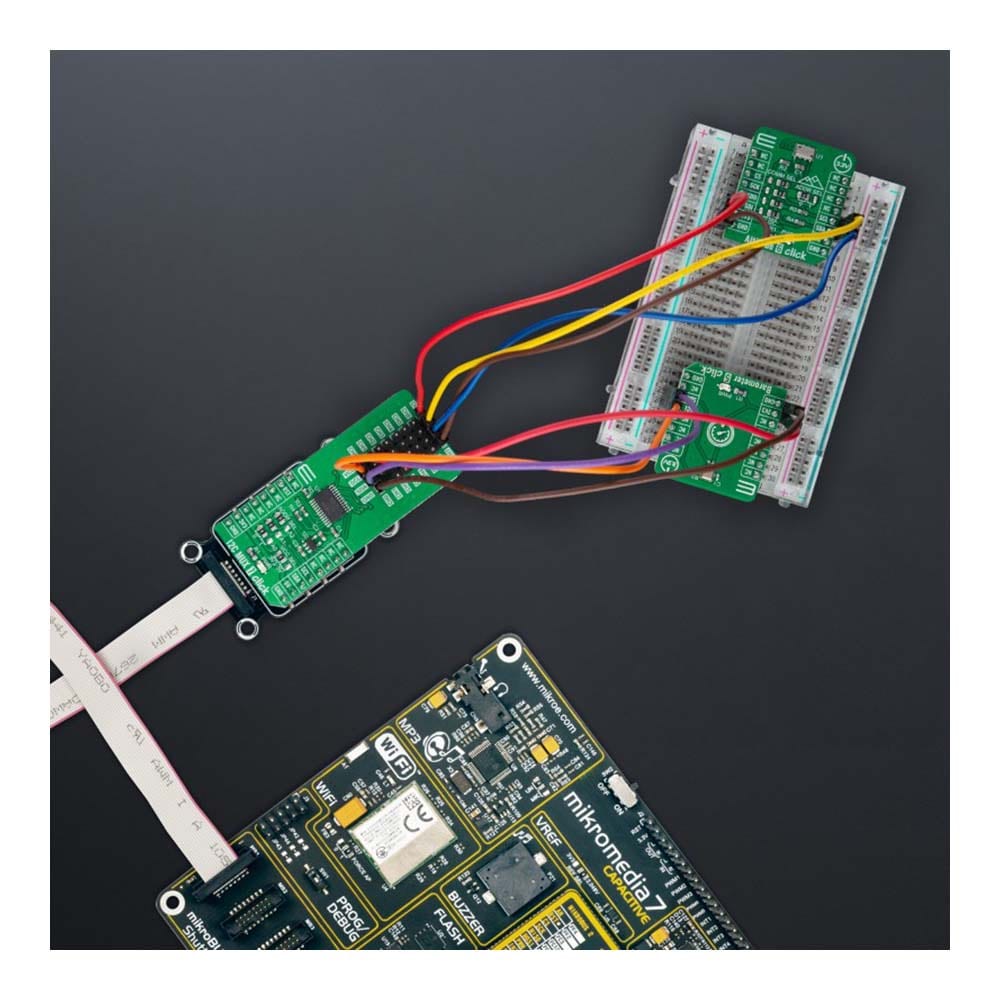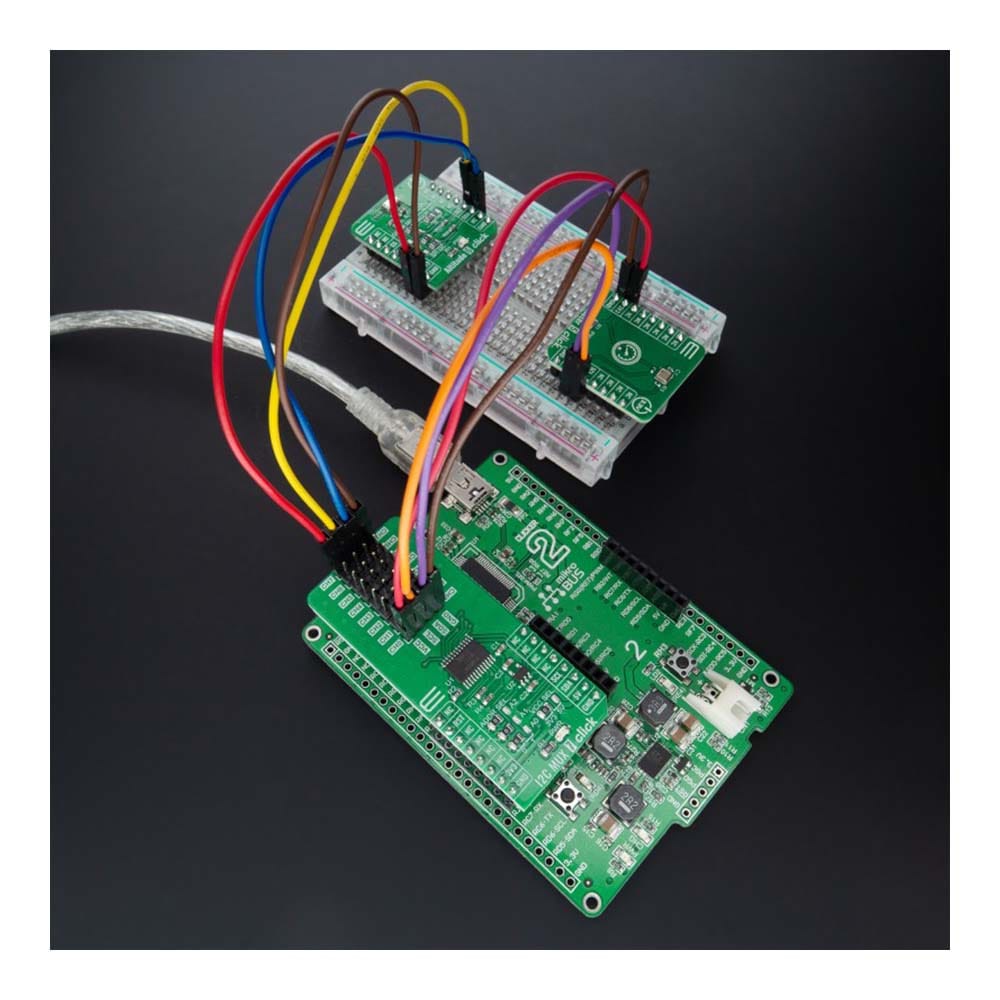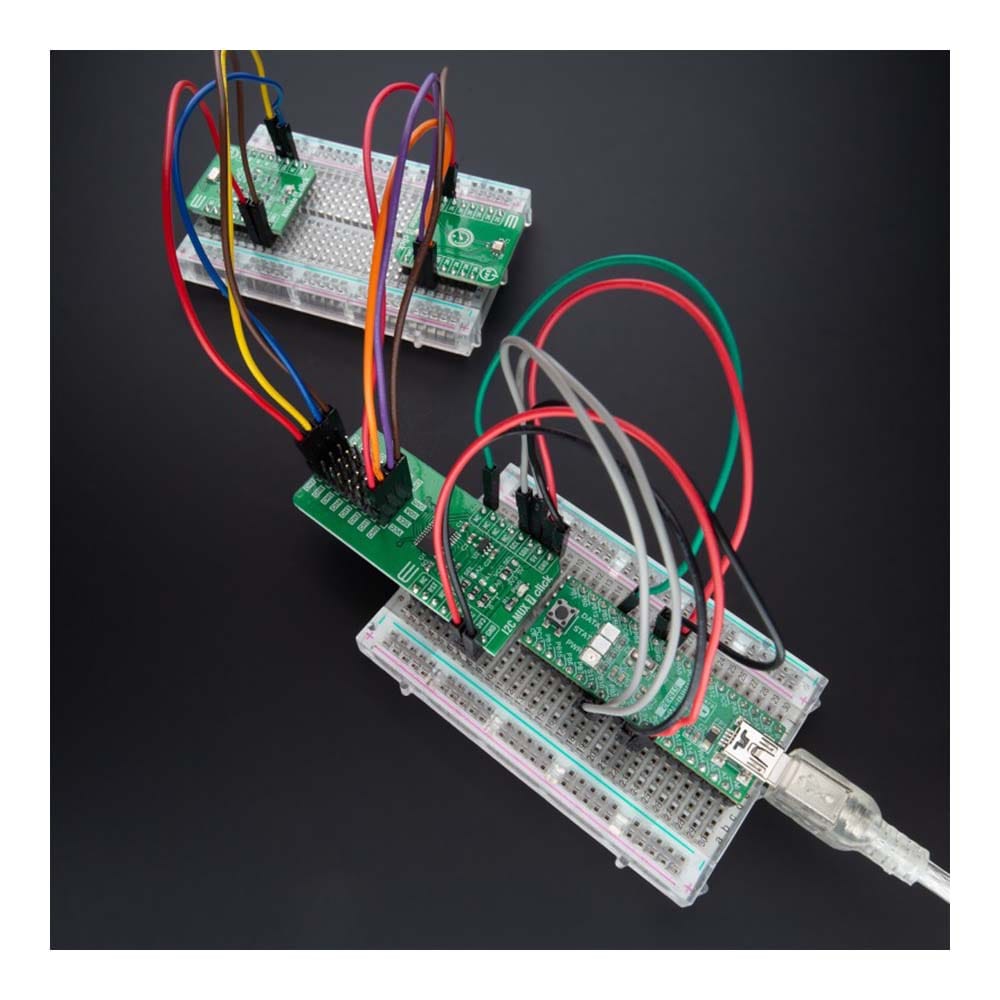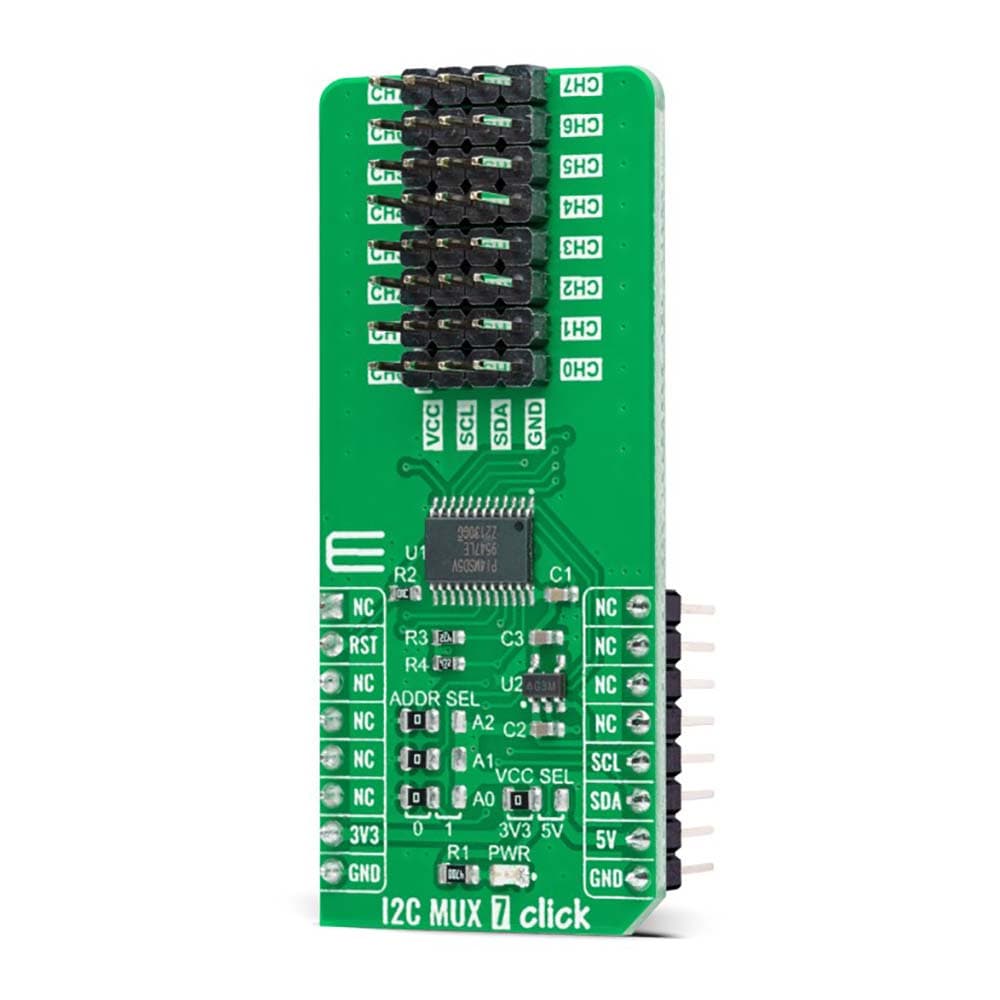
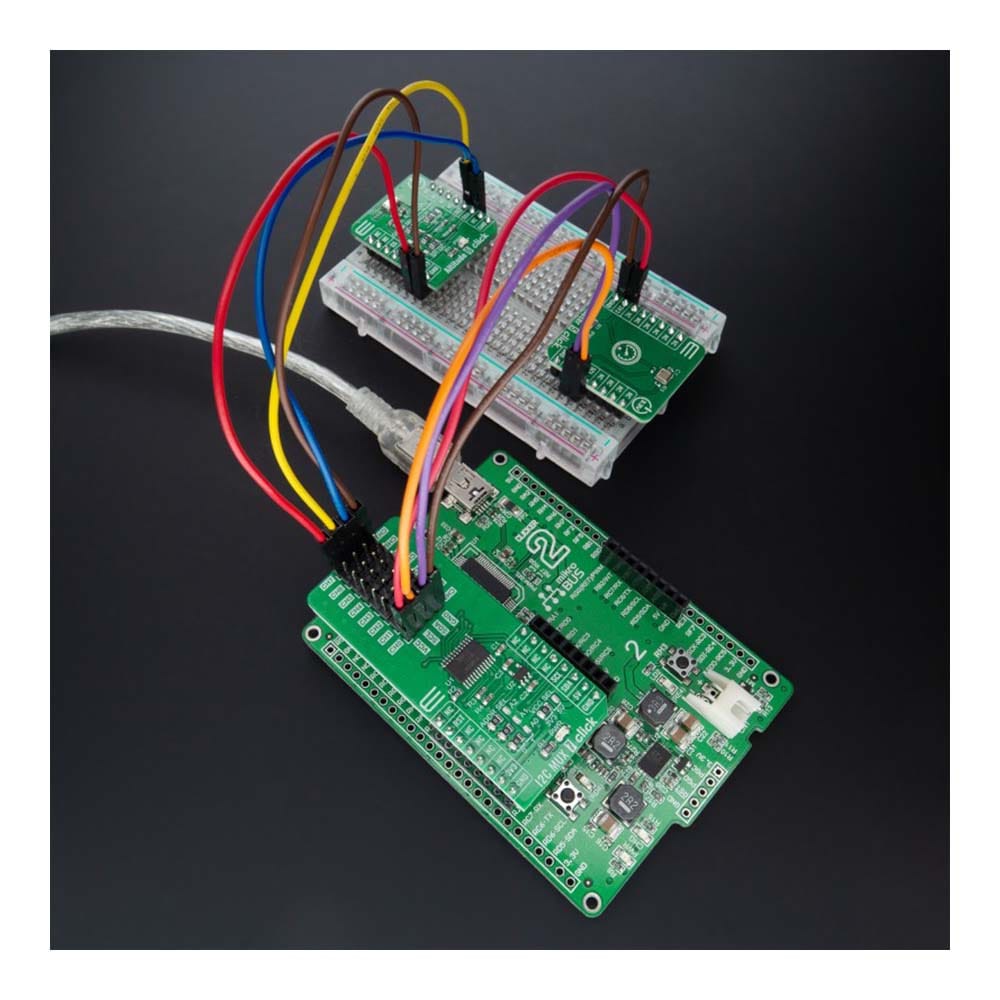
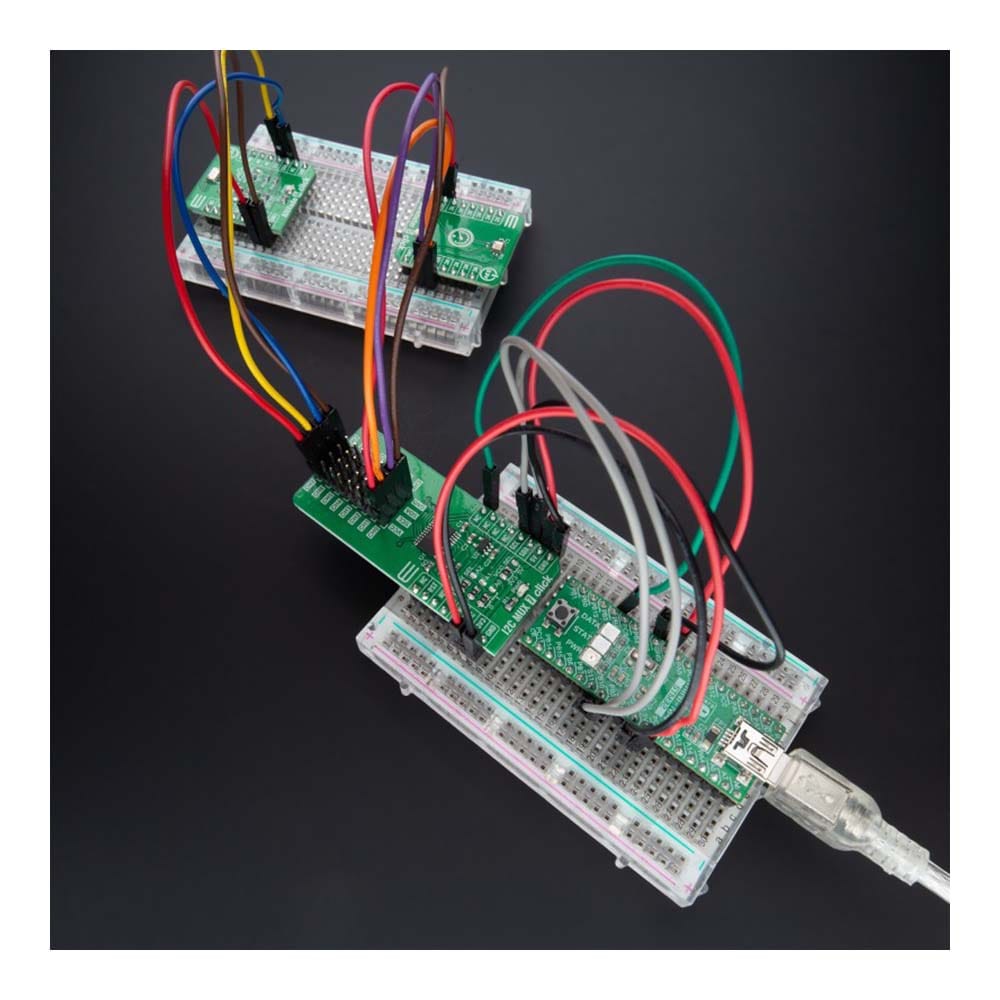
Overview
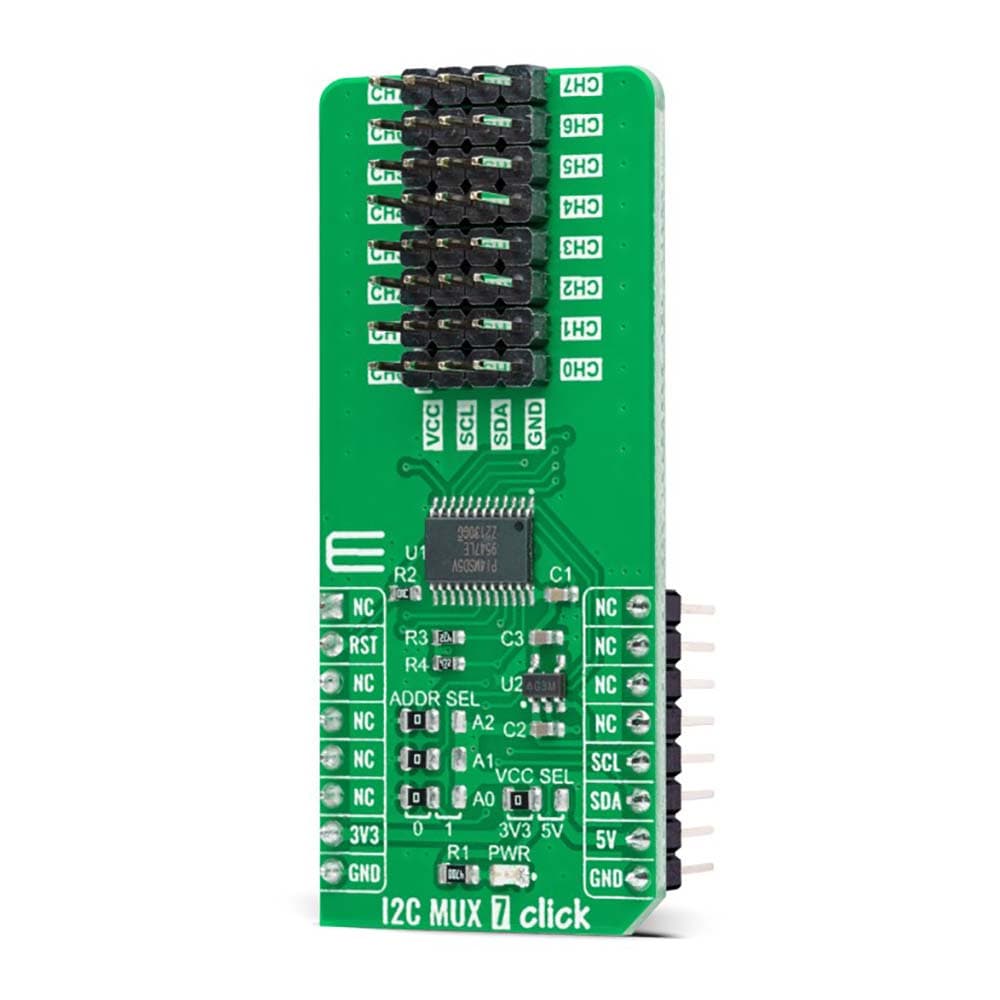
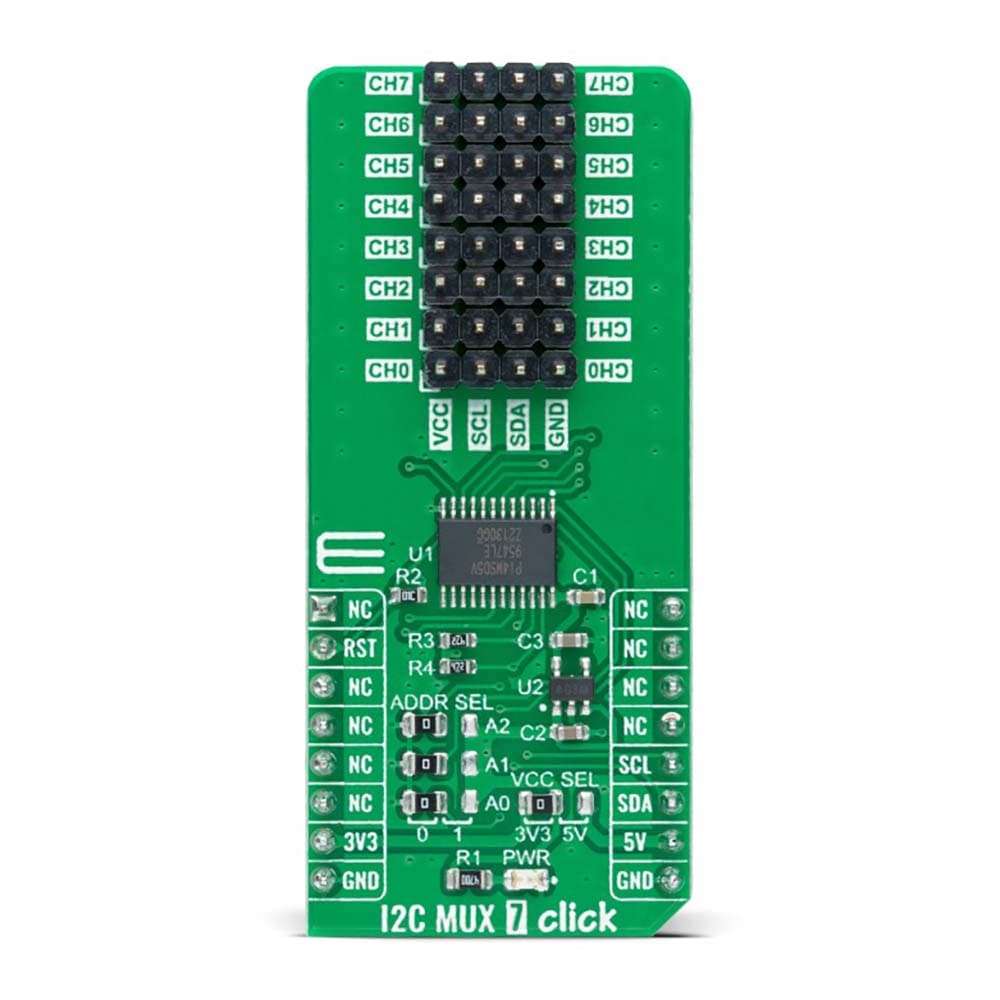
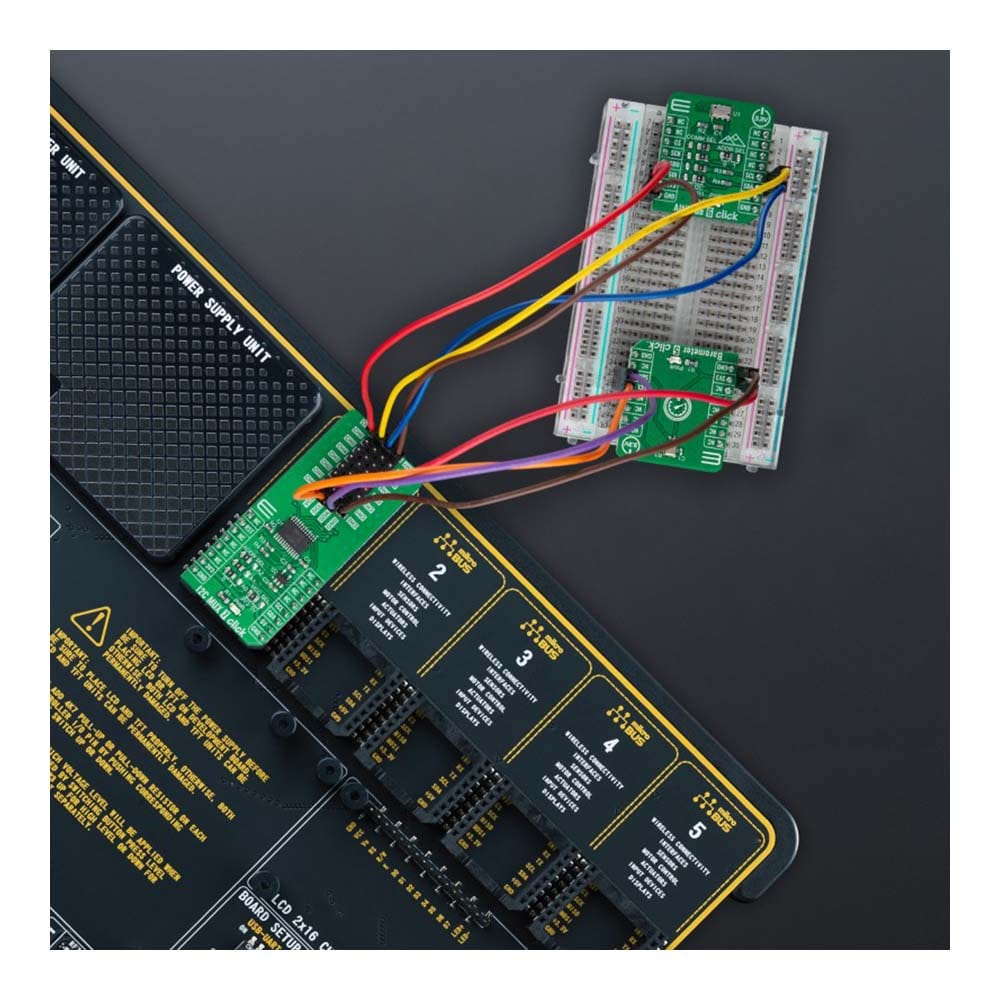
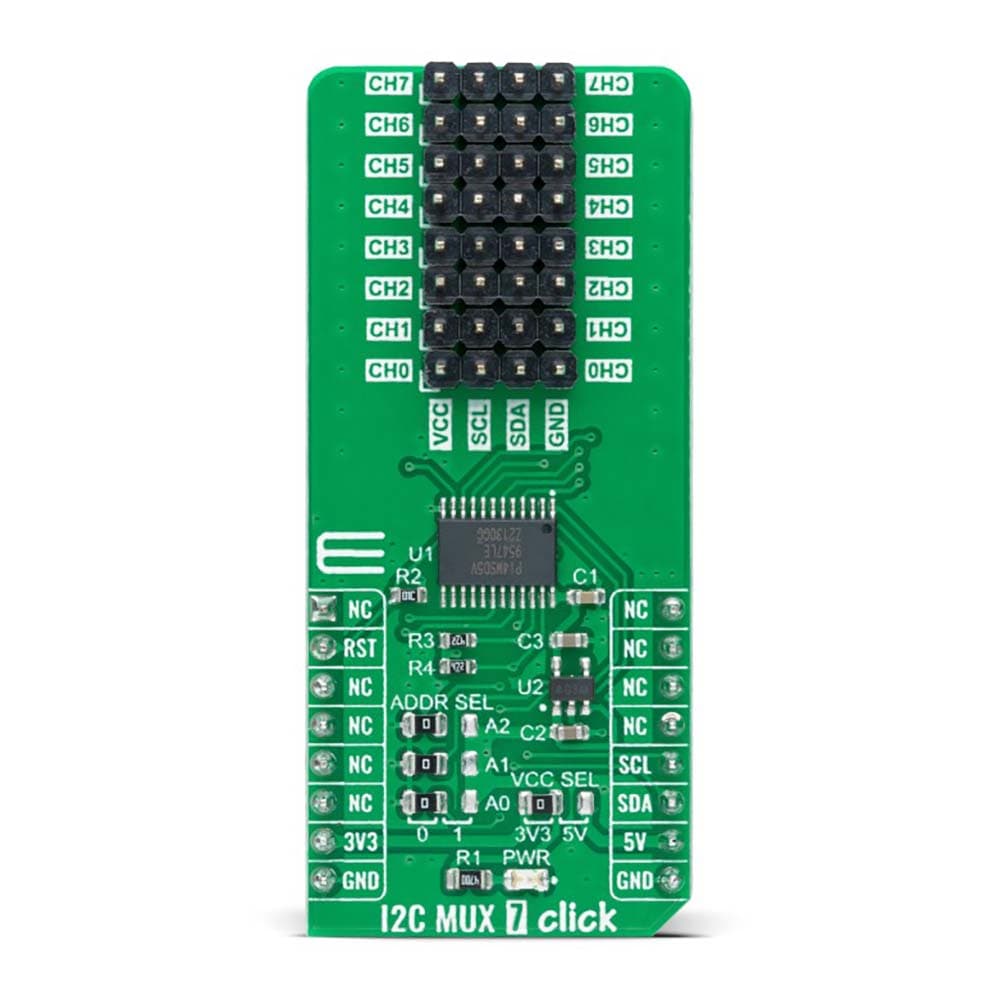
The I2C MUX 7 Click Board™ is a compact add-on board representing a bidirectional selector dedicated to applications with I2C slave address conflicts. This board features the PI4MSD5V9547, an octal bidirectional translating multiplexer controlled by the I2C-bus from Texas Instruments. Only one SCL/SDA channel can be selected at a time, determined by the contents of the programmable control register. The board powers up with Channel 0 connected, allowing immediate communication between the Master and downstream devices on that channel. The PI4MSD5V9547 also supports hot insertion, has a low Stand-by current, and has no glitch during the Power-Up sequence. This Click board™ is suitable for a wide range of applications from industrial to medical, communications, and automotive systems.
The I2C MUX 7 Click Board™ is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Downloads
Das I2C MUX 7 Click Board™ ist eine kompakte Zusatzplatine, die einen bidirektionalen Selektor für Anwendungen mit I2C-Slave-Adresskonflikten darstellt. Diese Platine verfügt über den PI4MSD5V9547, einen oktalen bidirektionalen Übersetzungsmultiplexer, der über den I2C-Bus von Texas Instruments gesteuert wird. Es kann jeweils nur ein SCL/SDA-Kanal ausgewählt werden, der durch den Inhalt des programmierbaren Steuerregisters bestimmt wird. Die Platine wird mit angeschlossenem Kanal 0 eingeschaltet, was eine sofortige Kommunikation zwischen dem Master und nachgeschalteten Geräten auf diesem Kanal ermöglicht. Der PI4MSD5V9547 unterstützt auch Hot Insertion, hat einen niedrigen Standby-Strom und hat während der Einschaltsequenz keine Störungen. Dieses Click Board™ ist für eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen geeignet, von industriellen bis hin zu medizinischen, Kommunikations- und Automobilsystemen.
Das I2C MUX 7 Click Board™ wird von einer mikroSDK-kompatiblen Bibliothek unterstützt, die Funktionen enthält, die die Softwareentwicklung vereinfachen. Dieses Click Board™ wird als vollständig getestetes Produkt geliefert und ist bereit für den Einsatz auf einem System, das mit der mikroBUS™-Buchse ausgestattet ist.
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-5069
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.02 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606027389429
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.