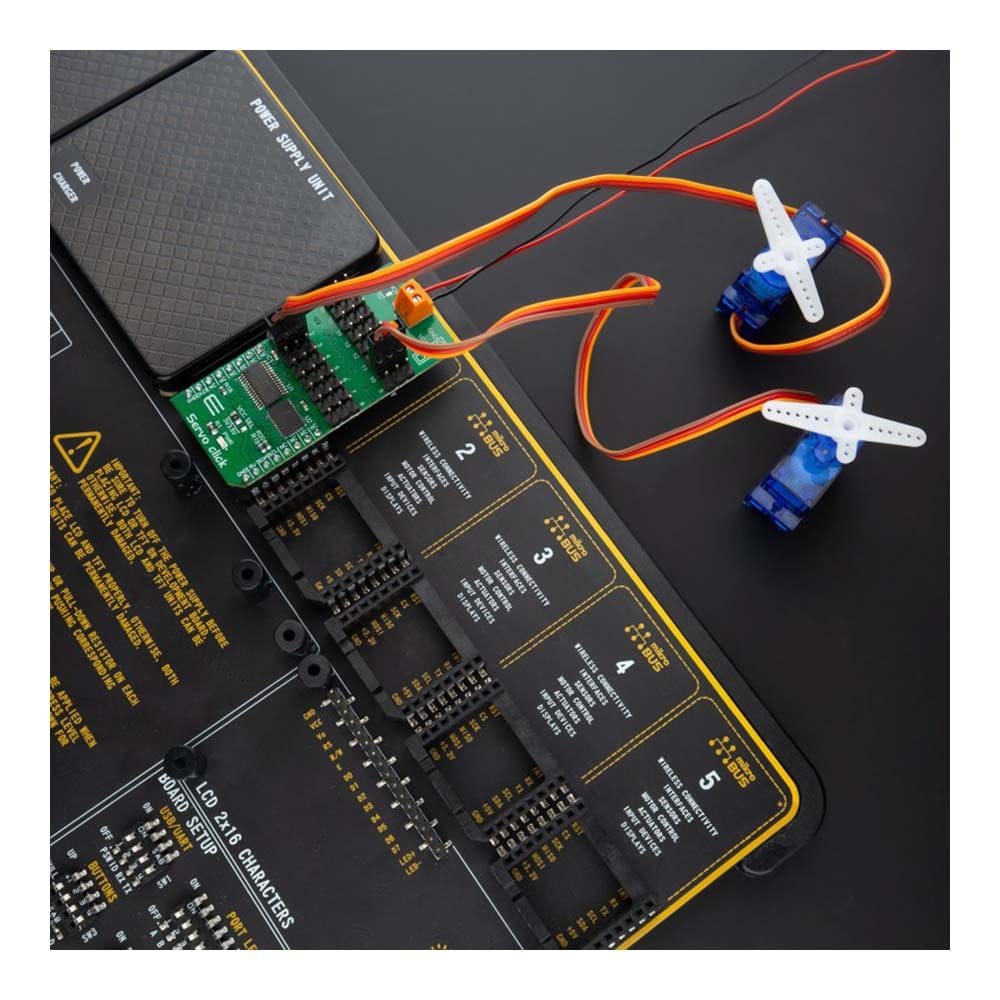
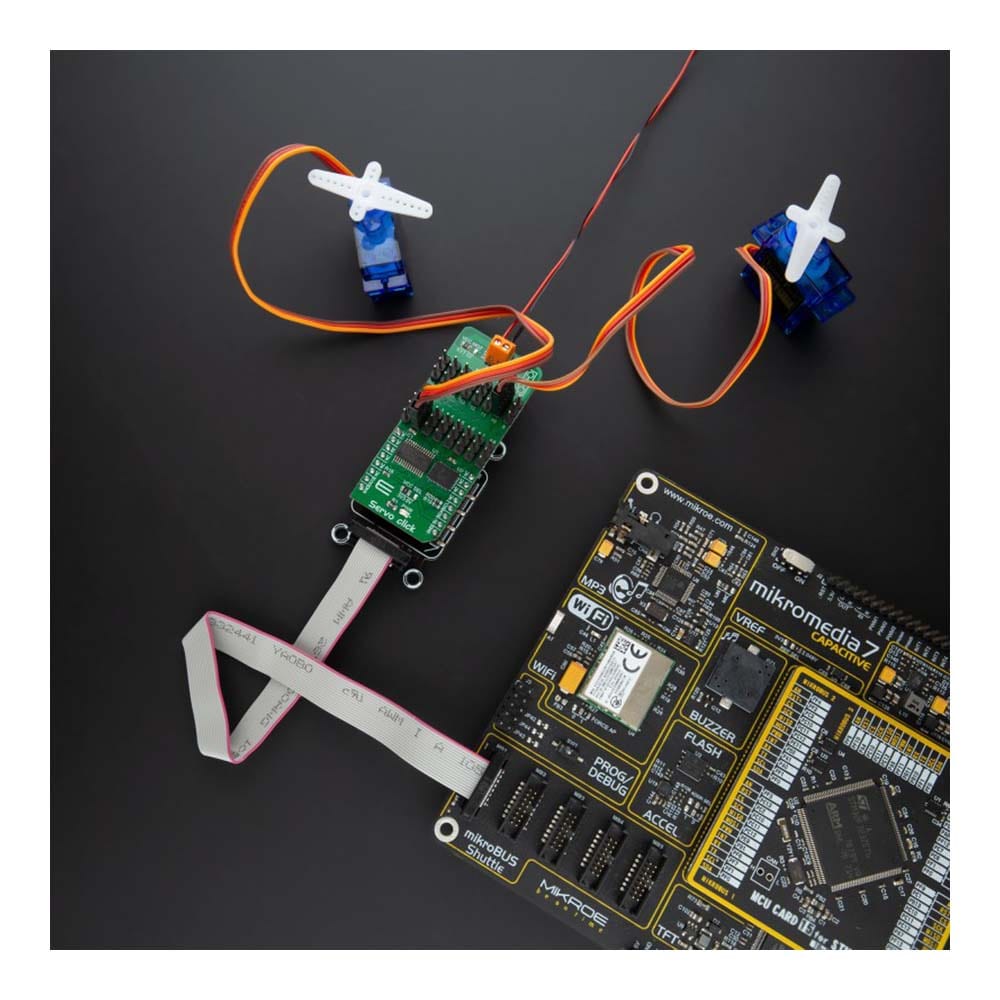
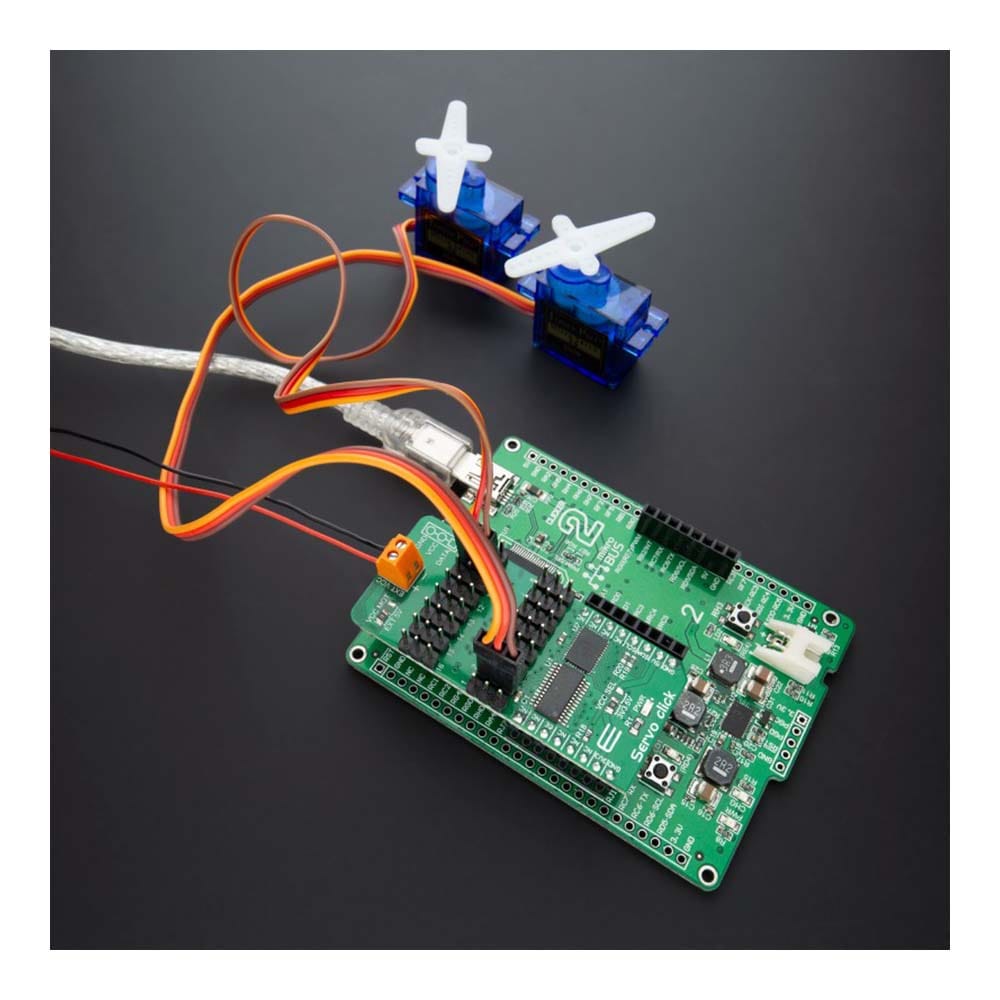

Overview
Introducing the Servo Click Board™: Revolutionize Your Servo Control
Are you tired of struggling with limited servo control options? Look no further! The Servo Click Board™ is here to transform your servo control experience.
Unleash the Power of 16-Channel PWM Control
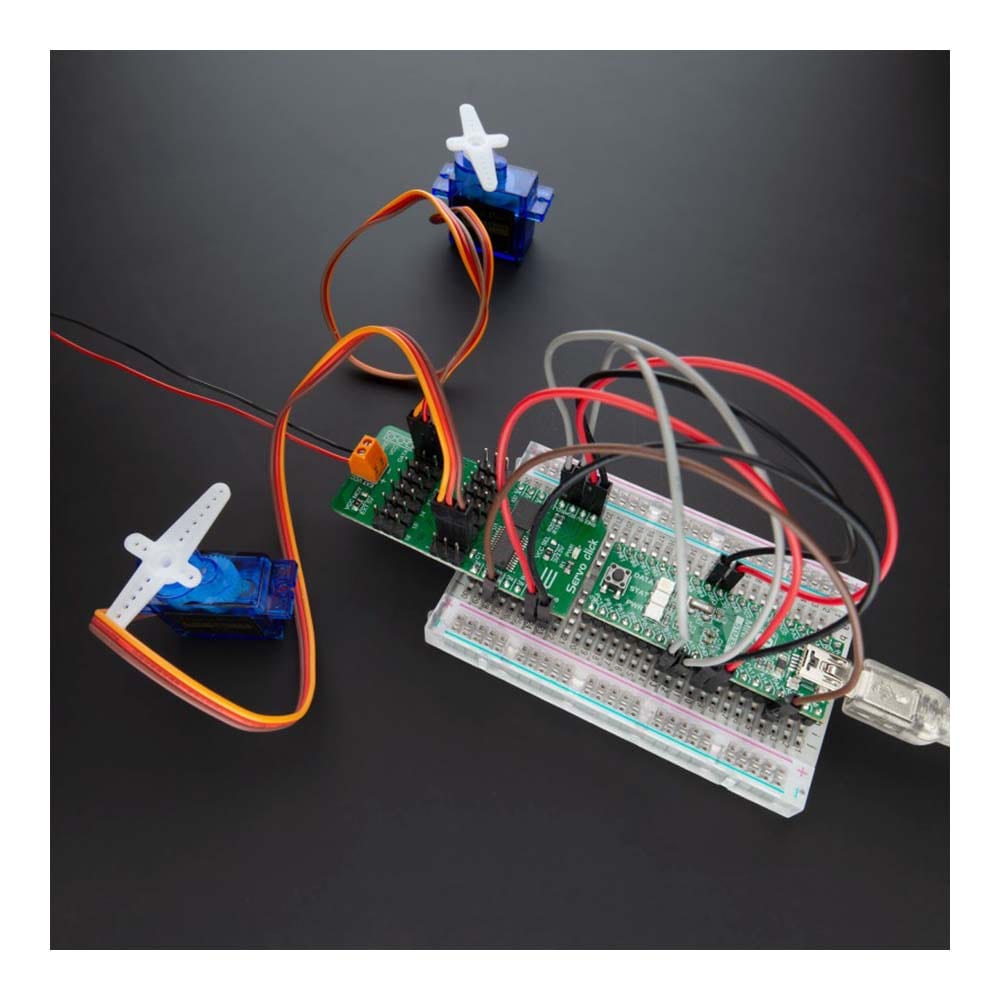
Say goodbye to single-channel limitations. With the Servo Click Board™, you can simultaneously control a whopping 16 servo motors! Each servo enjoys its own programmable PWM signal, giving you unparalleled flexibility and precision in your projects.
Fine-Tune Your Servo Performance
Precision matters. That's why we equipped the Servo Click Board™ with a programmable PWM signal frequency range from 24 Hz to 1526 Hz. This range is meticulously chosen to cater to various servo types, ensuring that your creations move with the utmost precision and accuracy.
Real-Time Insights with Voltage Sensing
What sets the Servo Click Board™ apart is its 16-bit A/D converter, which samples the voltage drop across each channel's shunt resistor. This means you get real-time feedback on servo current consumption, allowing you to optimize performance and prevent overheating without any need for modifying your servos.
Why Choose the Servo Click Board™?
- Effortless Control: Control up to 16 servos with ease, streamlining your projects and saving you time.
- Precision in Every Move: Fine-tune your servos to perfection with a wide PWM signal frequency range.
- Protect Your Servos: Monitor current consumption in real-time to prevent damage and enhance longevity.
Make the smart choice and experience a new level of servo control with the Servo Click Board™. Elevate your projects, unlock limitless possibilities, and join the ranks of satisfied customers who have already made the switch.
Ready to revolutionize your servo control? Click the button below and take the first step towards a brighter, more precise future!
Get Your Servo Click Board™ Now
Don't miss out on this game-changing innovation. Upgrade your servo control today!
Downloads
How Does The Servo Click Board™ Work?
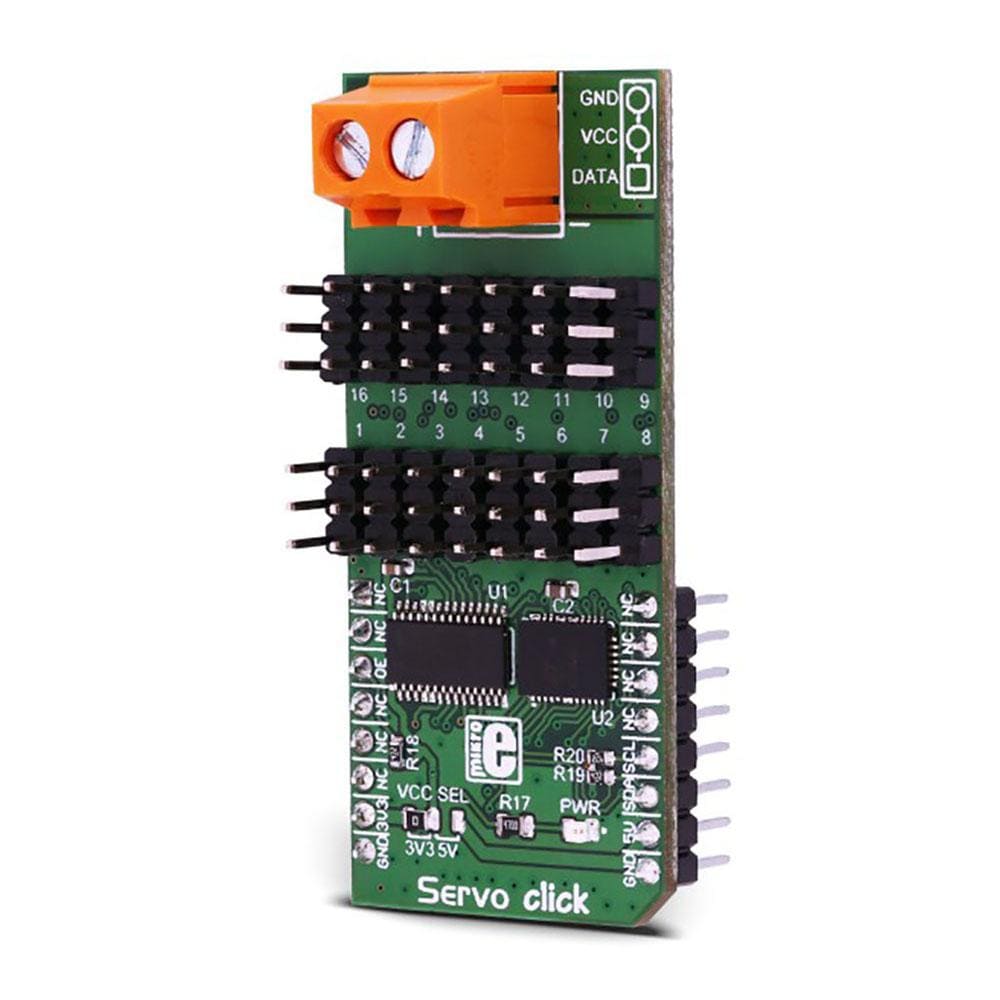
The Servo Click Board™ is based on the PCA9685, an integrated 12-bit 16-channel PWM driver which can be configured to either sink 25mA per channel or drive each channel sourcing up to 10mA from NXP. Each channel has its duty cycle independently set from 0% to 100%. Offering 16 independent channels, each with its own PWM duty cycle and current sensing ability, this Click board™ represents a powerful servo controller, especially useful when a large number of servos needs to be controlled simply and easily. The frequency of the control PWM signal can be programmed in the range from 24 Hz to 1526 Hz.
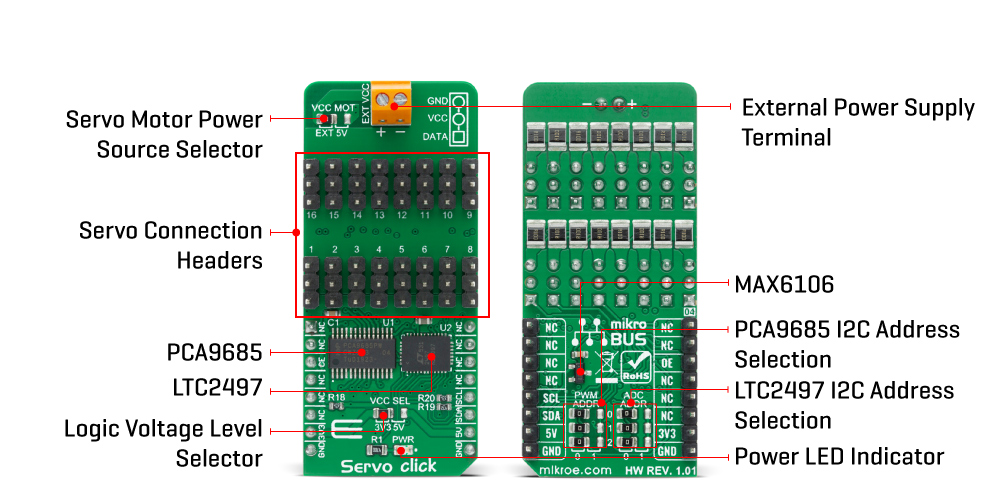
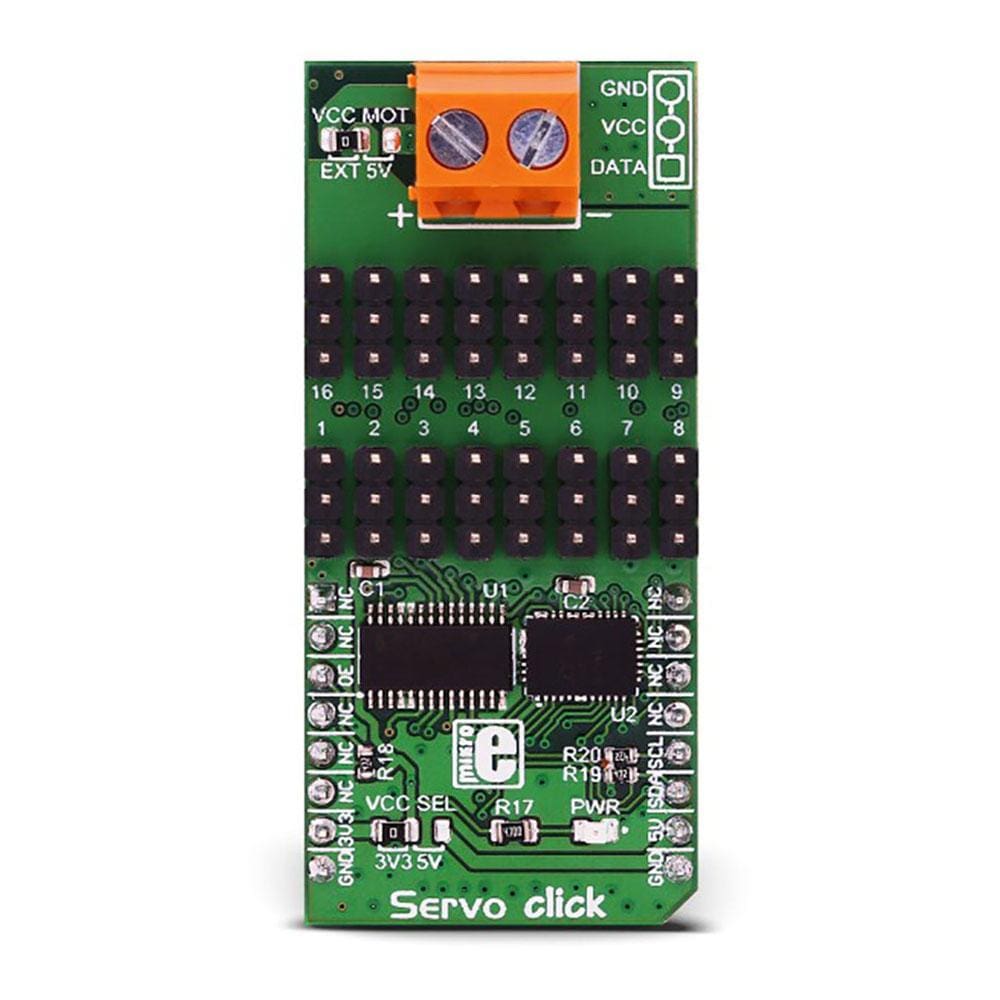
The servo can be connected to any of the sixteen headers located on the Servo Click Board™. The output signal frequency is determined by the Prescaler value, which is written to the appropriate register. The output channels can be set either in the open-drain or in the push-pull configuration. In the first case, they will be able to sink up to 25mA from up to 5V power supply, while in the second case, they will be able to both drive with up to 10mA or sink up to 25mA.
The Servo Click Board™ also has an accurate 16bit A/D converter the LTC2497 from Analog Devices used to sample the voltage drop across the shunt resistor on each of the 16 channels giving feedback on the servo current consumption. The ADC uses an accurate reference of 2.048V provided by an onboard reference voltage regulator MAX6106 from Maxim Integrated. An extremely low noise of this ADC coupled with a low reference voltage allows small voltage drops across the shunt resistor to be accurately converted.
The Servo Click Board™ communicates with MCU using the standard I2C 2-Wire interface with a frequency up to 100kHz in the Standard, up to 400 kHz in the Fast, and up to 1MHz in the Fast-Plus mode. There are two more SMD jumpers, labelled as the PWM and ADC, located at the bottom of the Click board™ that allows selection of the slave I2C address for each of the two onboard ICs. It also has an external connector that can provide more power for servos that operate with heavier loads. That's why the SMD jumper labelled as VCC MOT should be at the EXT position. In this case, an external PSU that can provide more current can be used.
The PCA9685 also offers Output Enable pin, routed to the mikroBUS™ CS pin, labelled as the OE. A LOW logic level on this pin will set all the outputs to the predefined logic state, turning the PWM generators OFF. This may either leave the servo into the fixed position or turn it down completely, depending on the servo model.
The Servo Click Board™ is designed to be operated with both 3.3V and 5V logic voltage levels that can be selected via VCC SEL jumper. This allows for both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs to use the I2C communication lines properly.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Type | Servo |
| Applications | The Servo Click Board™ can be used in applications when a large number of servos needs to be easily controlled in the movie or theater industry (animatronics), robotics, RC toys, and similar. |
| On-board modules | The Servo Click Board™ is based on the PCA9685, an integrated 12-bit 16-channel PWM driver which can be configured to either sink 25mA per channel or drive each channel sourcing up to 10mA from NXP. |
| Key Features | PWM driver with voltage sensing circuitry, programmable frequency, output enable and software reset feature, supports hot insertion, low standby current, and more. |
| Interface | I2C |
| Compatibility | mikroBUS |
| Click board size | L (57.15 x 25.4 mm) |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V or 5V |
PINOUT DIAGRAM
This table shows how the pinout on the Servo Click Board™ corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
| Notes | Pin |  |
Pin | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 1 | AN | PWM | 16 | NC | ||
| NC | 2 | RST | INT | 15 | NC | ||
| Output Enable | OE | 3 | CS | RX | 14 | NC | |
| NC | 4 | SCK | TX | 13 | NC | ||
| NC | 5 | MISO | SCL | 12 | SCL | I2C Clock | |
| NC | 6 | MOSI | SDA | 11 | SDA | I2C Data | |
| Power supply | 3.3V | 7 | 3.3V | 5V | 10 | 5V | Power supply |
| Ground | GND | 8 | GND | GND | 9 | GND | Ground |
ONBOARD SETTINGS AND INDICATORS
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | - | Power LED indicator |
| JP1 | VCC SEL | Left | Power Supply Voltage Selection 3V3/5V: Left position 3V3, Right position 5V |
| JP2 | VCC MOT | Left | Servo Motor Power Source Selection: Left position External, Right position 5V |
| JP3-JP5 | PWM ADR | Left | PCA9685 I2C Address Selection: Left position 0, Right position 1 |
| JP6-JP8 | ADC ADR | Left | LTC2497 I2C Address Selection: Left position 0, Right position 1 |
| HM1-HM16 | 1 - 16 | - | Servo Connection Headers |
SERVO CLICK ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
| Description | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | -0.5 | - | 6 | V |
| High Level Output Current | -10 | - | +10 | μA |
| Low Level Output Current | 12 | 25 | - | mA |
| Total Power Dissipation | - | - | 400 | mW |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40 | - | +85 | °C |
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-3133
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.027 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018713448
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.







