
Overview
Enhance your projects with the cutting-edge 13DOF Click Board. This remarkable board takes motion tracking to a new level of accuracy and functionality, catering to a wide range of applications, from immersive gaming to precise navigation.
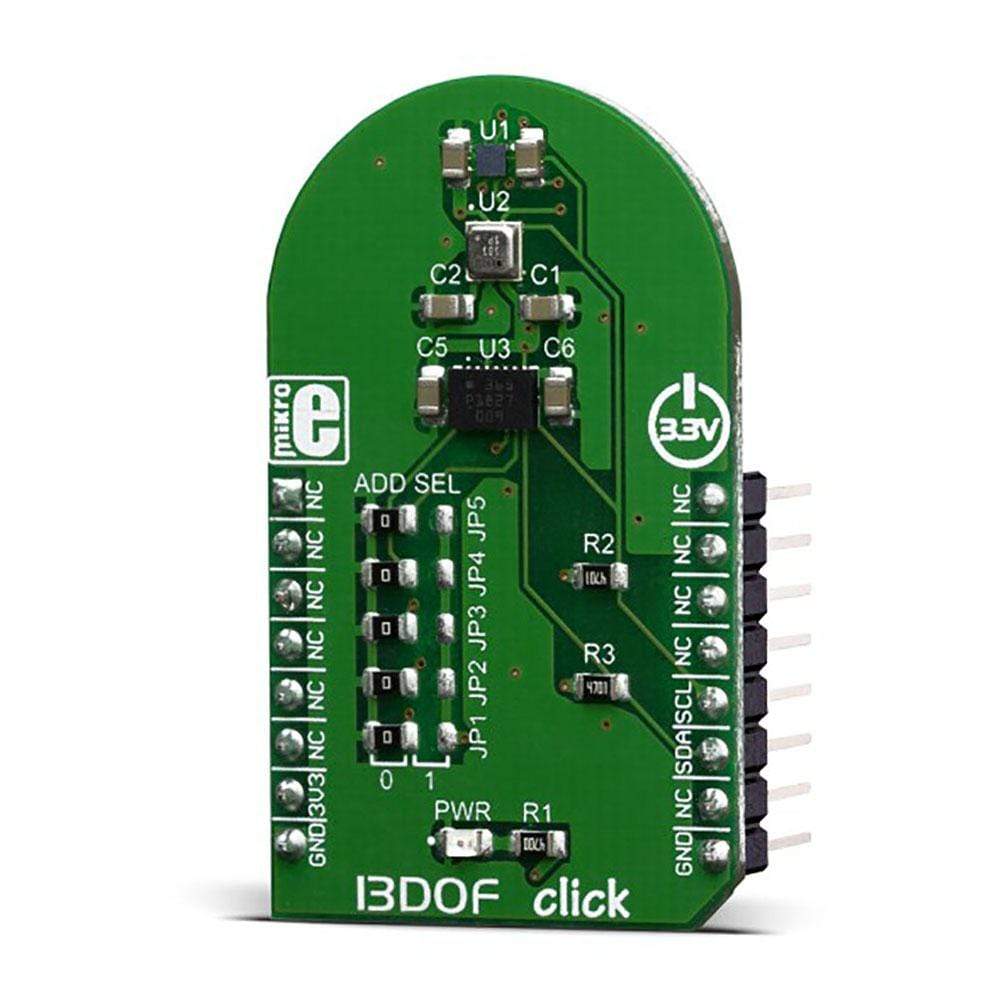
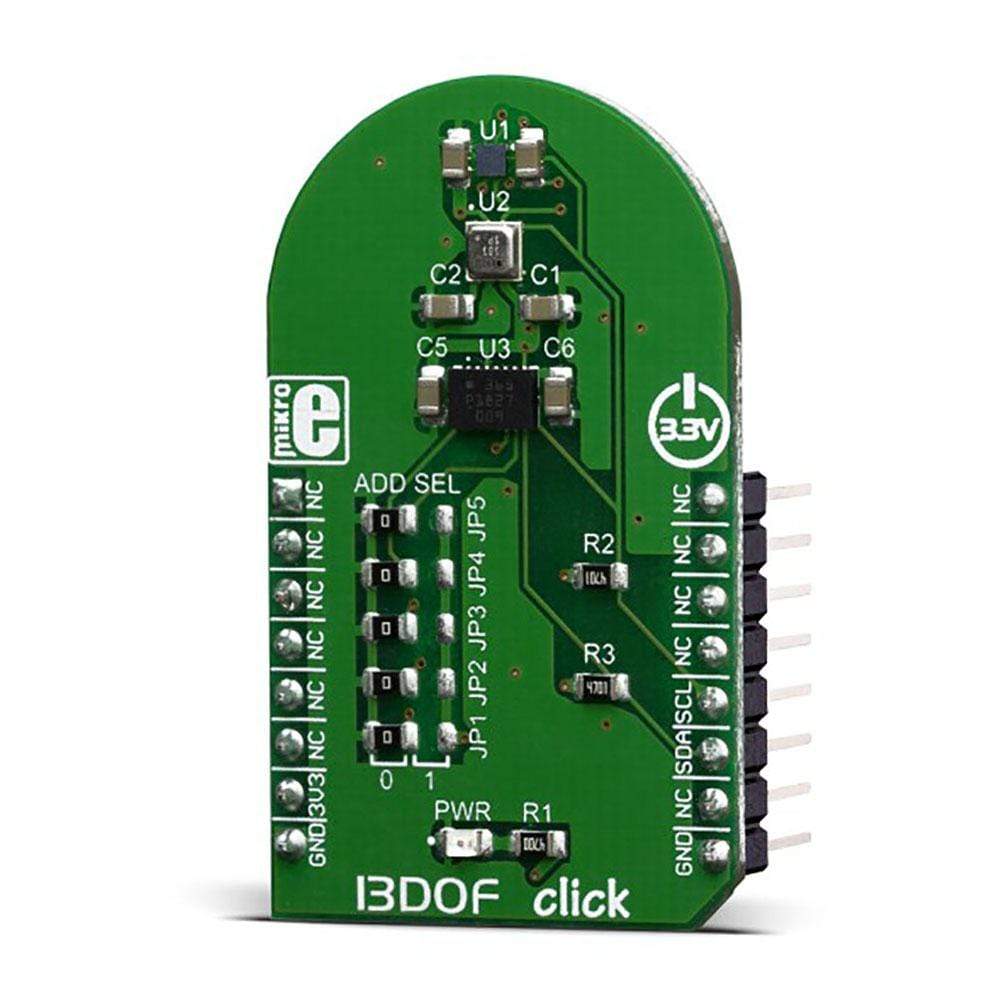
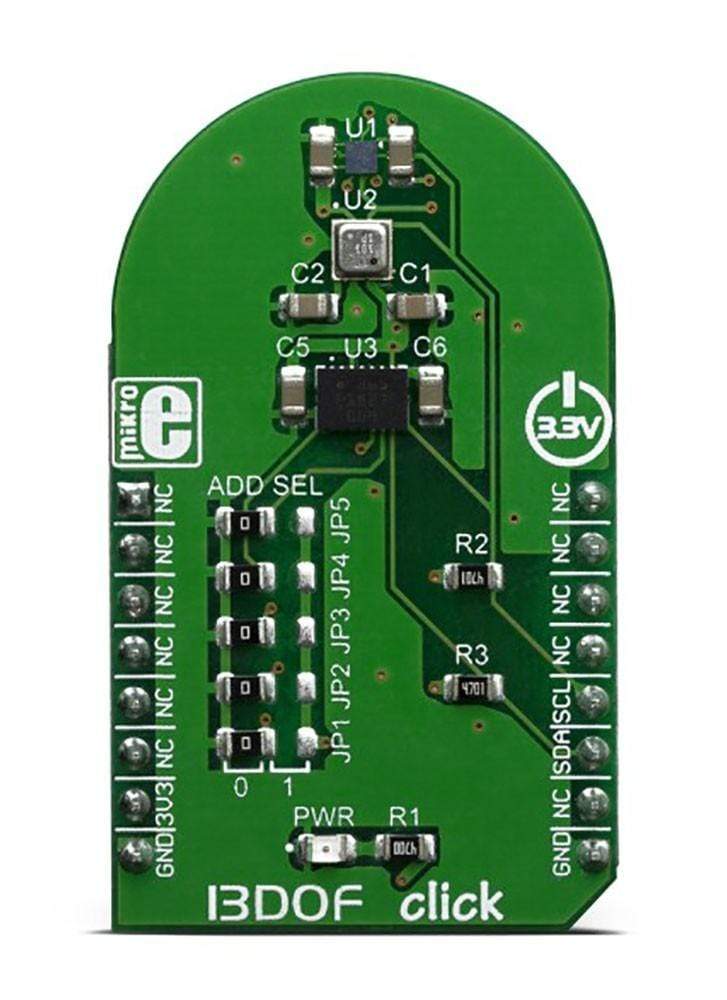
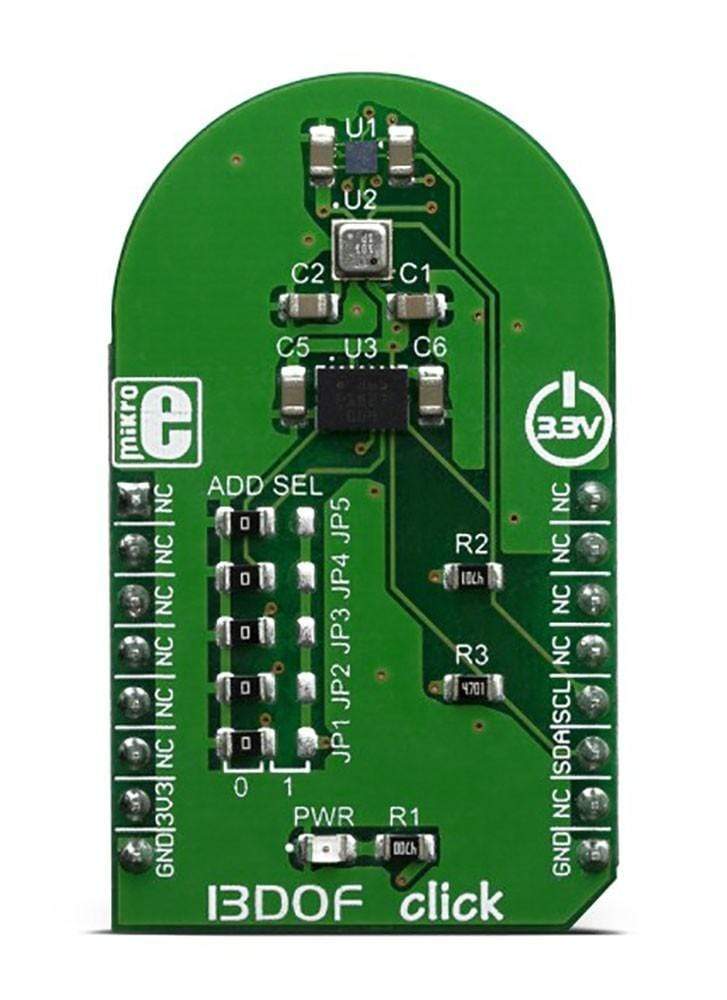
The 13DOF Click Board integrates three high-performance sensor ICs by Bosch Sensortec, ensuring exceptional sensor data fusion. It features the BME680 sensor for digital gas, pressure, humidity, and temperature sensing, as well as the BMM150 geomagnetic sensor for enhanced location-based accuracy.
Developers working on mobile phones, smartwatches, fitness devices, or GPS systems can rely on the 13DOF Click Board for unparalleled precision and reliability in sensor data acquisition. The board is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, simplifying software development, and comes fully tested and ready for immediate use in mikroBUS socket equipped systems.
Stay ahead in the rapidly evolving tech landscape with the 13DOF Click Board. This board is designed to meet the demands of modern technology, offering a perfect blend of accuracy, performance, and versatility to elevate user experiences across different platforms.
- Exceptional sensor data fusion with Bosch Sensortec ICs
- Compatibility with various applications including gaming and navigation
Specifications:
- Supported ICs: BME680, BMM150
- Compliance: mikroSDK
Downloads
Verbessern Sie Ihre Projekte mit dem hochmodernen 13DOF Click Board. Dieses bemerkenswerte Board bringt die Bewegungsverfolgung auf ein neues Niveau an Genauigkeit und Funktionalität und eignet sich für eine breite Palette von Anwendungen, von immersivem Gaming bis hin zu präziser Navigation.
Das 13DOF Click Board integriert drei Hochleistungs-Sensor-ICs von Bosch Sensortec und sorgt so für eine außergewöhnliche Sensordatenfusion. Es verfügt über den BME680-Sensor zur digitalen Gas-, Druck-, Feuchtigkeits- und Temperaturmessung sowie den geomagnetischen BMM150-Sensor für verbesserte ortsbezogene Genauigkeit.
Entwickler, die an Mobiltelefonen, Smartwatches, Fitnessgeräten oder GPS-Systemen arbeiten, können sich auf das 13DOF Click Board verlassen, das eine beispiellose Präzision und Zuverlässigkeit bei der Erfassung von Sensordaten bietet. Das Board wird von einer mikroSDK-kompatiblen Bibliothek unterstützt, was die Softwareentwicklung vereinfacht. Es ist vollständig getestet und sofort einsatzbereit für Systeme mit mikroBUS-Sockel.
Bleiben Sie mit dem 13DOF Click Board in der sich schnell entwickelnden Technologielandschaft immer einen Schritt voraus. Dieses Board wurde entwickelt, um den Anforderungen moderner Technologie gerecht zu werden und bietet eine perfekte Mischung aus Genauigkeit, Leistung und Vielseitigkeit, um das Benutzererlebnis auf verschiedenen Plattformen zu verbessern.
- Außergewöhnliche Sensordatenfusion mit Bosch Sensortec ICs
- Kompatibilität mit verschiedenen Anwendungen, einschließlich Spielen und Navigation
Spezifikationen:
- Unterstützte ICs: BME680, BMM150
- Konformität: mikroSDK
| General Information | |
|---|---|
Part Number (SKU) |
MIKROE-3775
|
Manufacturer |
|
| Physical and Mechanical | |
Weight |
0.018 kg
|
| Other | |
Country of Origin |
|
HS Code Customs Tariff code
|
|
EAN |
8606018719990
|
Warranty |
|
Frequently Asked Questions
Have a Question?
Be the first to ask a question about this.